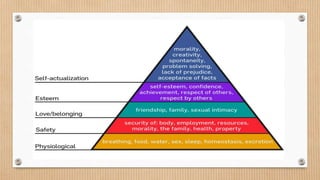
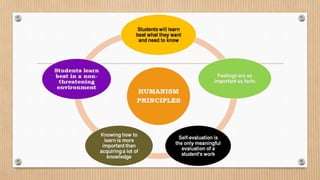
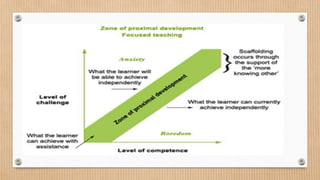
Humanism is a paradigm that focuses on human freedom, dignity, and potential. It emerged in the 1960s. Key figures in humanistic models of learning include Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers. Maslow proposed a hierarchy of needs and believed in human potential and dignity. Rogers believed that feelings and emotions should be included in education. Constructivism is a theory of learning where students actively construct their own knowledge rather than having it transferred from teachers. Key theorists include Piaget, Vygotsky, and Bruner. Piaget believed that learning is developmental while Vygotsky emphasized social interaction and the zone of proximal development. Constructivism sees the student as an active learner.