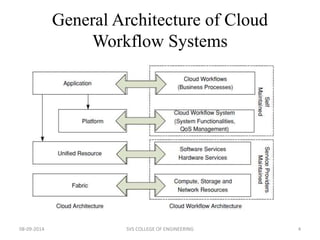
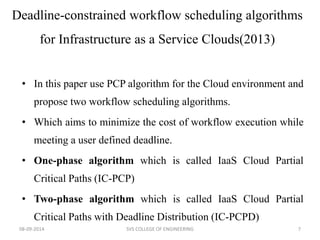
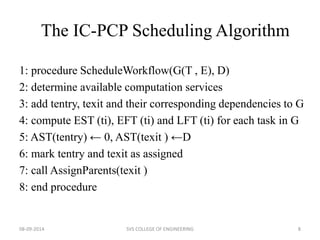
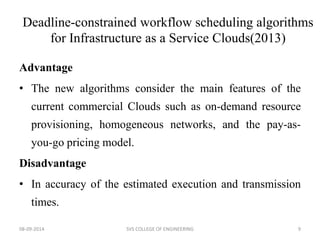
The document discusses meeting deadlines for scientific workflows running on public clouds. It proposes replicating tasks to utilize idle resources and budgets to minimize workflow execution time while still meeting deadlines. The proposed approach models workflows as directed acyclic graphs and replicates tasks to reduce the impact of performance variations in public cloud resources. Existing work focuses on either minimizing time ignoring deadlines and budgets or minimizing cost while meeting deadlines.