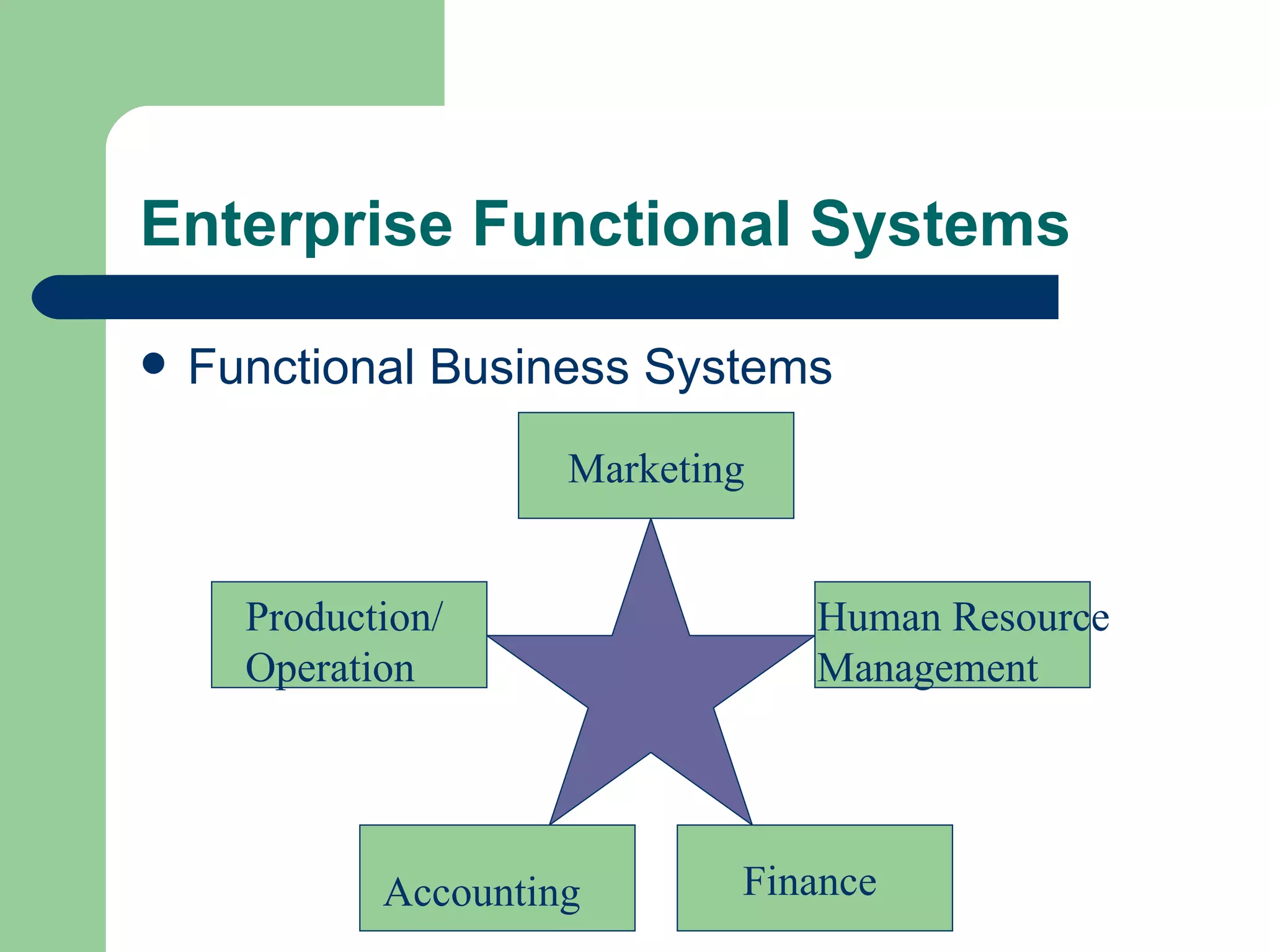
