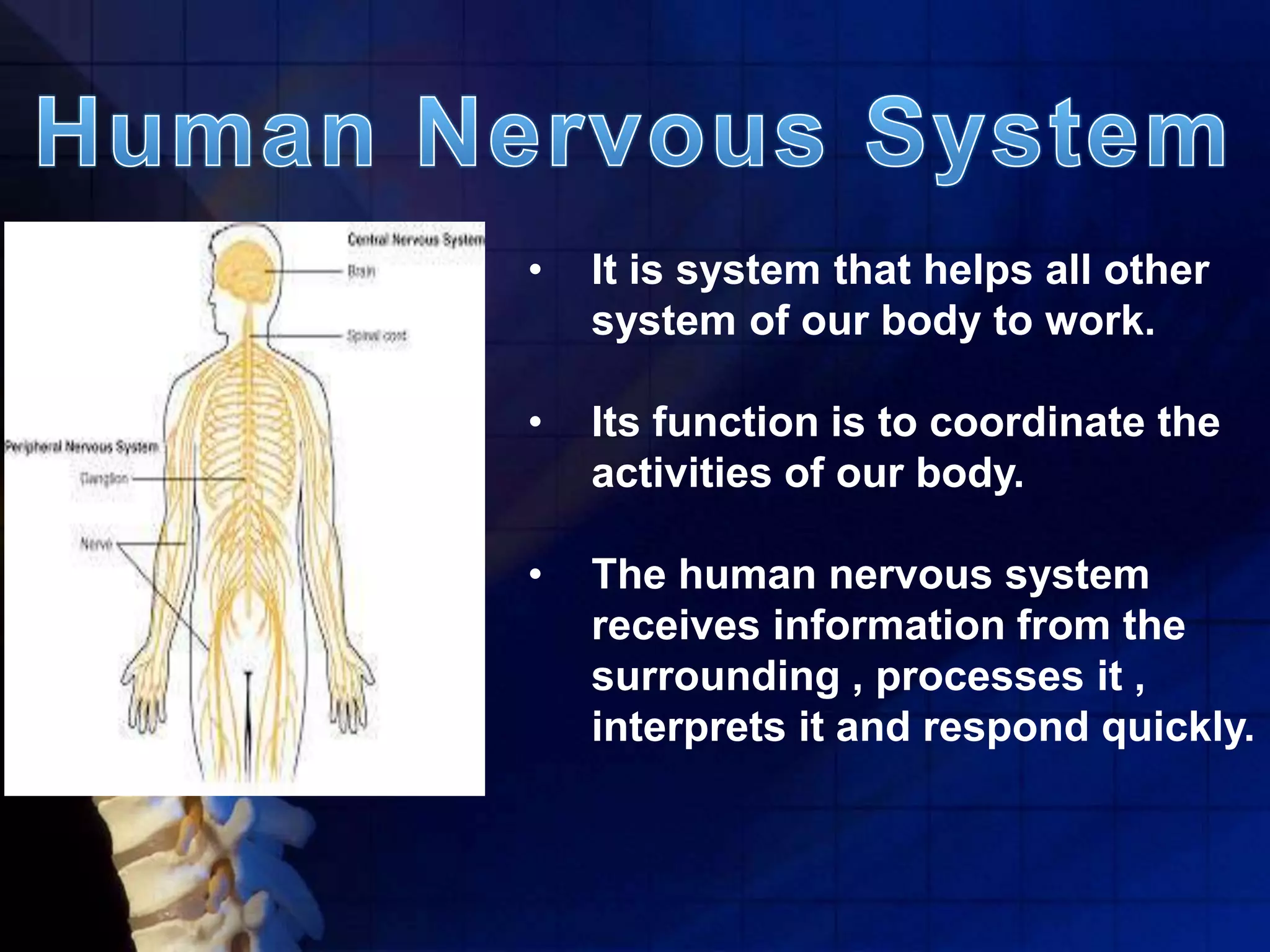
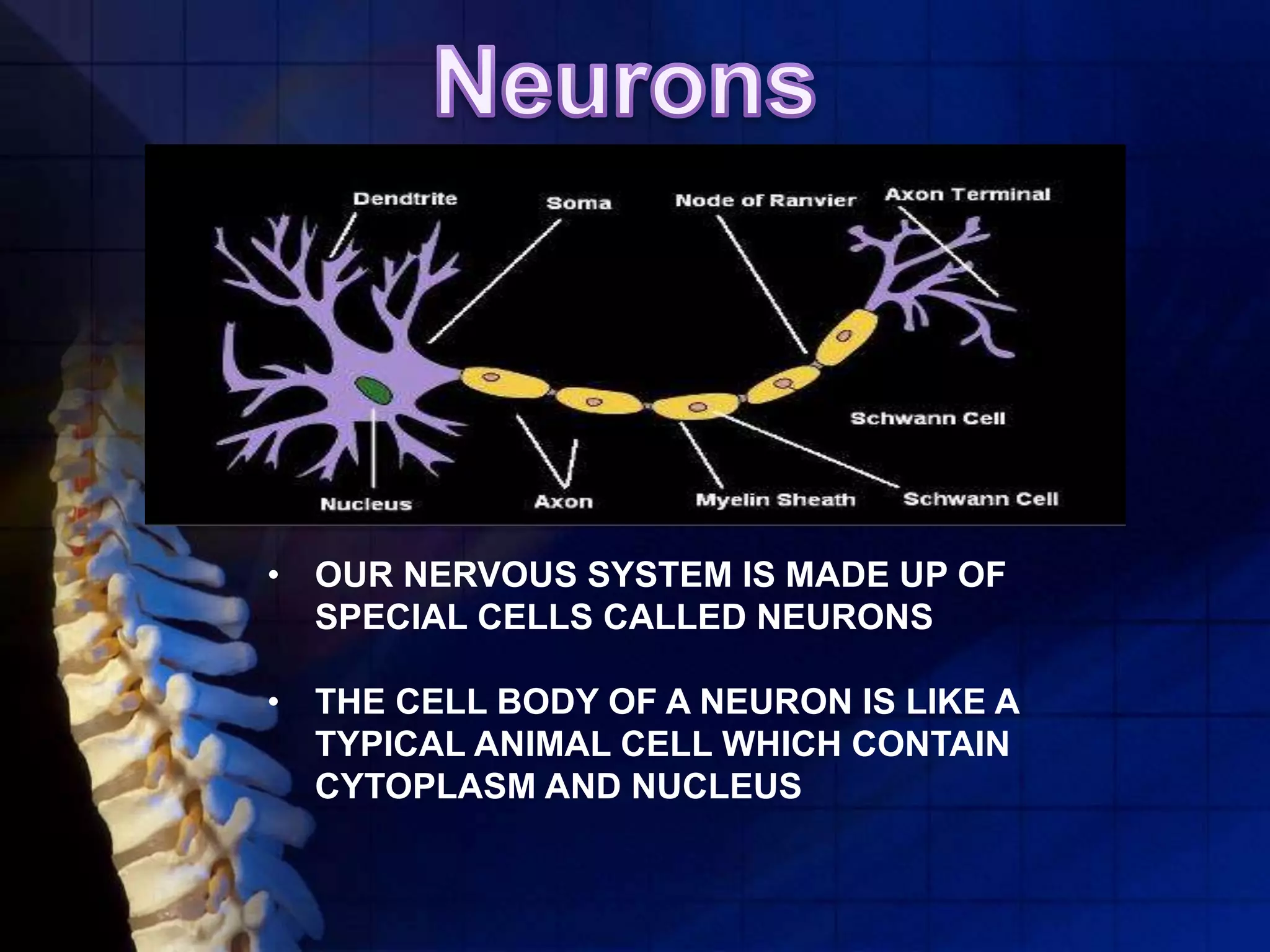
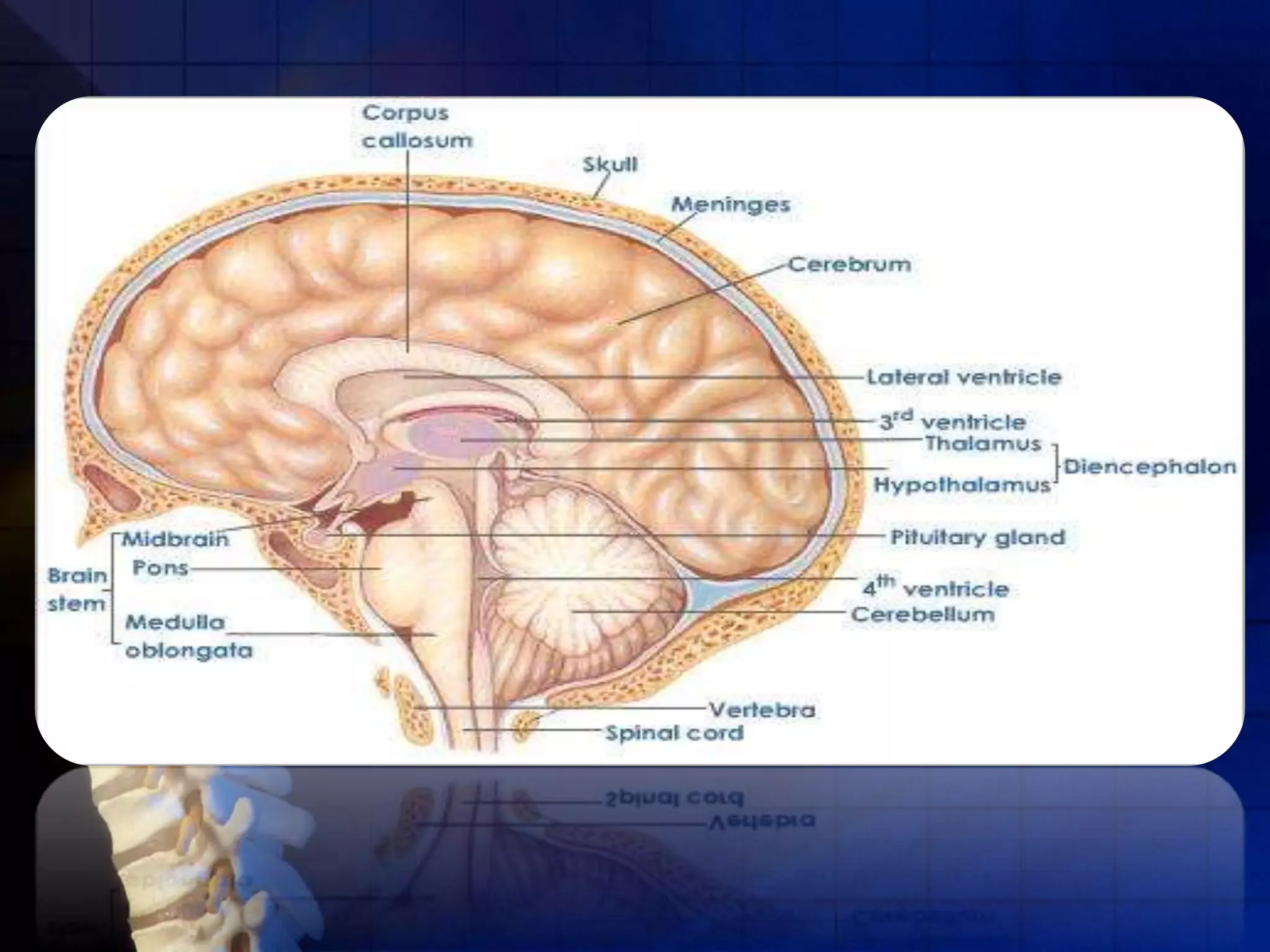
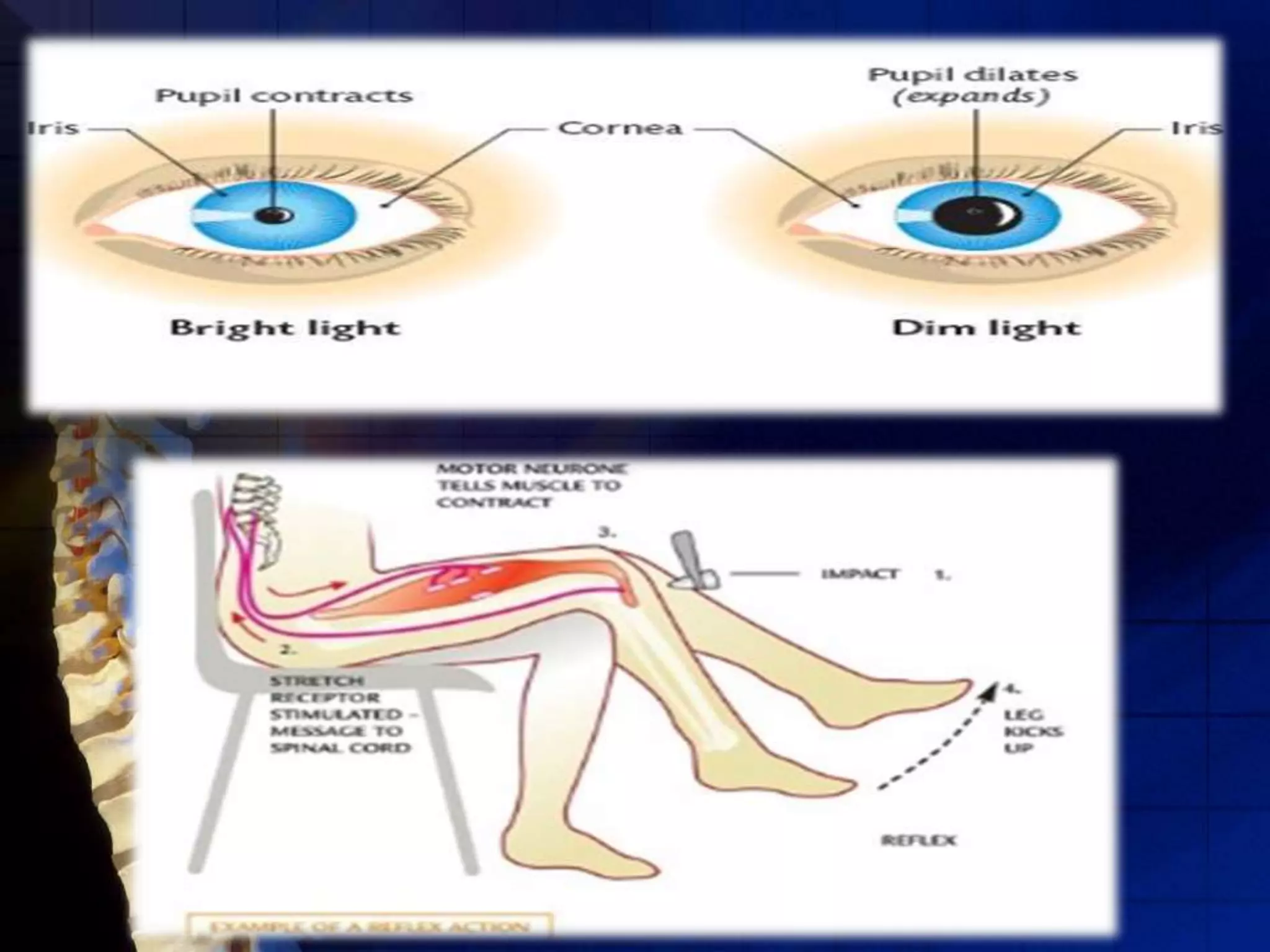
