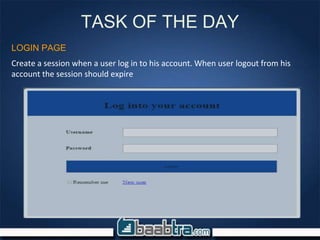
The document provides an introduction to using PHP sessions and cookies to maintain state across multiple requests. It discusses how cookies store small amounts of data on the client browser, while sessions allow storing data on the server. The document then provides steps to create a login system using sessions: 1) Check login credentials and create a session variable on successful login, 2) Display user profile details on the profile page by fetching the session variable, 3) Include a logout link that destroys the session to end the user session. Key differences between cookies and sessions are also summarized - cookies are stored on the client while sessions are stored on the server.






![Accessing a Cookie
• echo $_COOKIE[’userid’]; // prints 100
• Cookie as array
– setcookie("test_cookie[0]", "foo");
– setcookie("test_cookie[1]", "bar");
– setcookie("test_cookie[2]", "bar");
– var_dump($_COOKIE[‘test_cookie’]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-10-320.jpg)


![Creating and accessing session
• Once session is started you can create and access
session variables like any other arrays in PHP
– $_SESSION[‘userid’] = 100;
– echo $_SESSION[‘userid’]; //prints 100
Session variable name
variable value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-14-320.jpg)
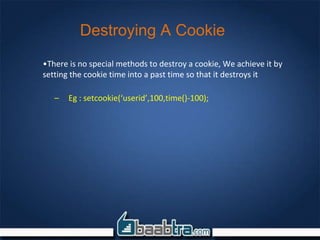
![Destroying A Session
•There are two methods to destroy a session variable
1. Using unset() function
• Eg unset($_SESSION[‘userid’])
1. Calling session_destroy() method. This will effectively destroy all the
session variables. So for deleting only one variable you should go for
the previous method
• Session_destroy()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-15-320.jpg)

![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
}
checks whether there is any
resultant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-19-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
}
starts a session](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-20-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
} sets a session variable
userid
with value of pk_int_user_id
field of the resultant set](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-21-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
} sets a session variable
userid
with value of pk_int_user_id
field of the resultant set](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-22-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
}
sets a session variable
userid
with value of pk_int_user_id
field of the resultant set](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-23-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Login_action.php Page
Check whether id is valid or not.if valid user then create session
if(mysql_num_rows($result)){
while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id']=$row['pk_int_user_id'];
header(‘Location: profile.php’);
}
}
header function is used for
page redirection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-24-320.jpg)

![Step 5
Profile.php
session_start();
$user_id=$_SESSION['user_id'];
mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
mysql_select_db("Baabtra");
$result=mysql_query("select * from tbl_academic_qualificaion where
fk_int_user_id='$user_id'");
echo “ qualification name-----college--------percentage--------passout”;
while($data=mysql_fetch_assoc($result)){
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['int_percentage'];
echo $data['dat_passout_date'];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-27-320.jpg)
![Step 5
Profile.php
session_start();
$user_id=$_SESSION['user_id'];
mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
mysql_select_db("Baabtra");
$result=mysql_query("select * from tbl_academic_qualificaion where
fk_int_user_id='$user_id'");
echo “ qualification name-----college--------percentage--------passout”;
while($data=mysql_fetch_assoc($result)){
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['int_percentage'];
echo $data['dat_passout_date'];
}
fetches the session variable
user_id and stores to
variable $userid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-28-320.jpg)
![Step 5
Profile.php
session_start();
$user_id=$_SESSION['user_id'];
mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
mysql_select_db("Baabtra");
$result=mysql_query("select * from tbl_academic_qualificaion where
fk_int_user_id='$user_id'");
echo “ qualification name-----college--------percentage--------passout”;
while($data=mysql_fetch_assoc($result)){
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['vchr_qualification_name'];
echo $data['int_percentage'];
echo $data['dat_passout_date'];
}
selects the qualification
details of the user that
matches with session value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-29-320.jpg)
![Step 6
Logout.php
unset($_SESSION[‘user_id’]);
header(‘Location: Login_baabtra.php’);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpsessionscookies-150702103338-lva1-app6891/85/Php-sessions-cookies-31-320.jpg)

