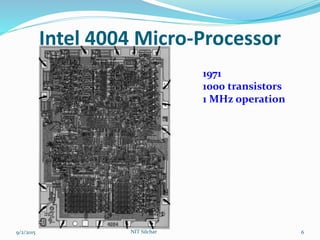
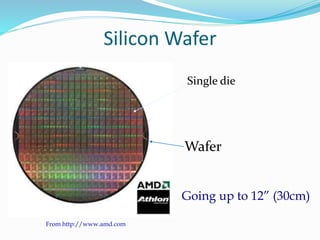
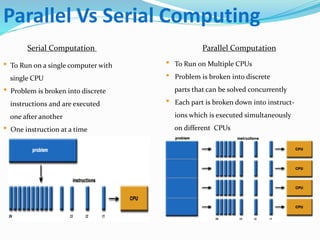
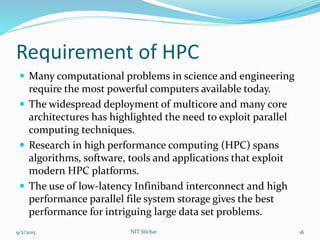
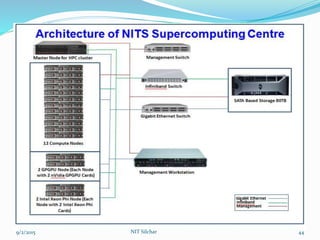
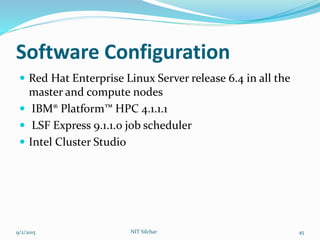
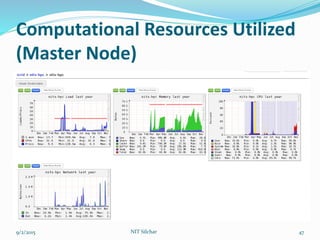
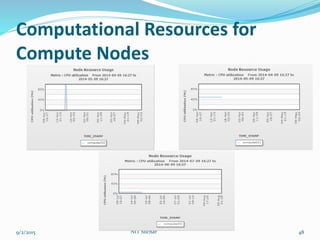
This document outlines the history and capabilities of VLSI and high performance computing (HPC). It discusses how VLSI technology has enabled exponential growth in transistor counts and computing power over decades. HPC utilizes parallel processing across computer clusters and supercomputers to efficiently handle massive data and solve complex problems. The document describes common HPC metrics like FLOPS and provides examples of HPC applications in fields such as manufacturing, entertainment, science and more. It also provides details about the HPC center established at NIT Silchar, including its computational resources and role in supporting research.