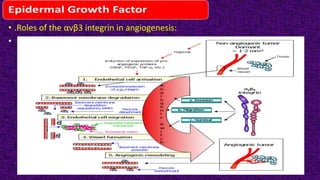
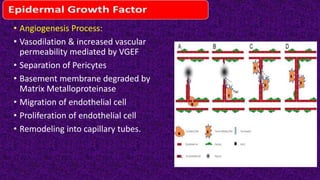
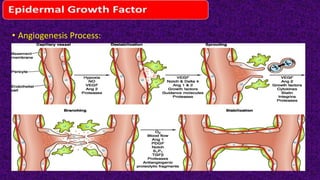
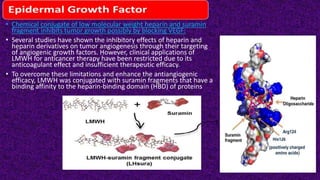
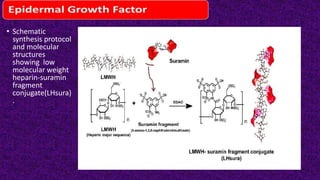
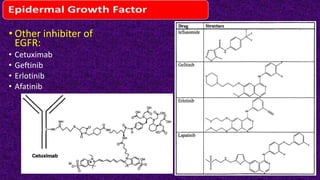
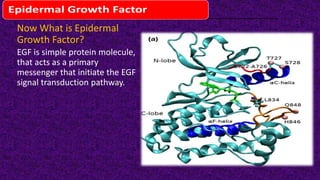
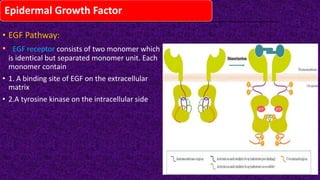
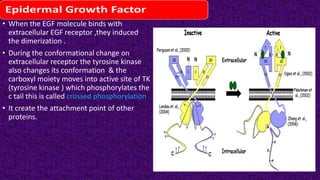
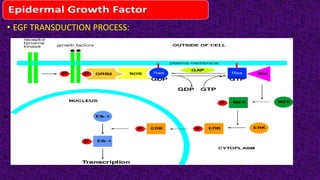
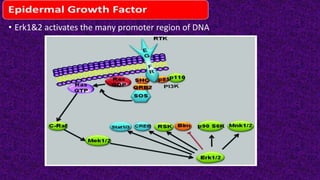
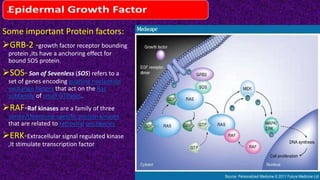
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that binds to EGF receptors on epithelial and epidermal cells and initiates the EGF signaling pathway. When EGF binds to EGF receptors, it causes them to dimerize and activate their tyrosine kinase activity, leading to phosphorylation and activation of downstream proteins in the MAPK pathway. Mutations that cause constitutive activation of this pathway can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer. Potential cancer treatments discussed include RGD-based peptides that target the αvβ3 integrin receptor involved in angiogenesis, and a conjugate of low molecular weight heparin and suramin that may inhibit tumor growth by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).




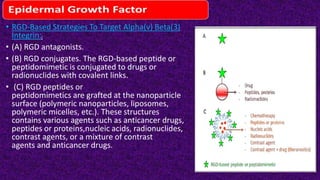
![Chemical structures.
(A) The original RGD
sequence.
(B) Cyclic RGD peptide
antagonist (c(RGDf[N-
Me]V) or cilengitide.
(C) Cyclic peptide
c(RGDfK).
(D) ACDCRGDCFCG (RGD4C).
(E) Example of RGD
peptidomimetic-containing
the RGD sequence (S-
247).28
(F)Example of RGD
peptidomimetic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epidermalgrowthfactoregf-160909195235/85/Epidermal-growth-factor-egf-15-320.jpg)