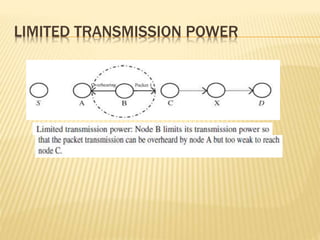
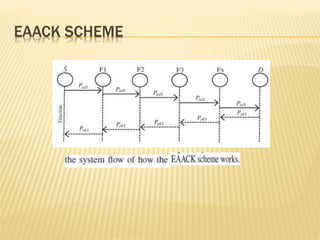
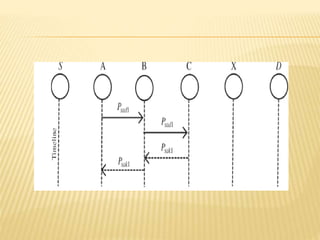
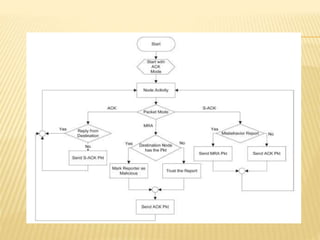
The Enhanced Adaptive Acknowledgment (EAACK) system comprises three main components: acknowledgment (ACK), secure acknowledgment (S-ACK), and misbehavior report authentication (MRA), designed to improve network reliability and reduce false reporting of node misbehavior. S-ACK detects misbehaving nodes by forming groups of three consecutive nodes, while MRA addresses weaknesses in existing detection systems and verifies reports of misbehavior. The proposed secure enhanced adaptive acknowledgment scheme (SEAACK) and the anonymous leak detector mechanism aim to handle energy-related issues and identify colluding malicious nodes effectively.