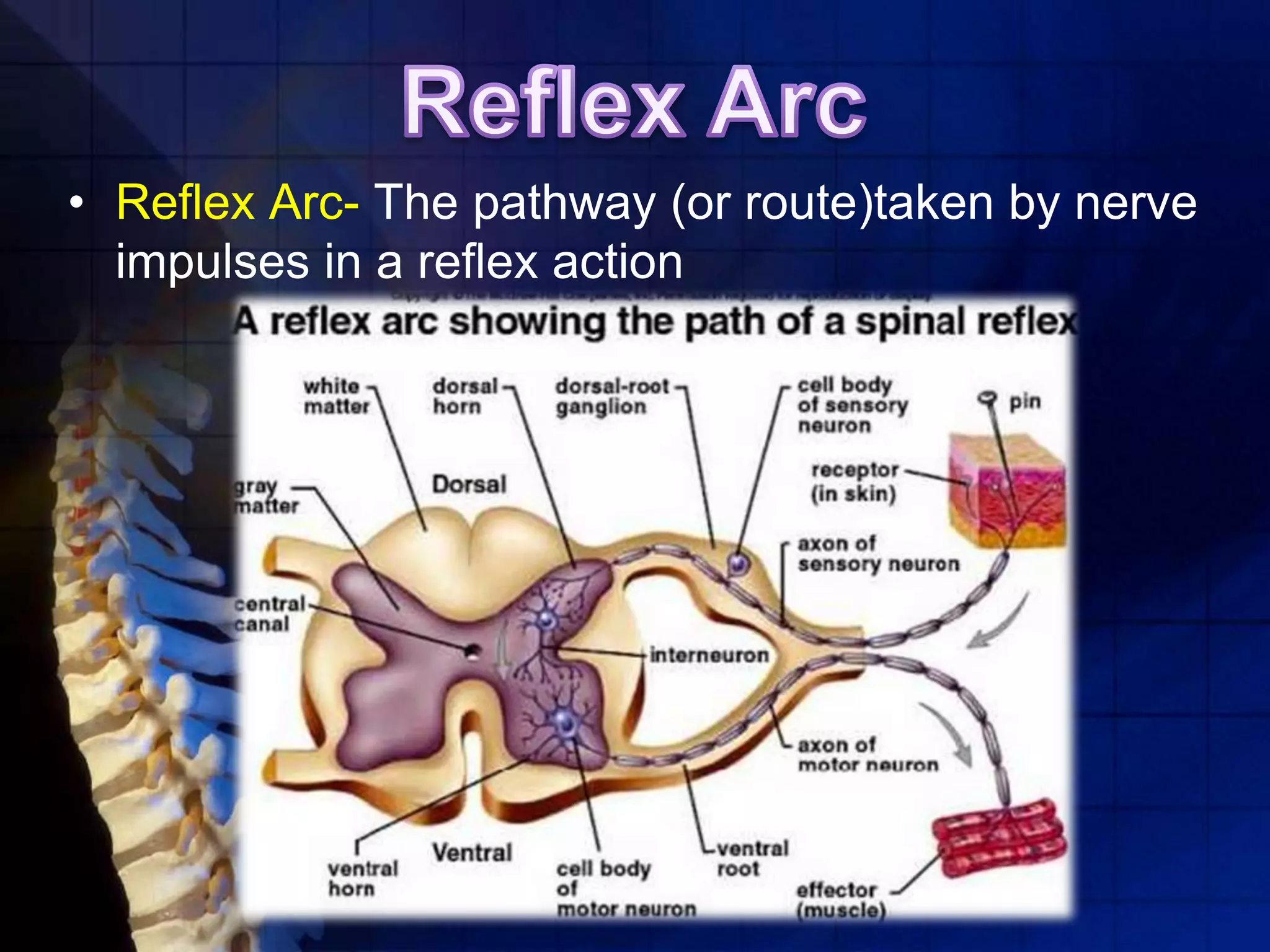
The human nervous system coordinates the activities of the body and allows it to respond quickly to external stimuli. It is composed of neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit signals. Neurons have an axon, which transmits signals, dendrites, which receive signals, and a cell body. The central nervous system, made up of the brain and spinal cord, processes all information and is protected by bone and fluid. Reflexes are automatic responses that travel through a reflex arc in the spinal cord without involving the brain.