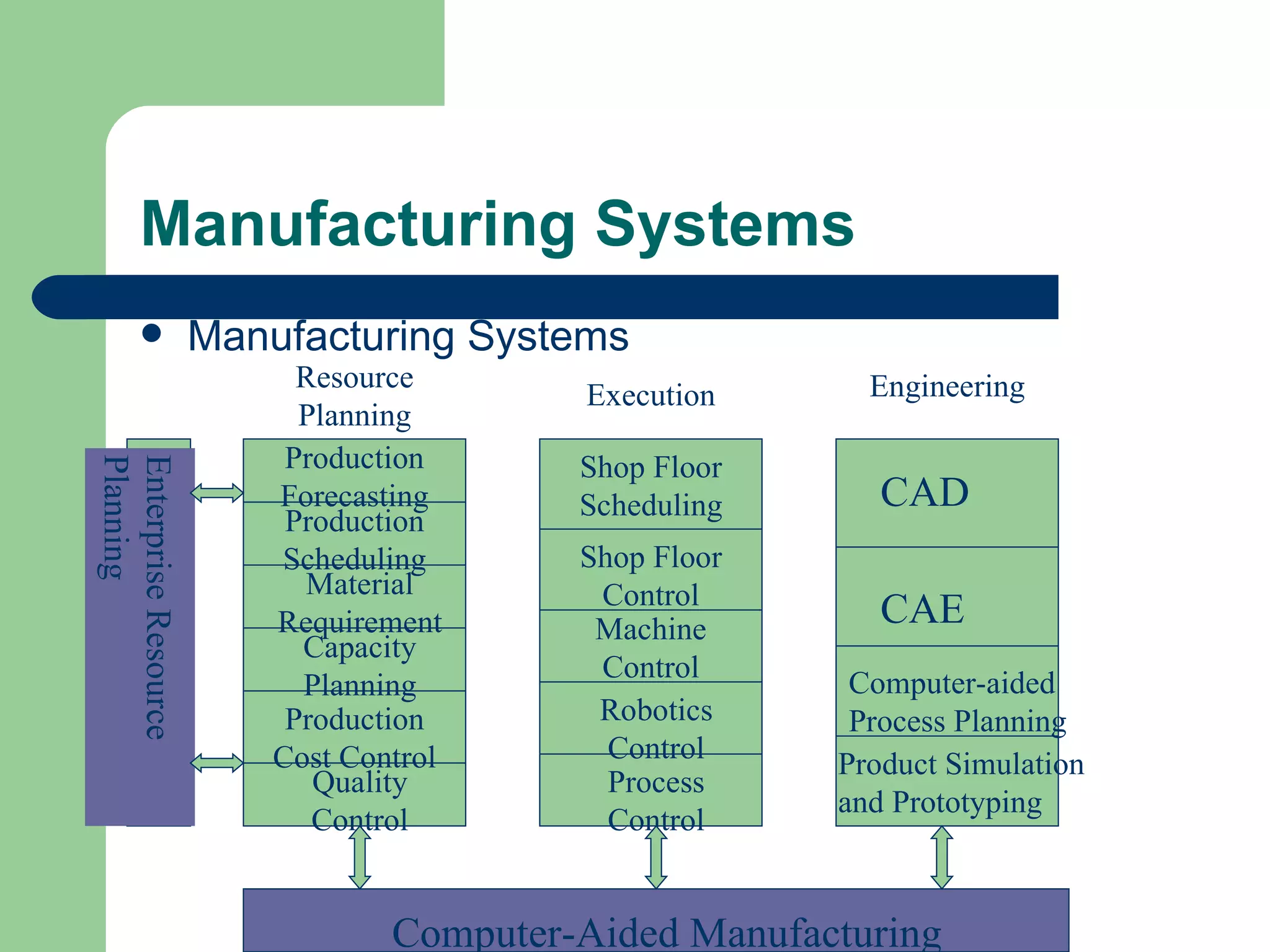
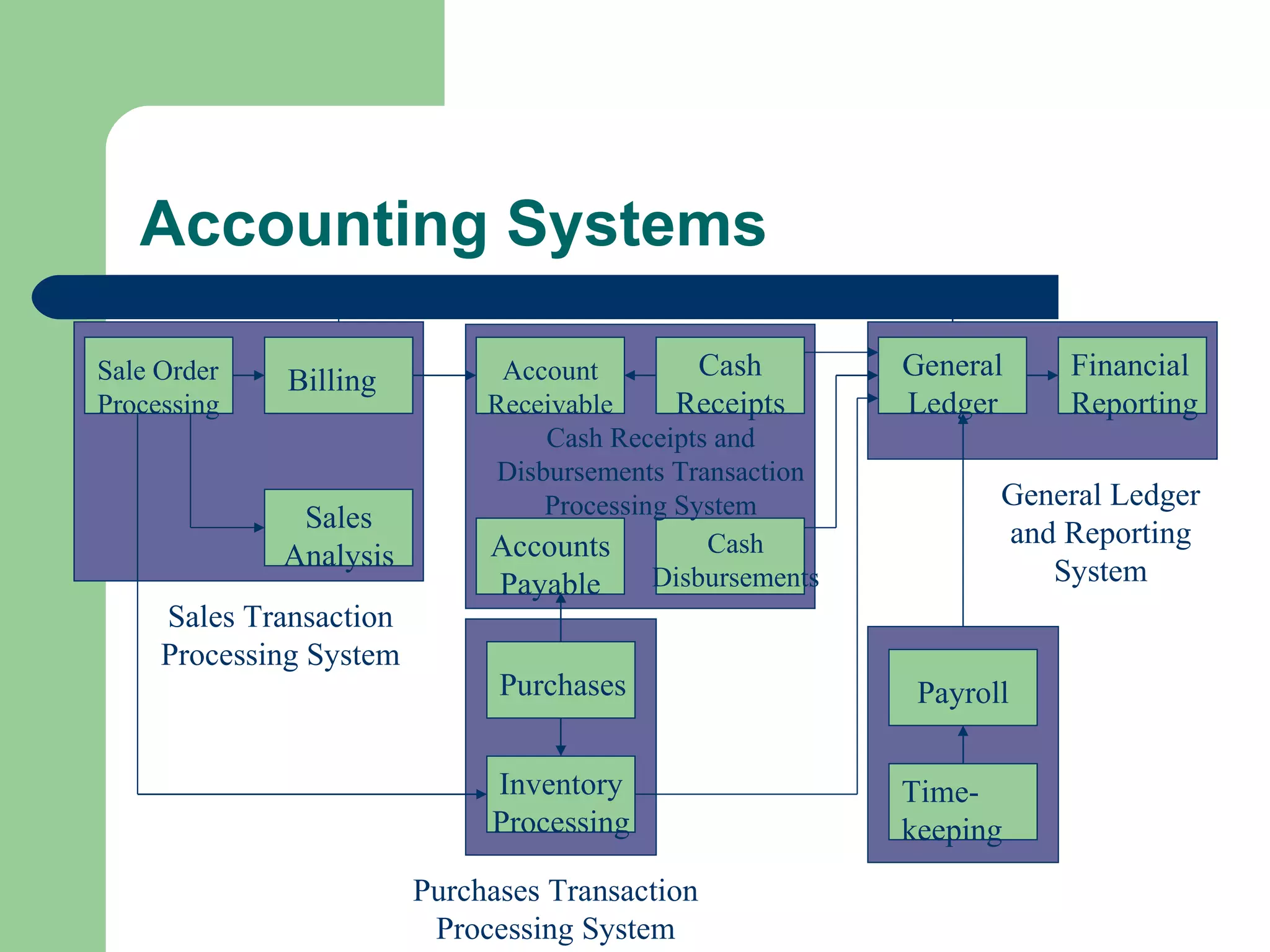
