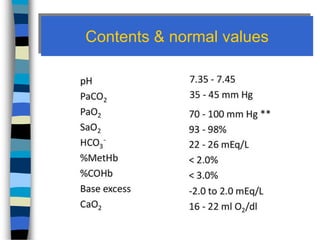
This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including what it is, its purpose, interpretation, and conditions it can assess like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). ABG measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH in blood and helps evaluate lung and kidney function in acid-base balance. It determines pH levels and the partial pressures of carbon dioxide and oxygen. The 6 steps to interpret ABGs are analyzing pH, pCO2, HCO3, matching acid-base disturbances, checking for compensation, and analyzing pO2 and oxygen saturation. DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes where lack of insulin causes ketone production from fat breakdown.