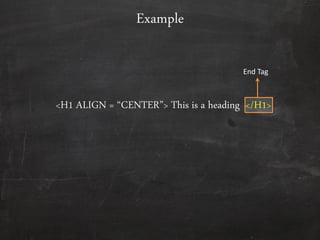
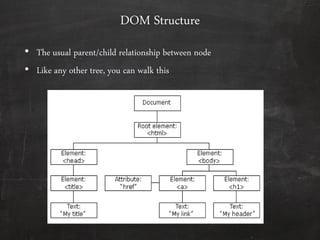
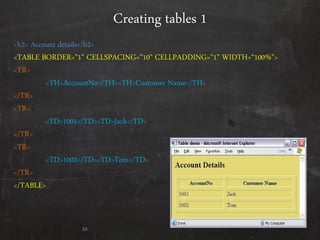
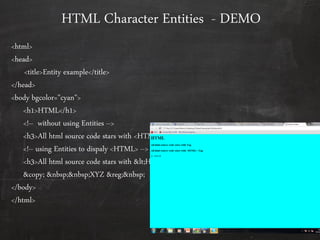
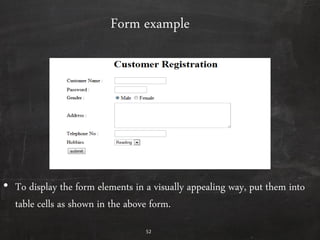
HTML is used to design web pages and is not a programming language. It uses tags like <h1> and <p> to structure and style text content. Common tags are used to create headings, paragraphs, lists, links, and tables. Forms allow users to enter interactive content through elements like text boxes and buttons. Overall, HTML provides the building blocks for displaying structured documents on the web.