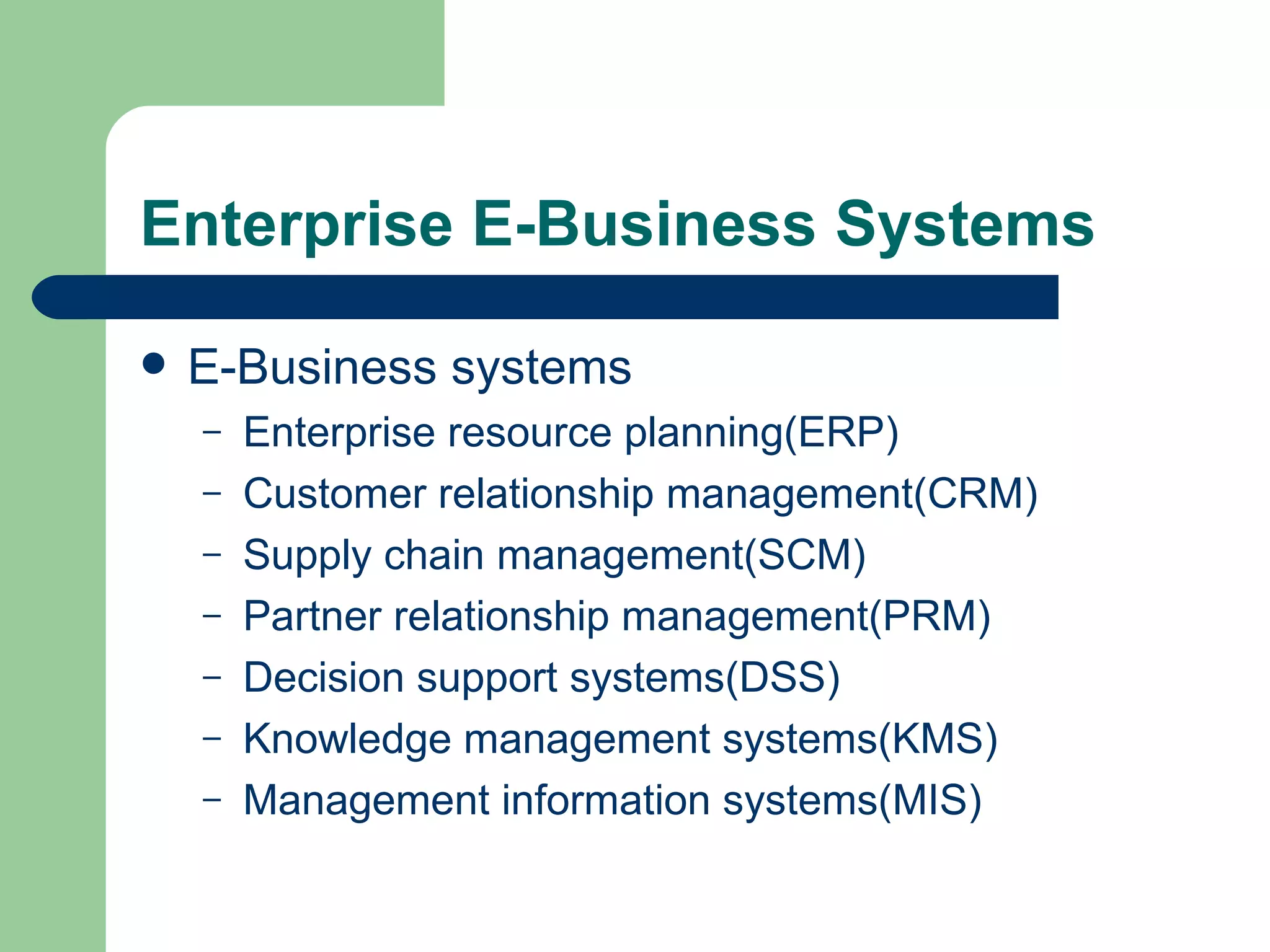
