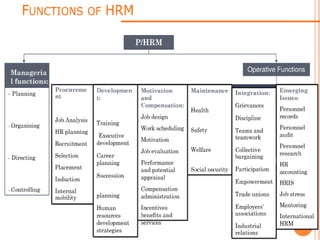
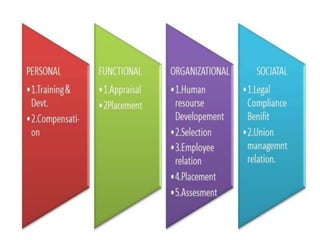
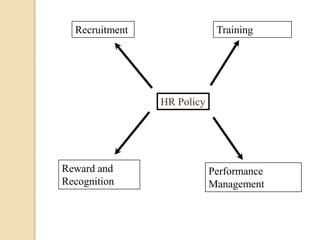
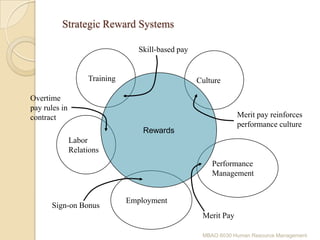
This document discusses human resource management (HRM). It defines HRM as a management function concerned with hiring, motivating, and maintaining employees in an organization. The key functions of HRM include procuring employees, developing employees, compensating employees, integrating employee and organizational interests, motivating employees, and providing employee welfare. The objectives of HRM are to achieve individual development, effectively utilize human resources, establish good work relations, ensure employee satisfaction, help the organization achieve its goals, and maintain a competent and willing workforce.