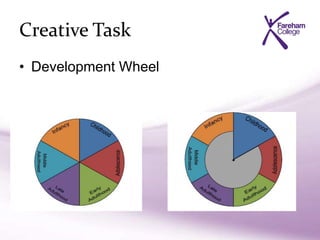
This document provides an overview of a class on human growth and development across the six life stages:
- It introduces key terminology like growth, development, and life stages.
- It outlines learning objectives around identifying stages and describing physical, intellectual, emotional and social development in infancy.
- The class covers physical, intellectual, emotional and social development in different life stages like infancy, childhood and adolescence.
- Later sections discuss factors affecting development in adulthood and how intellectual development can be impacted by conditions like dementia in late adulthood.