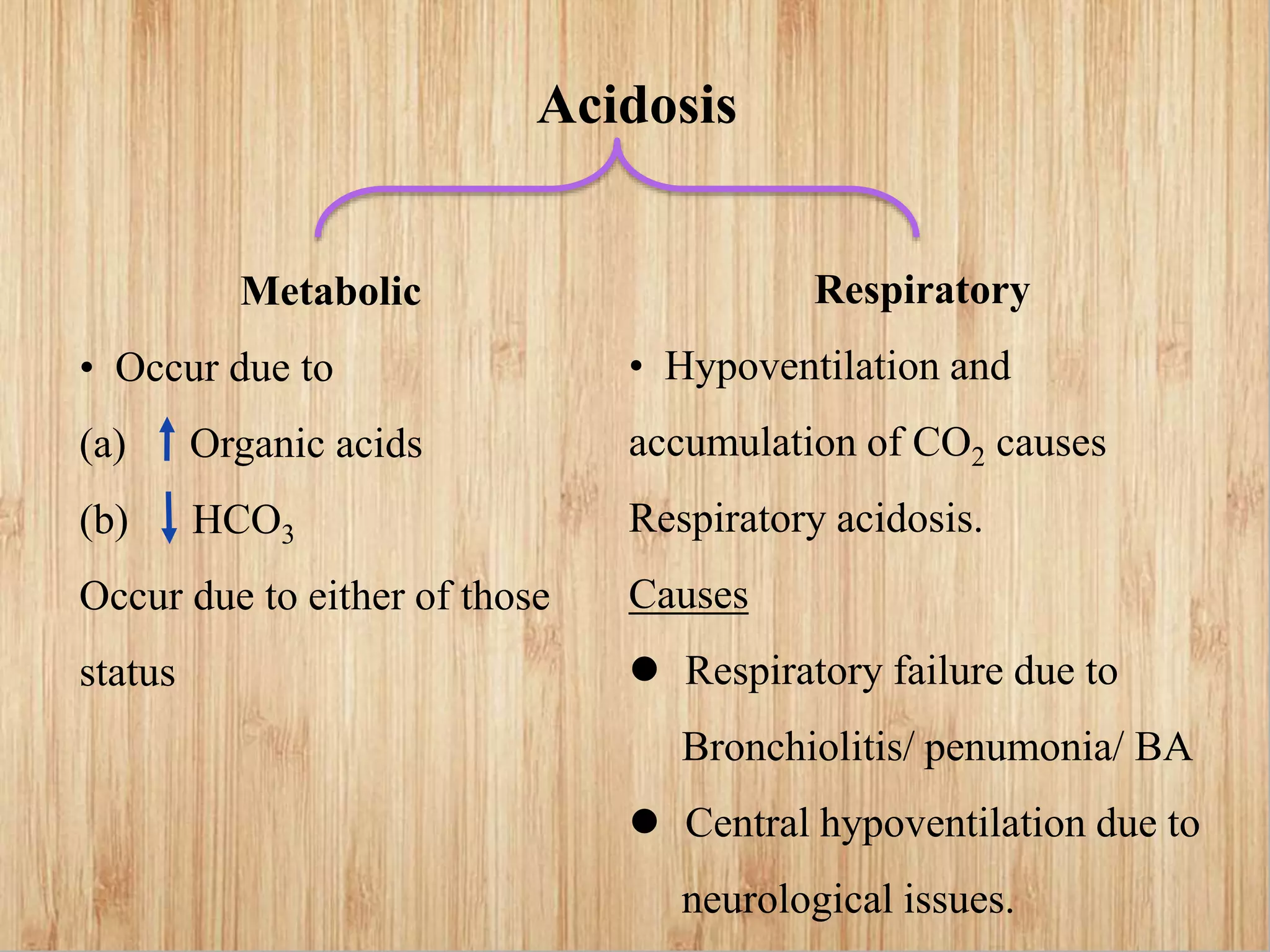
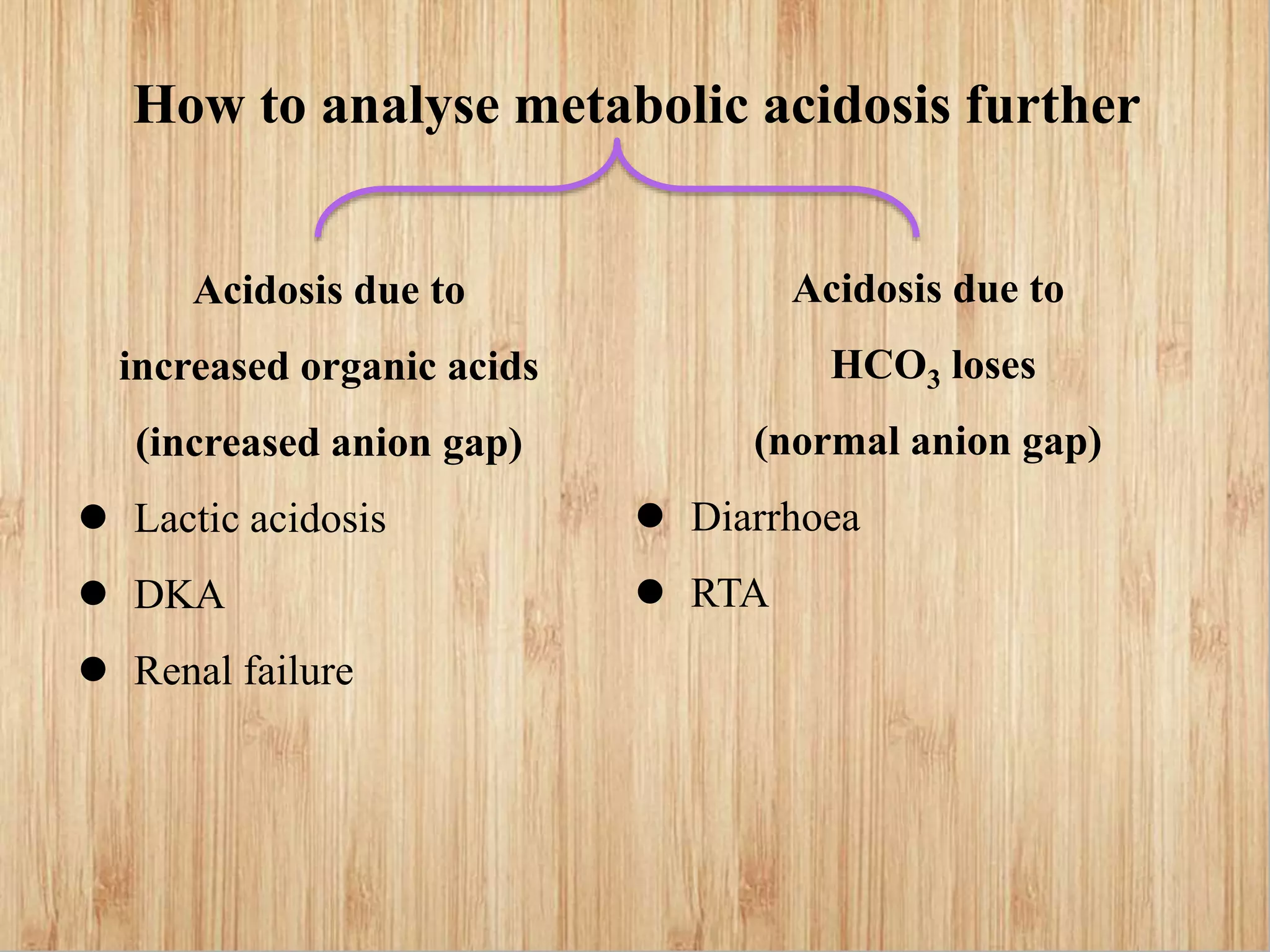
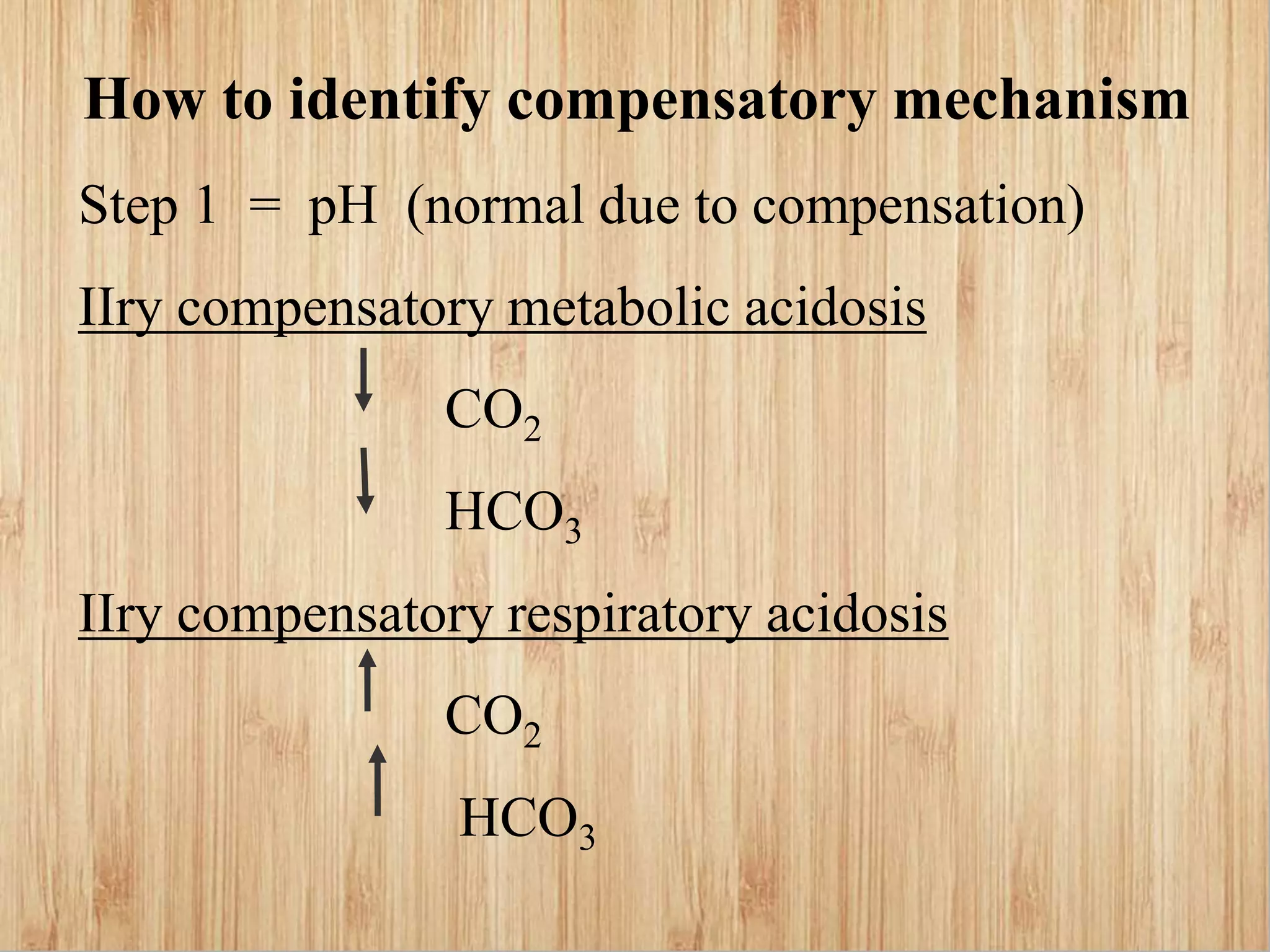
This document provides guidance on interpreting arterial blood gas reports. It outlines the key parameters measured in an ABG including pH, PaCO2, PaO2, HCO3, and anion gap. Normal ranges for each parameter are provided. The document explains how to analyze the report to determine a patient's oxygenation and acid-base status, and whether they have respiratory or metabolic acidosis or alkalosis. Compensatory mechanisms are discussed. The importance of considering age-specific norms for neonates is also highlighted.