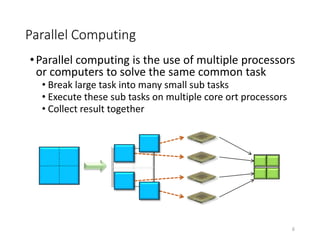
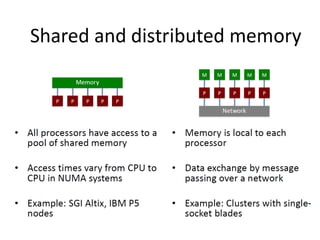
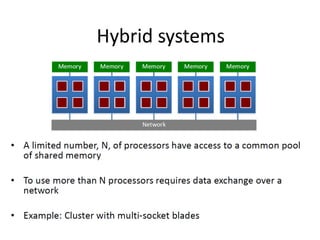
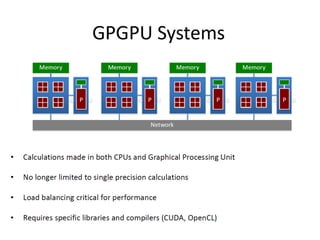
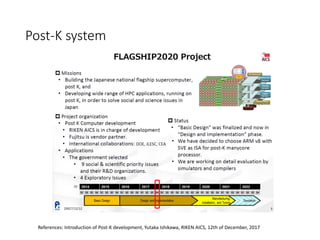
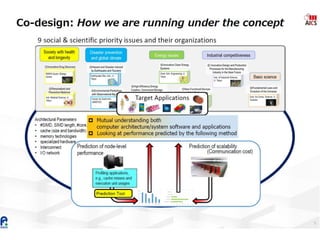
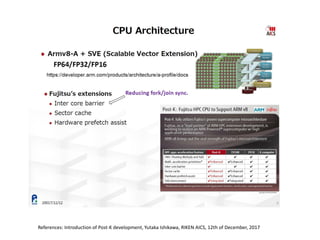
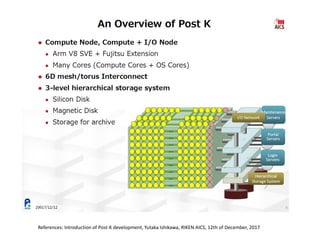
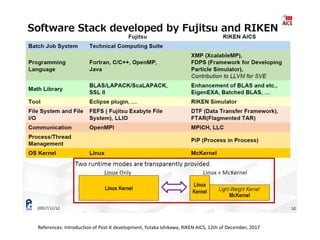
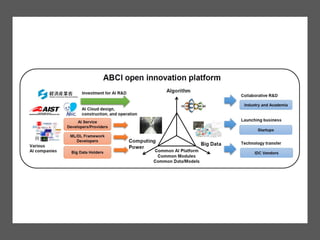
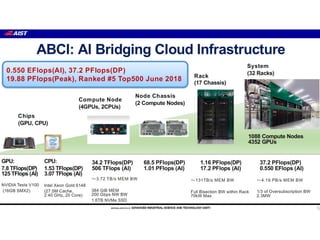
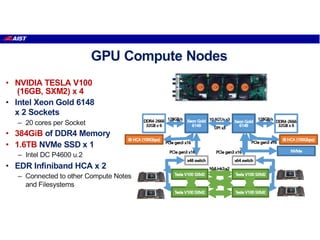
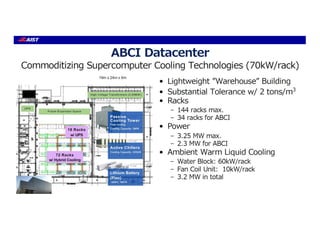
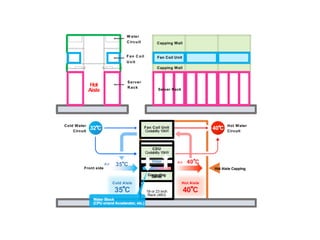
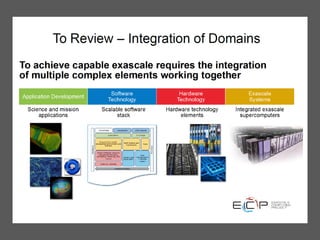
The document discusses the future of high performance computing (HPC). It covers several topics:
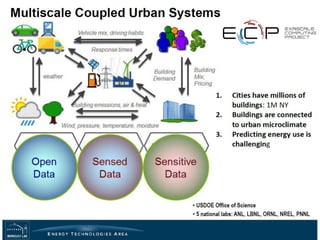
- Next generation HPC applications will involve larger problems in fields like disaster simulation, urban science, and data-intensive science. Projects like the Square Kilometer Array will generate exabytes of data daily.
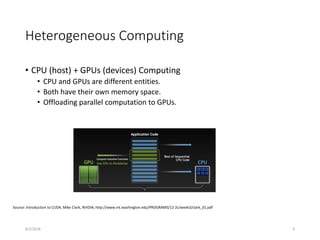
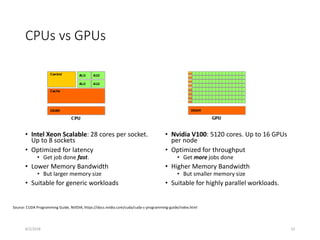
- Hardware trends include using many-core processors, accelerators like GPUs, and heterogeneous computing with CPUs and GPUs. Future exascale systems may use conventional CPUs with GPUs or innovative architectures like Japan's Post-K system.
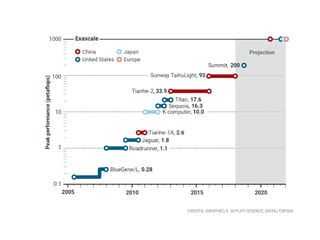
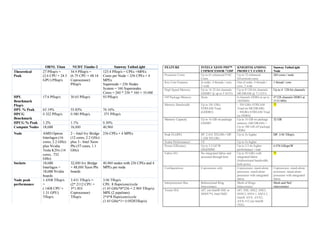
- The top supercomputers in the world currently include Summit, a IBM system combining Power9 CPUs and Nvidia Voltas at Oak Ridge, and China's Sunway Taihu