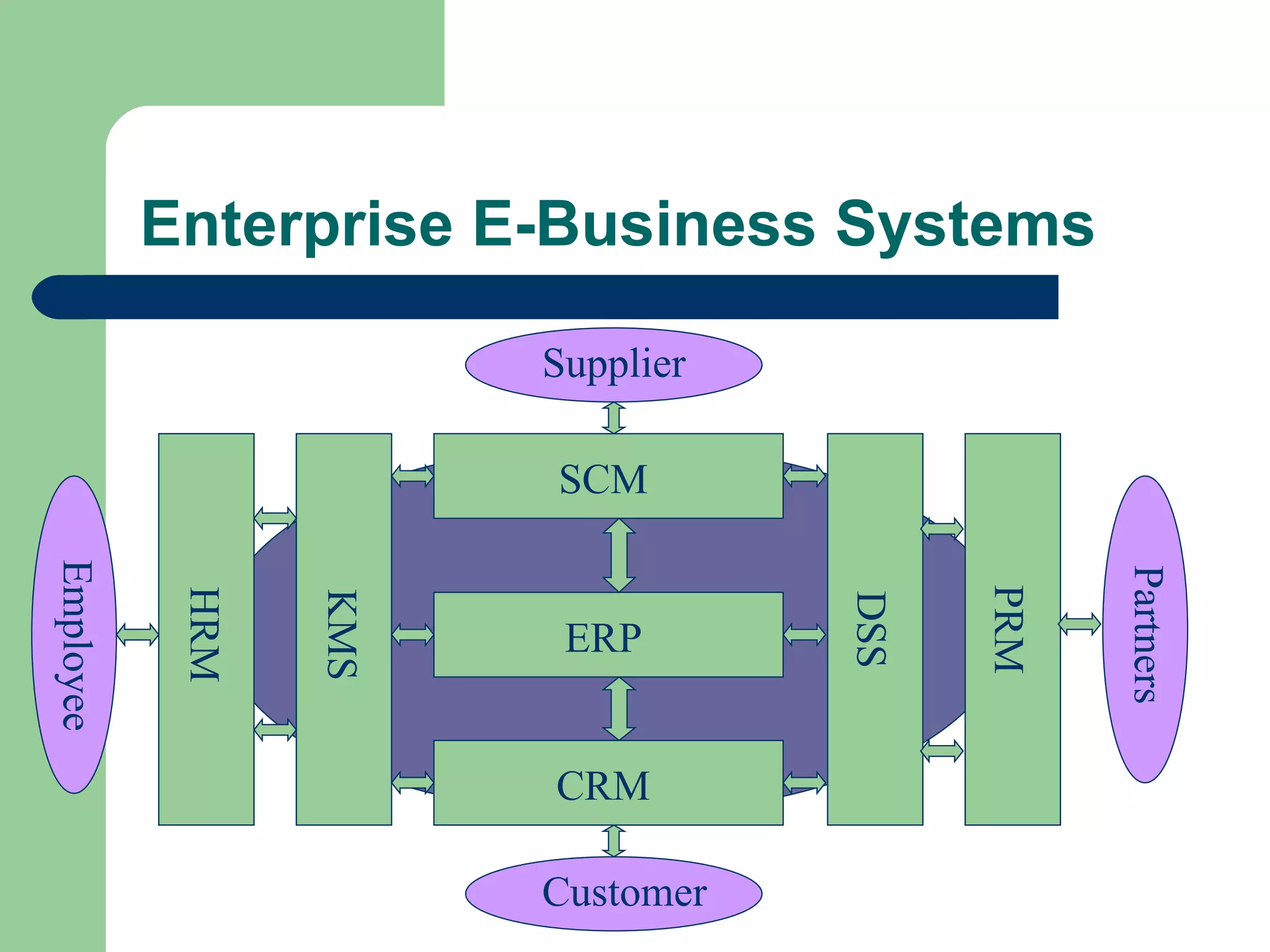
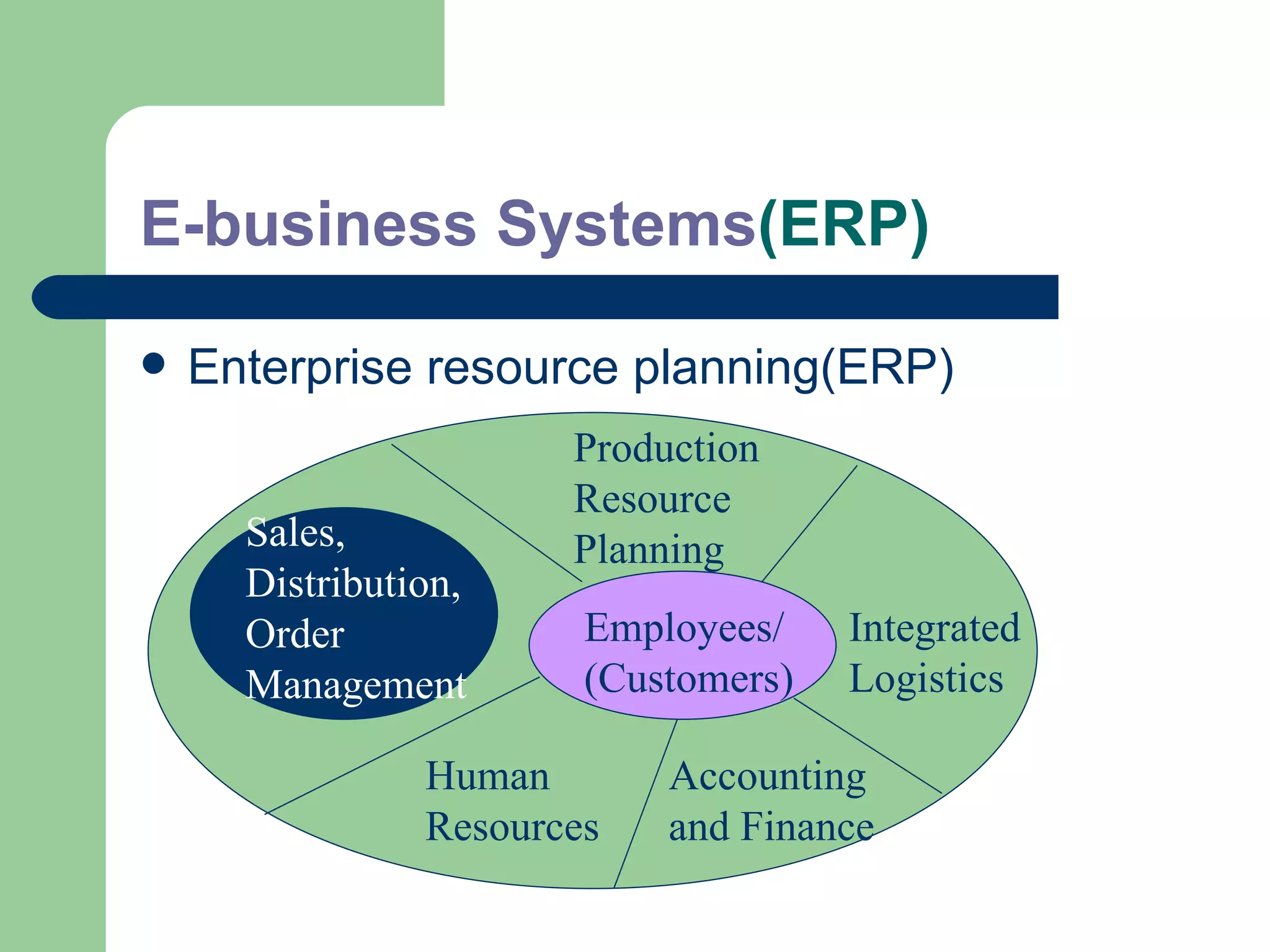
