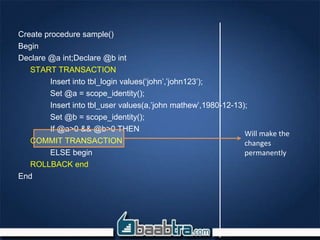
This document discusses transactions in SQL Server. It introduces transactions and their relevance in ensuring data integrity when multiple tables need to be updated together. Transactions group a set of database operations so that if any operation fails, all operations are rolled back. The document demonstrates creating a transaction using START TRANSACTION, COMMIT TRANSACTION, and ROLLBACK TRANSACTION statements. It also shows handling transactions within try/catch blocks so that failures cause a rollback. Transactions ensure atomicity and integrity by committing all operations together as a single unit, or rolling them all back if any fail.