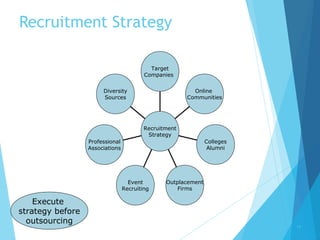
This document discusses recruitment and the recruitment process. It begins by defining recruitment as attracting qualified individuals in sufficient numbers through various methods. It then discusses internal recruitment methods like job postings and employee referrals. Next, it describes the role of an internal recruiter in handling various recruitment activities. The document outlines the recruitment process including job analysis, sourcing candidates, selection methods, and key metrics to track like time-to-hire and cost-per-hire. It also discusses recruitment strategy, sources, and methods both internal and external to the organization.

















![Key metrics to monitor and
track [Time-to-hire]
[The total time required for hiring.]
[Quality-of-hire]
[How satisfied an organization is with a hire.]
[Number of vacancies outstanding]
[The total number of job vacancies
the company has.]
[Cost-per-hire]
[The total cost associated with a given
position and hire.]
[Recruit source effectiveness]
[The effectiveness of each source the
company uses to generate candidates.]
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recruitment-160310140938/85/Recruitment-process-19-320.jpg)