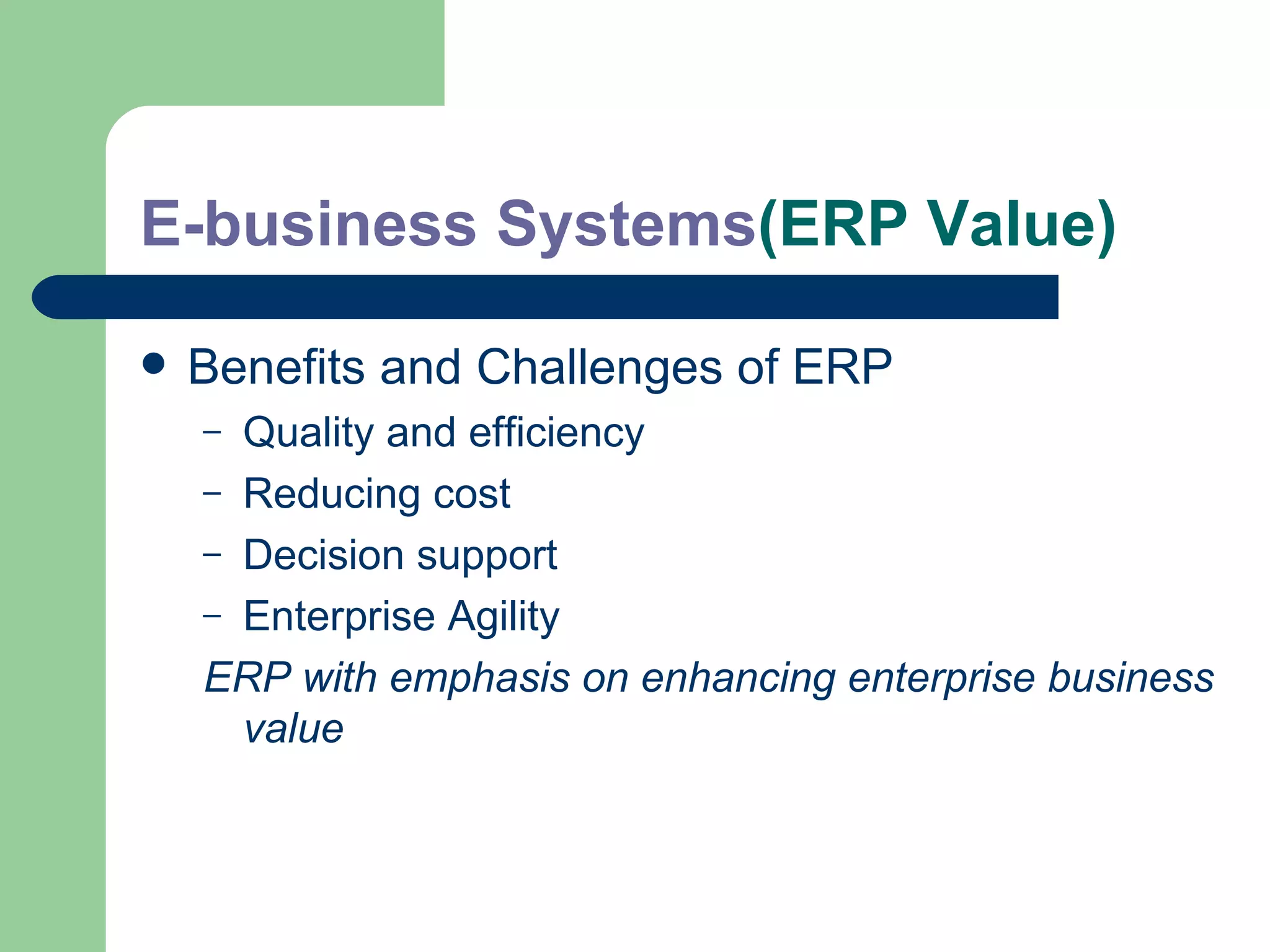
