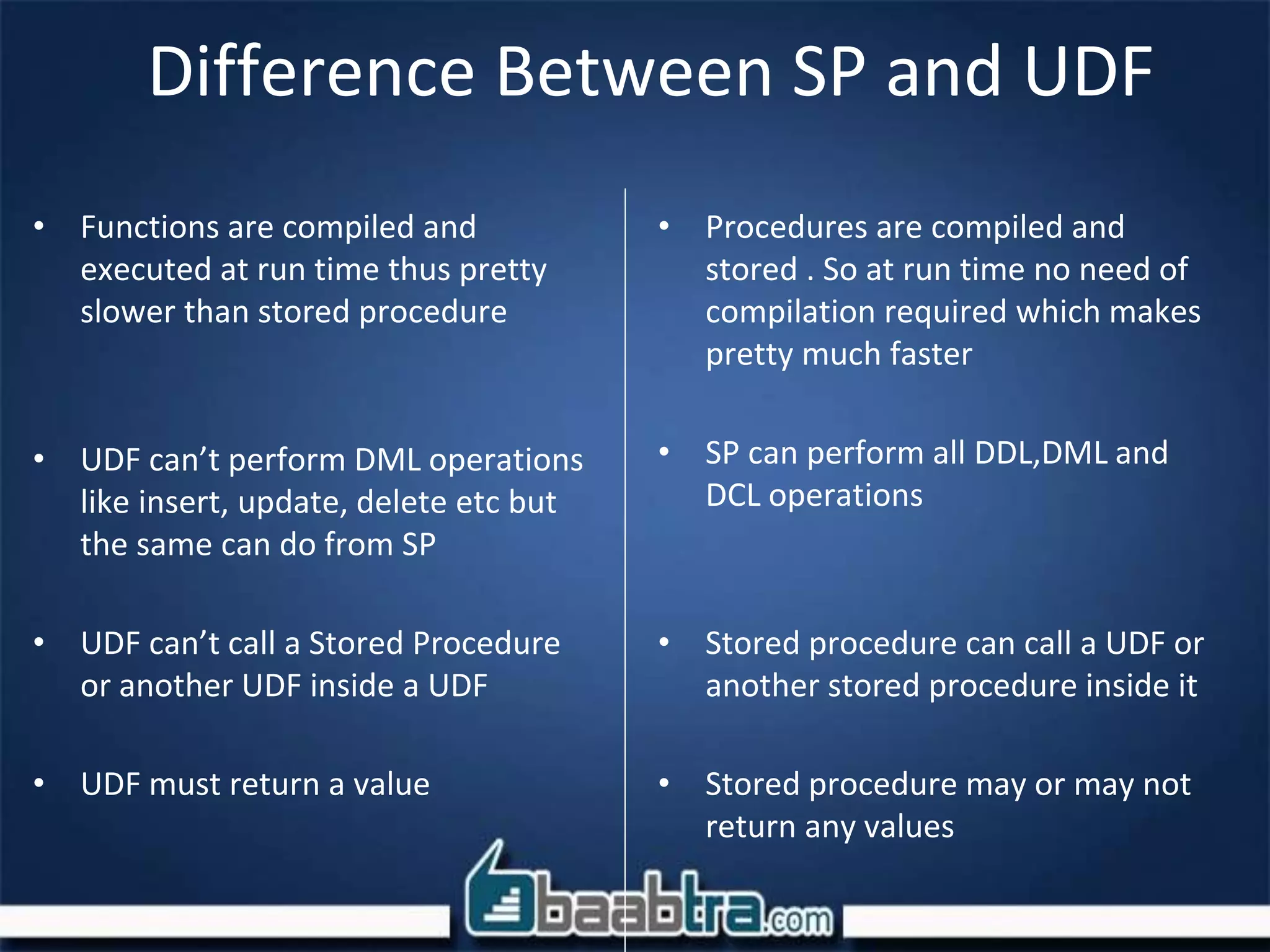
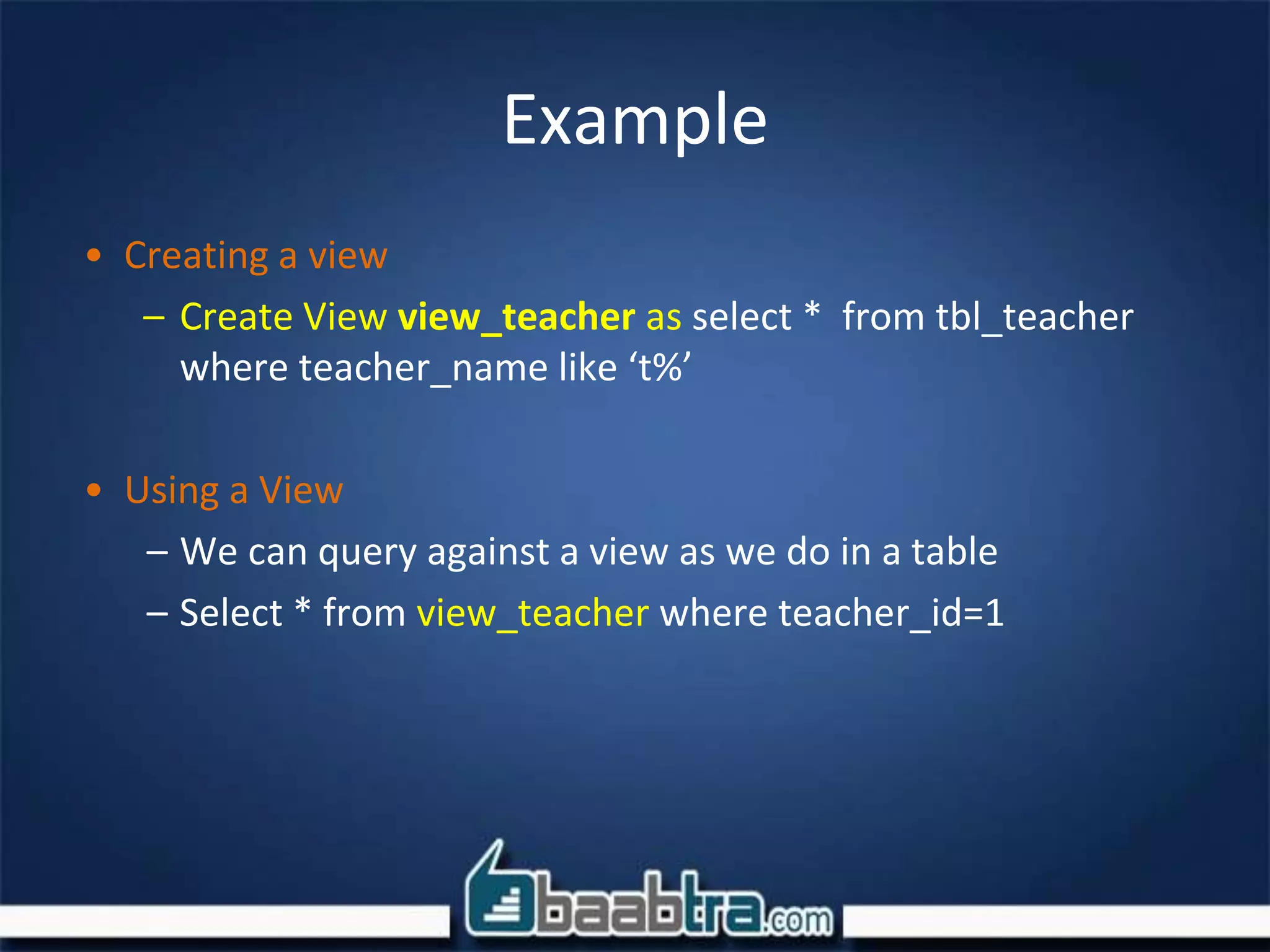
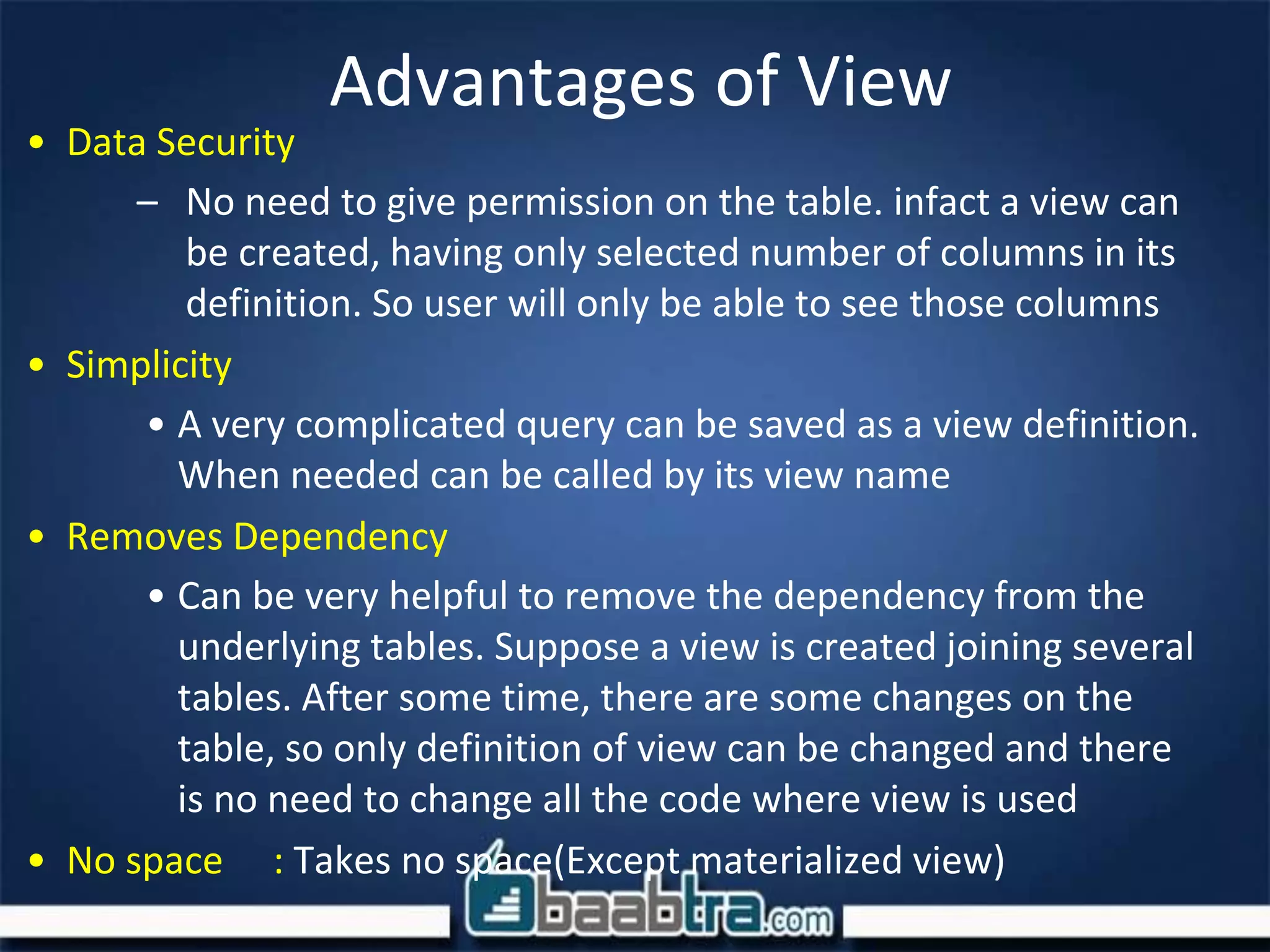
The document discusses user defined functions (UDF), views, and indexing in SQL Server. It provides an example of a UDF that returns a teacher's name based on their ID. Key differences between stored procedures and UDFs are that UDFs are compiled at runtime, can't perform DML operations, and must return a value. Views are described as customized representations of data from tables that don't take up storage space themselves. Indexing improves the speed of operations by organizing data to allow faster searches.

![User Defined functions [ UDF ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-functionsviewsindexing-150612115233-lva1-app6891/75/Chapter-4-functions-views-indexing-2-2048.jpg)