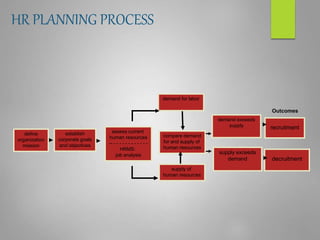
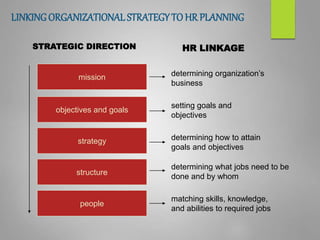
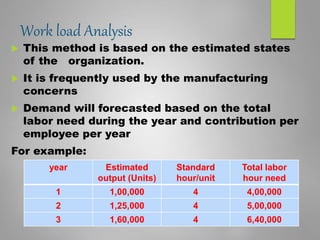
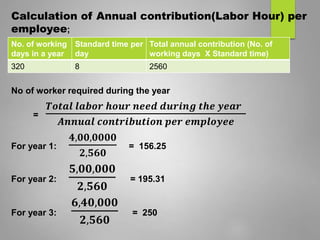
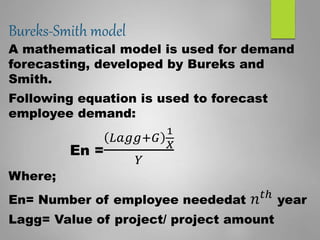
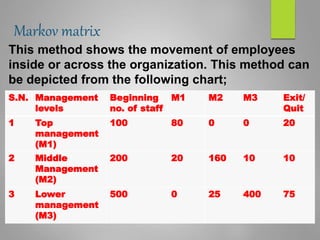
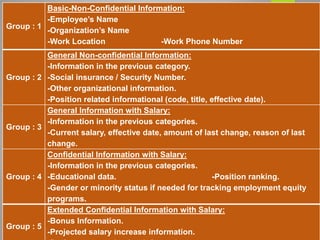
Human resource planning is a systematic process that ensures an organization will have the right number and type of employees with the necessary skills to implement strategies and achieve goals. It involves forecasting future human resource needs based on organizational strategies, assessing current human resources, developing action plans to address gaps, and auditing and adjusting plans. Key aspects of HR planning include linking it to organizational strategy, forecasting HR demand and supply, developing acquisition, utilization, and development plans, and implementing programs for recruitment, training, career development, and more. It is an important element for organizational success.