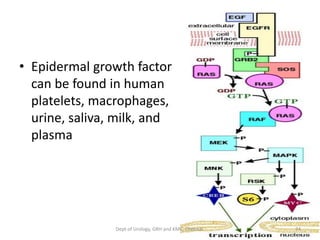
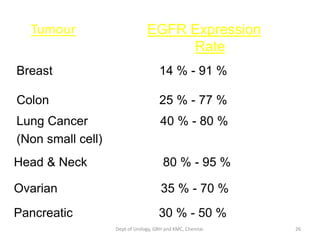
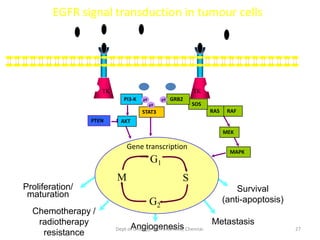
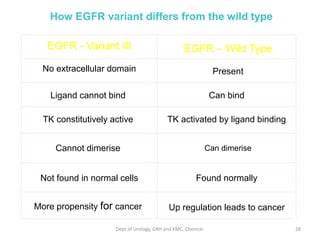
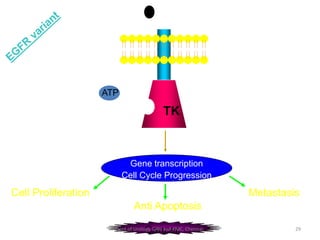
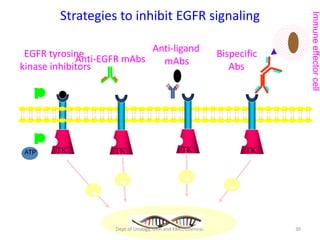
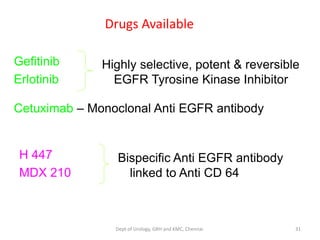
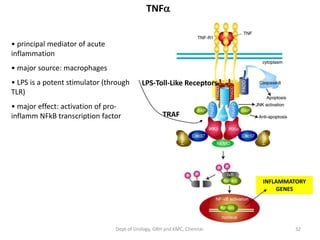
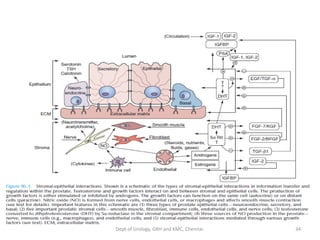
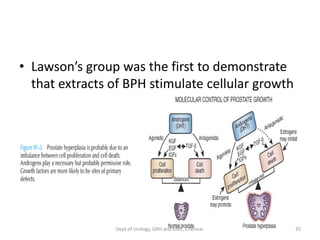
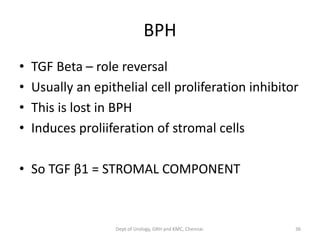
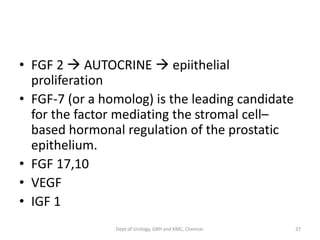
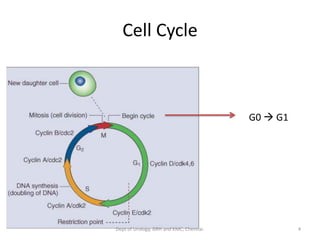
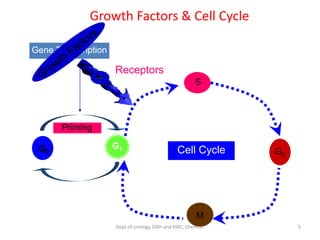
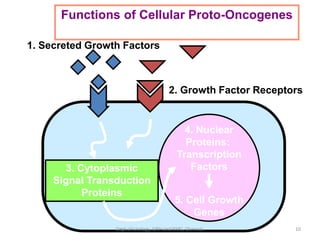
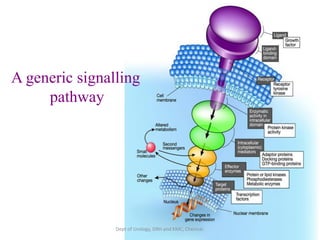
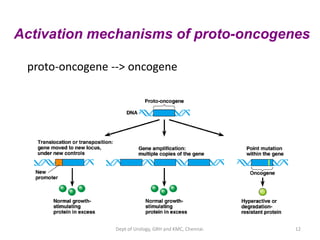
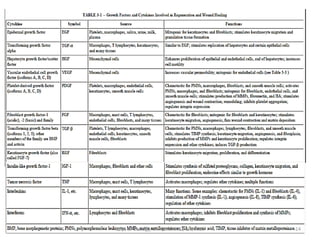
This document discusses human growth factors and their roles in various processes from the Department of Urology at GRH and KMC in Chennai. It lists the moderators and their roles. Growth factors are defined as signaling molecules that stimulate cellular growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Examples include cytokines and hormones. The document discusses the cell cycle and how growth factors interact with cell surface receptors to affect gene transcription and cell cycle progression. It provides examples of many growth factors including their functions and roles in various conditions.







![FGF Family
• In humans, 22 members of the FGF family have been identified
• structurally related signaling molecules
• Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors
• FGF1 is also known as acidic, and FGF2 is also known as basic fibroblast
growth factor.
• Members FGF11, FGF12, FGF13, and FGF14, also known as FGF
homologous factors 1-4 (FHF1-FHF4), have been shown to have distinct
functional differences compared to the FGFs - "iFGF".
• Human FGF20 was identified based on its homology to Xenopus FGF-20
(XFGF-20).[6][7]
• FGF15 through FGF23 were described later and not all their functions have
been characterized.
• FGF15/19, FGF21 and FGF23 have systemic effects.[8][9]
16
Dept of Urology, GRH and KMC, Chennai.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humangrowthfactor-converted-210614083108/85/Human-growth-factorS-16-320.jpg)





![EGF
Human EGF is a 6045-Da protein[2] with 53
amino acid residues and three
intramolecular disulfide bonds
The discovery of EGF won Stanley Cohen
and Rita Levi-Montalcini a Nobel Prize in
Physiology and Medicine in 1986
First purified from the mouse submandibular
gland, but since then found in many human
tissues including submandibular gland, parotid
gland.
Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by
dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an
important mucosal healer
23
Dept of Urology, GRH and KMC, Chennai.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humangrowthfactor-converted-210614083108/85/Human-growth-factorS-23-320.jpg)