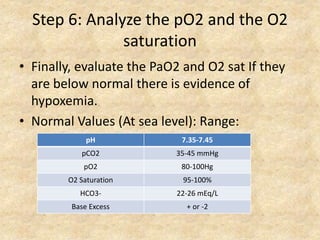
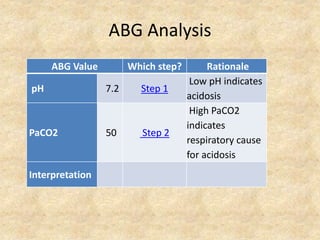
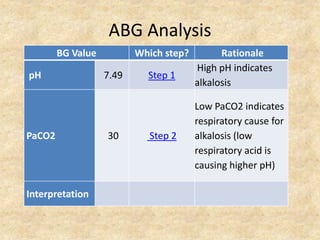
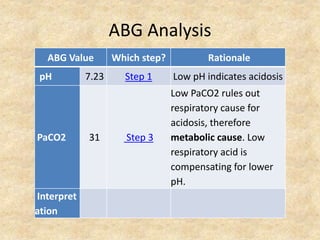
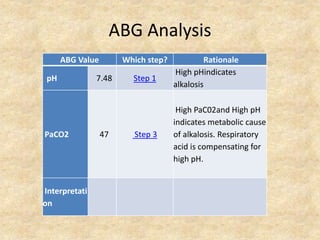
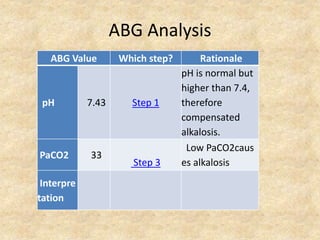
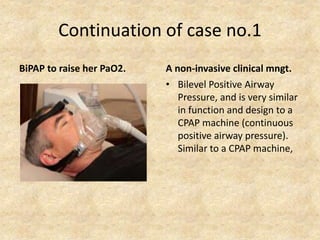
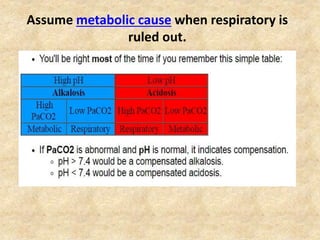
The document provides a comprehensive guide to arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, detailing the steps involved in interpreting the results, including normal ranges for pH, pCO2, and HCO3. It explains how to determine if acid-base imbalances are of respiratory or metabolic origin, the process of compensatory mechanisms, and offers clinical case examples to solidify understanding. Key concepts such as the anion gap, respiratory and metabolic acidosis and alkalosis, and the importance of assessing oxygenation levels are highlighted.



















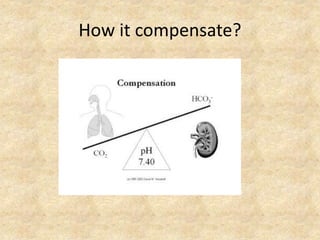



![Is there appropriate compensation? Is
it acute or chronic ?
Metabolic Acidosis
Winter’s formula: pCO2 = 1.5[HCO3] + 8 ± 2
MEMORIZE
If serum pCO2 > expected pCO2 -> additional
respiratory acidosis
Another useful tool in estimating the PCO2 in
metabolic acidosis is the recognition that the pCO2 is
always approximately equal to the last 2 digits of the
pH.
Metabolic Alkalosis
For every 10 increase in HCO3 -> pCO2 increases by 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abganalysis-180126025037/85/ABG-Analysis-Interpretation-25-320.jpg)