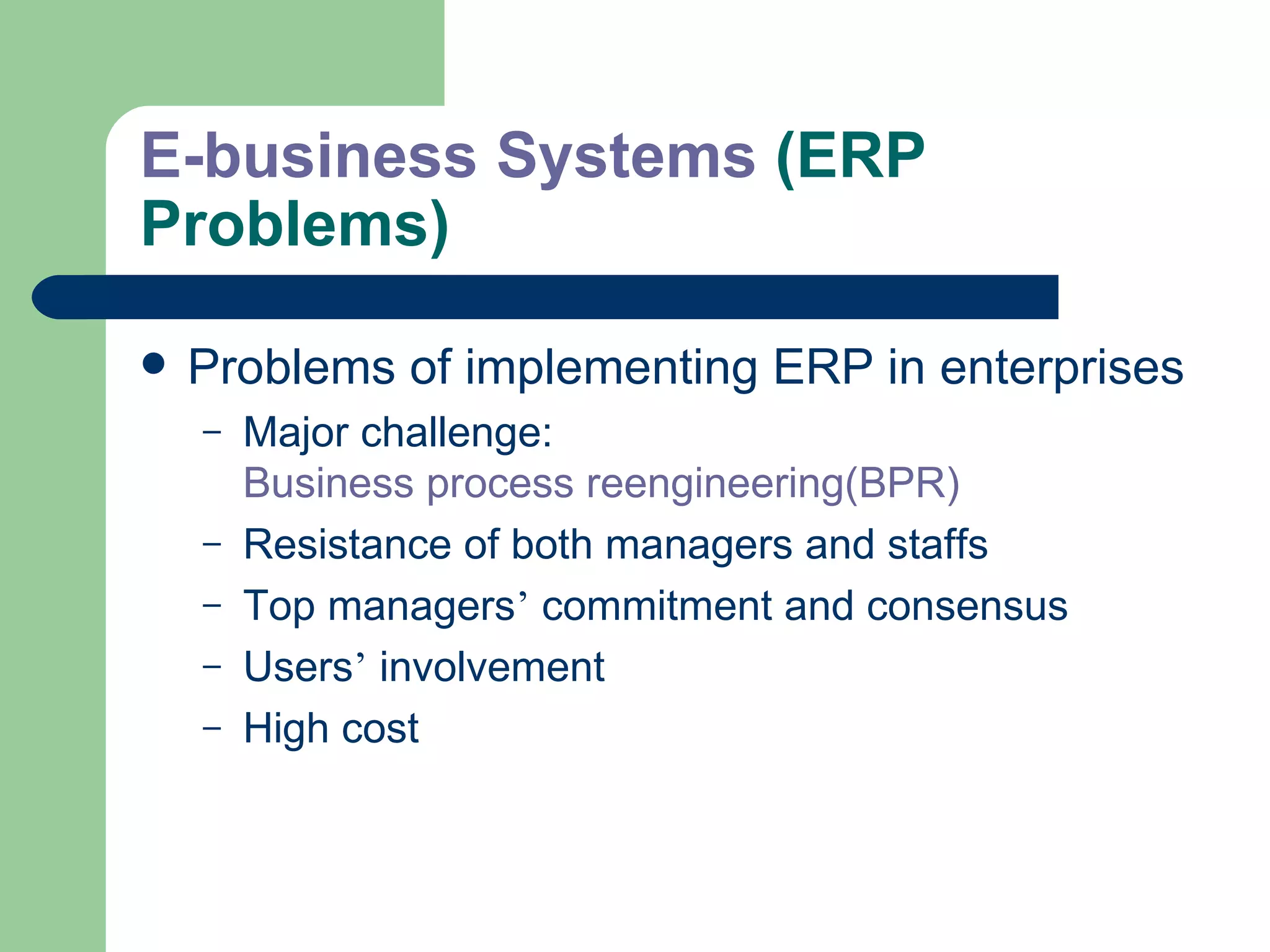
