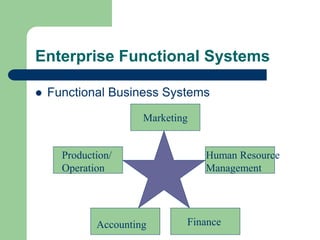
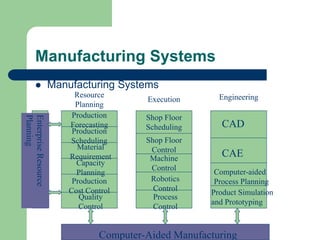
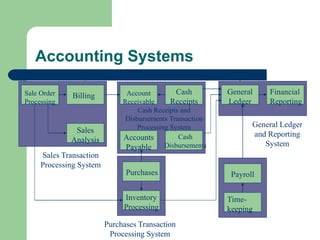
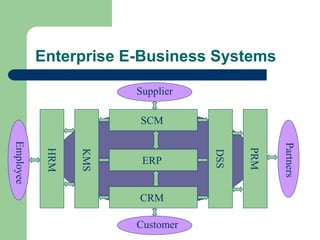
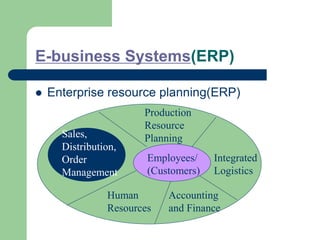
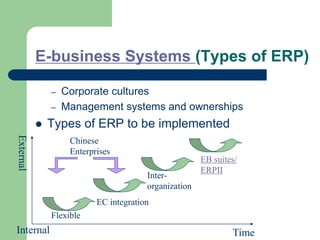
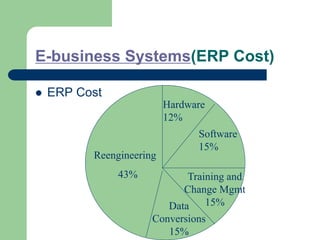
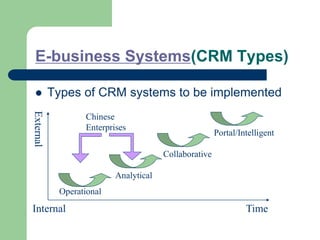
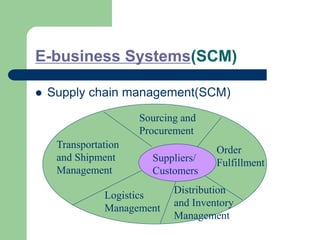
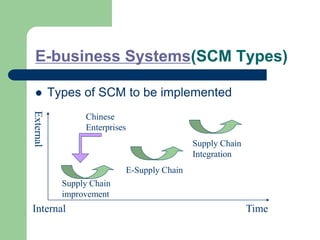
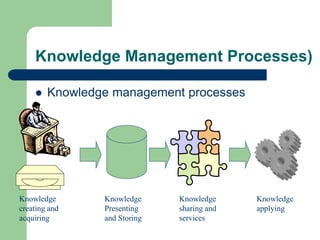
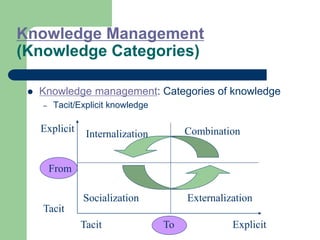
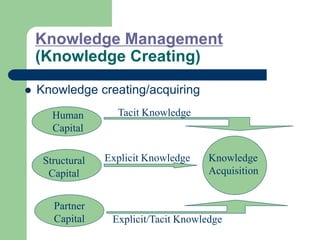
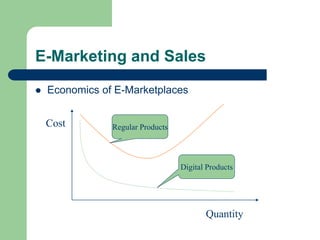
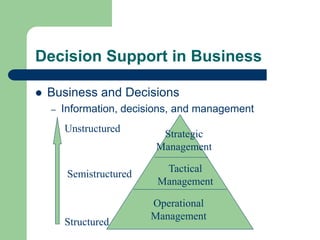
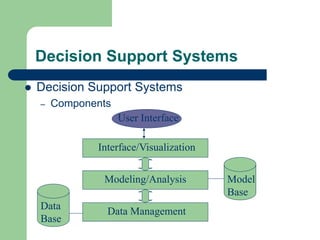
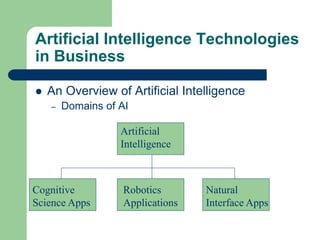
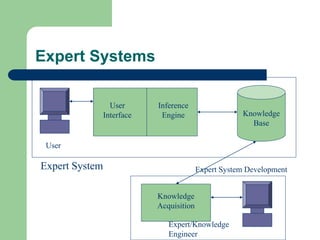
The document outlines various enterprise systems including functional systems, e-business systems, and knowledge management. It describes marketing, manufacturing, human resource, accounting, and financial management systems as part of functional systems. For e-business systems it discusses ERP, CRM, SCM, and other systems. It also explains knowledge management processes and applications.