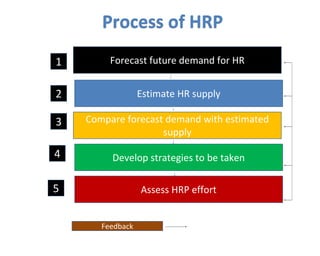
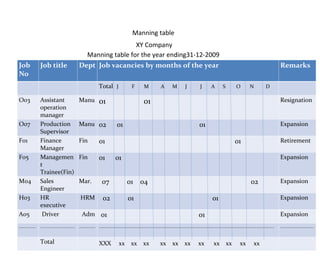
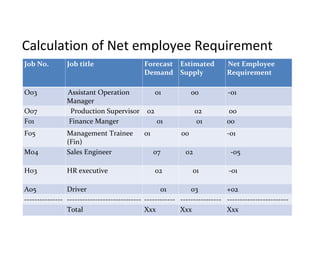
The document outlines the human resource planning (HRP) process, which involves 5 steps: 1) forecasting future HR demand, 2) estimating internal and external HR supply, 3) comparing demand and supply to determine surpluses or shortages, 4) developing strategies like hiring freezes or overtime to address imbalances, and 5) assessing the effectiveness of the HRP effort. Key aspects of HRP include determining future staffing needs, utilizing HR efficiently, controlling costs, and informing strategic planning. Common techniques for forecasting demand are informal estimates, expert surveys, and extrapolation of past trends.