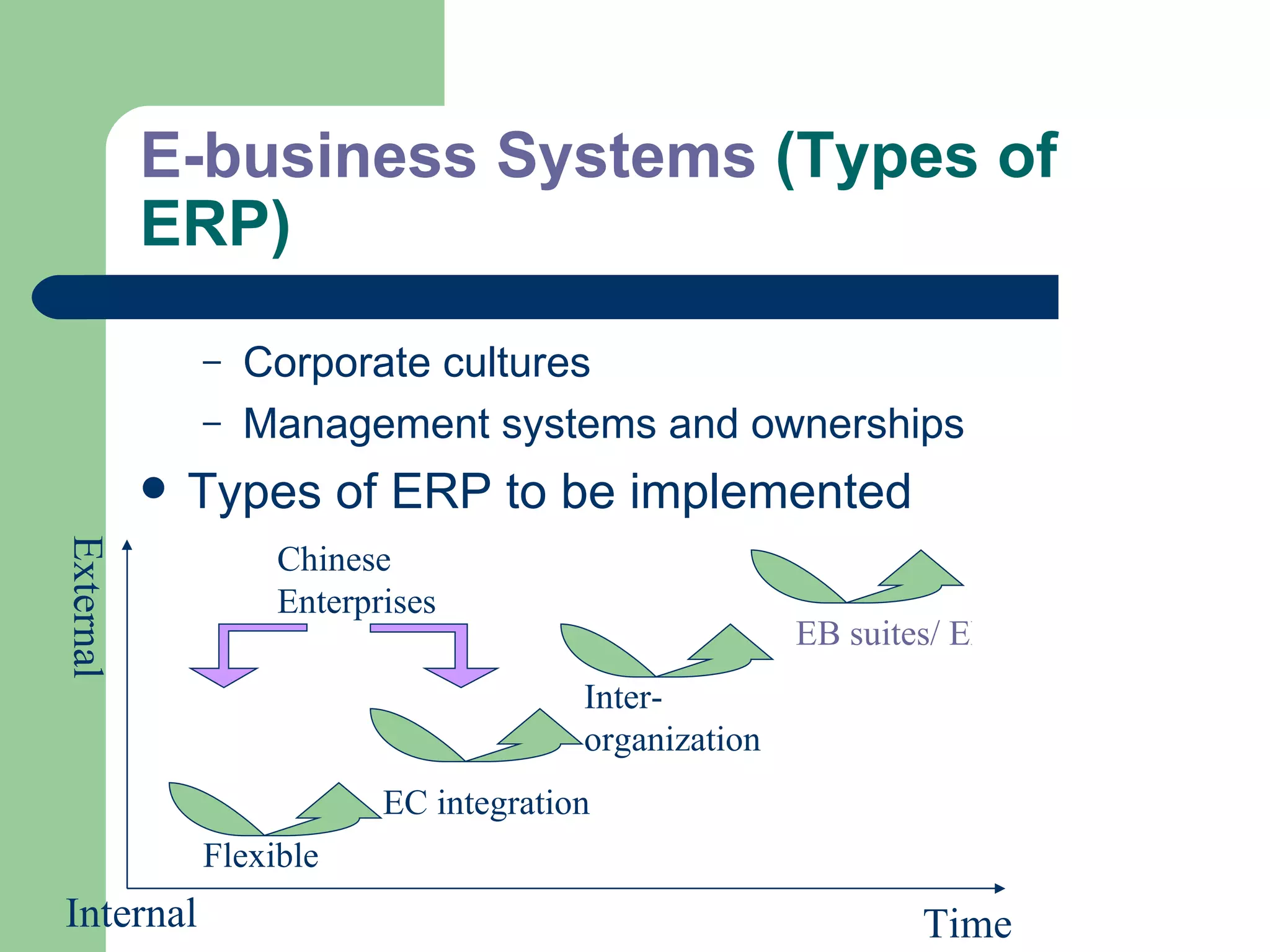
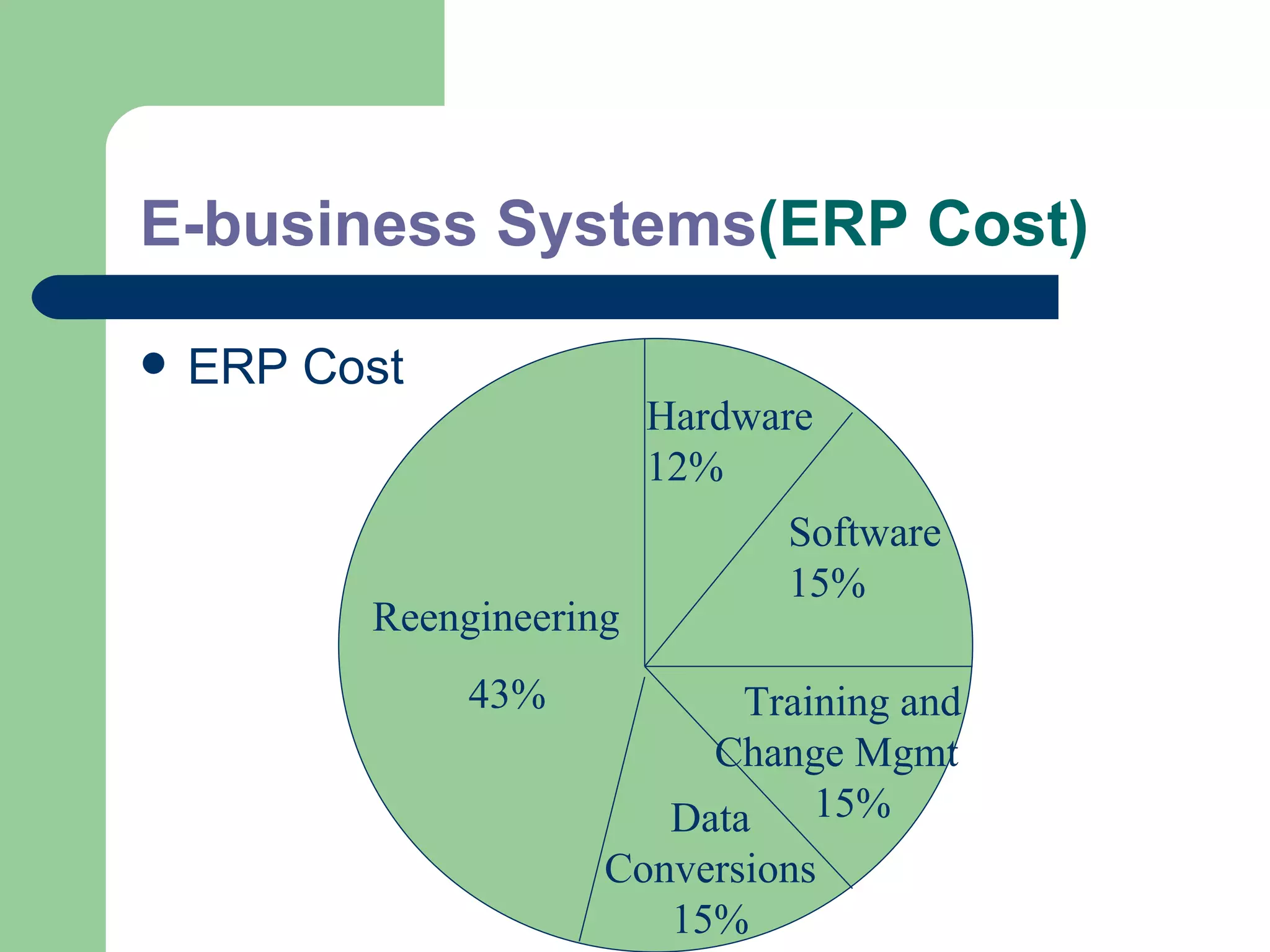
