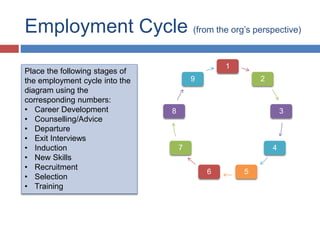
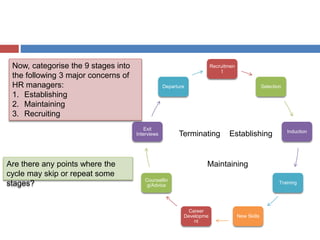
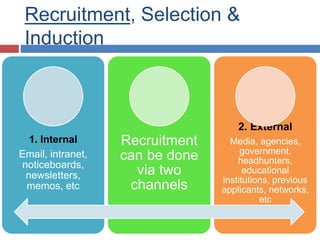
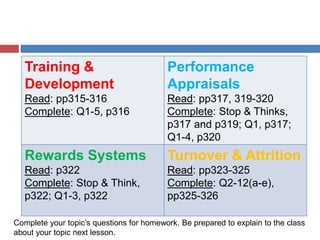
Here are the key points from the group on Training and Development:
- Training and development helps employees improve skills and knowledge to perform better in their roles.
- On-the-job training includes coaching, mentoring and shadowing more experienced employees.
- Off-the-job training takes place away from the work environment, such as seminars, conferences or online courses.
- Development focuses more on career progression through further education or new experiences.
- Benefits of training include improved performance, motivation and retention of employees. It also ensures employees can adapt to changes in technology and work processes.
- Training needs are identified through performance reviews comparing actual to required skills.
- Evaluation of training programs



![What is Human Resources?
‘…is the management of the employment
relationship…it covers establishing,
maintaining and terminating
employment…[HRM] involves planning,
organising, leading and controlling the staffing
needs of an organisation.’
Mylonas, et al (2007), p283](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrpowerpoint-150812042226-lva1-app6892/85/HR-PowerPoint-4-320.jpg)