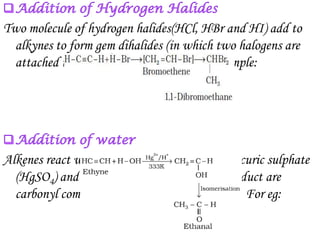
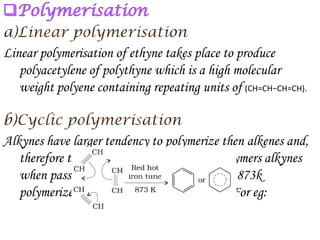
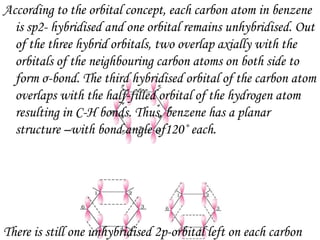
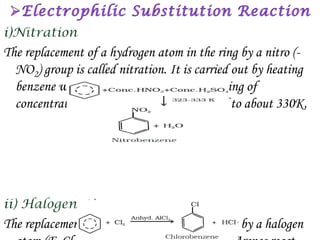
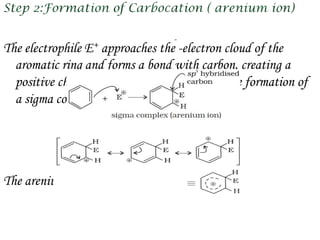
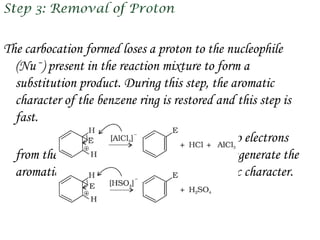
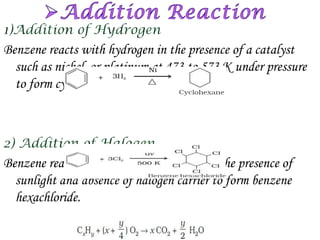
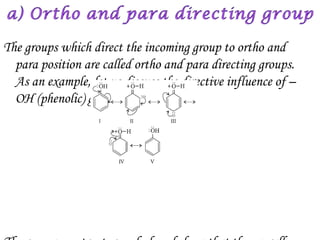
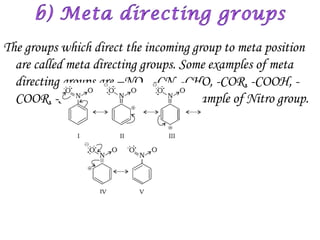
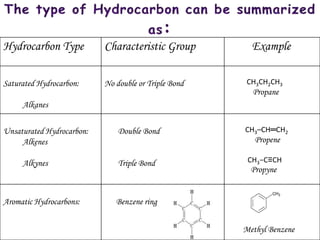
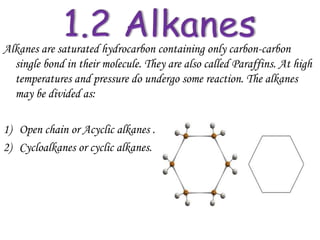
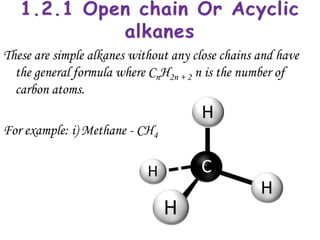
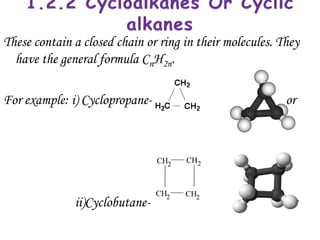
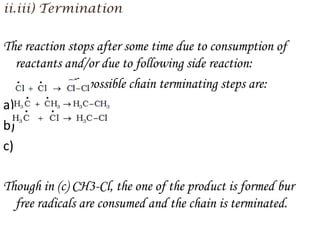
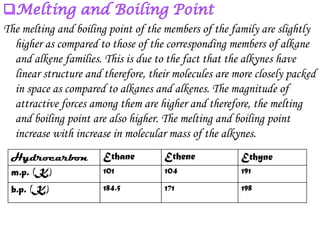
Hydrocarbons can be classified into three main categories based on the types of carbon-carbon bonds present: saturated hydrocarbons containing single bonds, unsaturated hydrocarbons containing double or triple bonds, and aromatic hydrocarbons containing benzene rings. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that can be open chain or cyclic. Their properties depend on molecular size, with boiling points generally increasing with more carbon atoms. Alkanes undergo substitution and combustion reactions.
































![Alkenes react with cold dilute aqueous or alkaline potassium
permanganate solution to form 1,2-diols called glycols.
The glycols contain two –OH groups on adjacent carbon
atoms. This reaction of addition of two hydroxyl groups
to each end of double bond is called hydroxylation of the
double bond.
2KMnO4+H2O 2KOH+2MnO2+3[O]
When alkene is treated with hot acidic potassium
permanganate or potassium dichromate solution the
alkene gets split up at the double bond forming carboxylic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrocarbon-arjavpatel-130217122824-phpapp02/85/Hydrocarbon-arjav-patel-56-320.jpg)

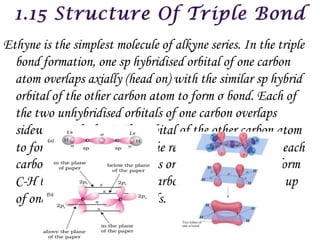

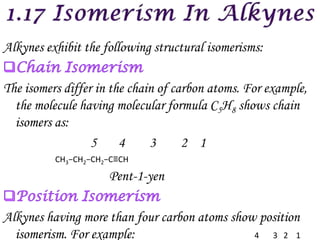

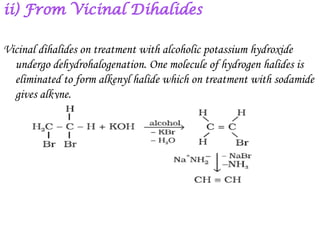

![Alkynes react readily with hydrogen in the presence of finely
divided Ni, Pt or Pd as a catalyst. The reaction is called
hydrogenation.
HC≡CH+H2 Pt/Pd/Ni [H2C=CH2] H CH3−CH3
2
Reddish orange colour of the solution of bromine in carbon
tetrachloride is decolourised. This is used as a test for
unsaturation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrocarbon-arjavpatel-130217122824-phpapp02/85/Hydrocarbon-arjav-patel-67-320.jpg)