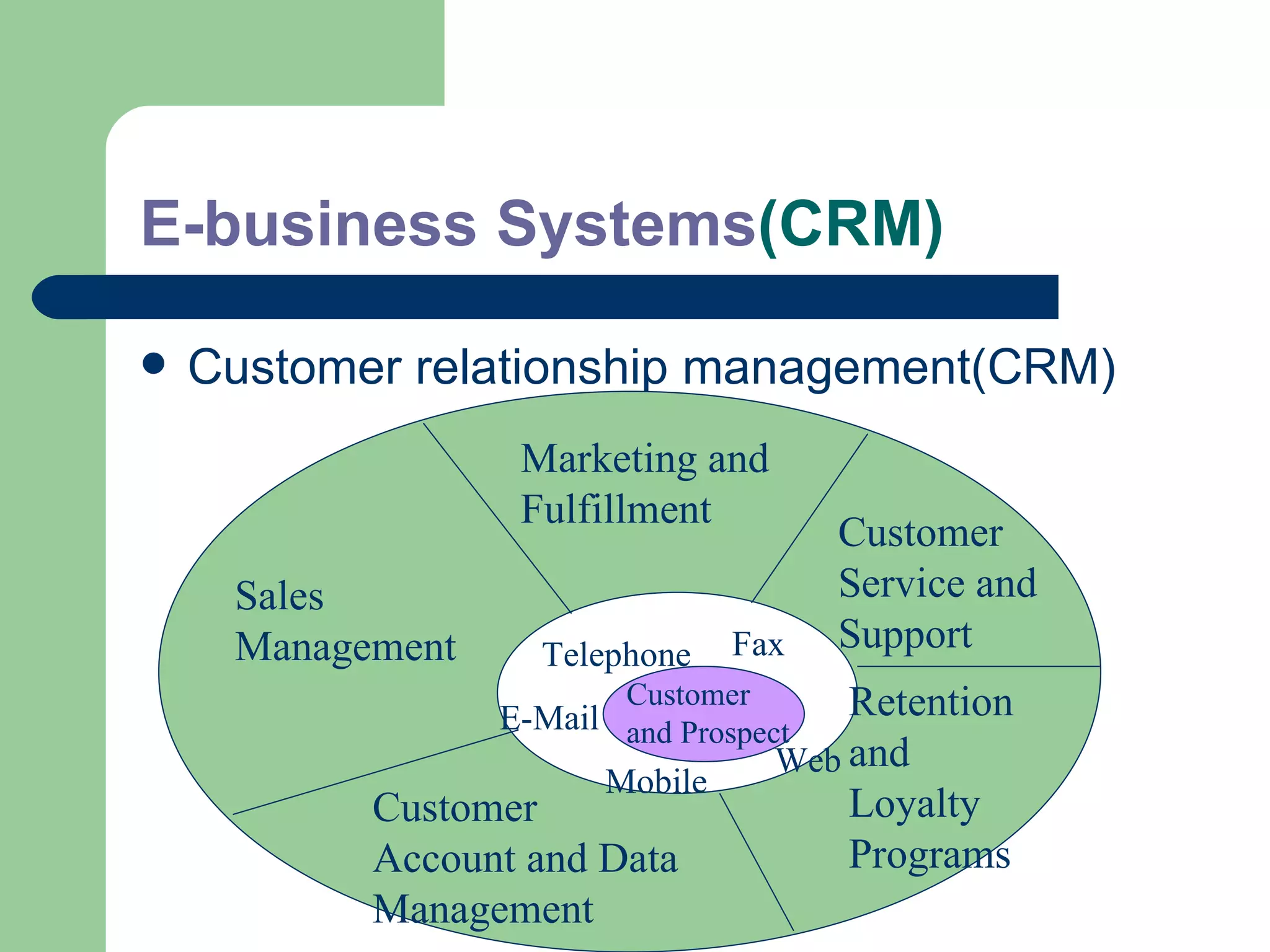
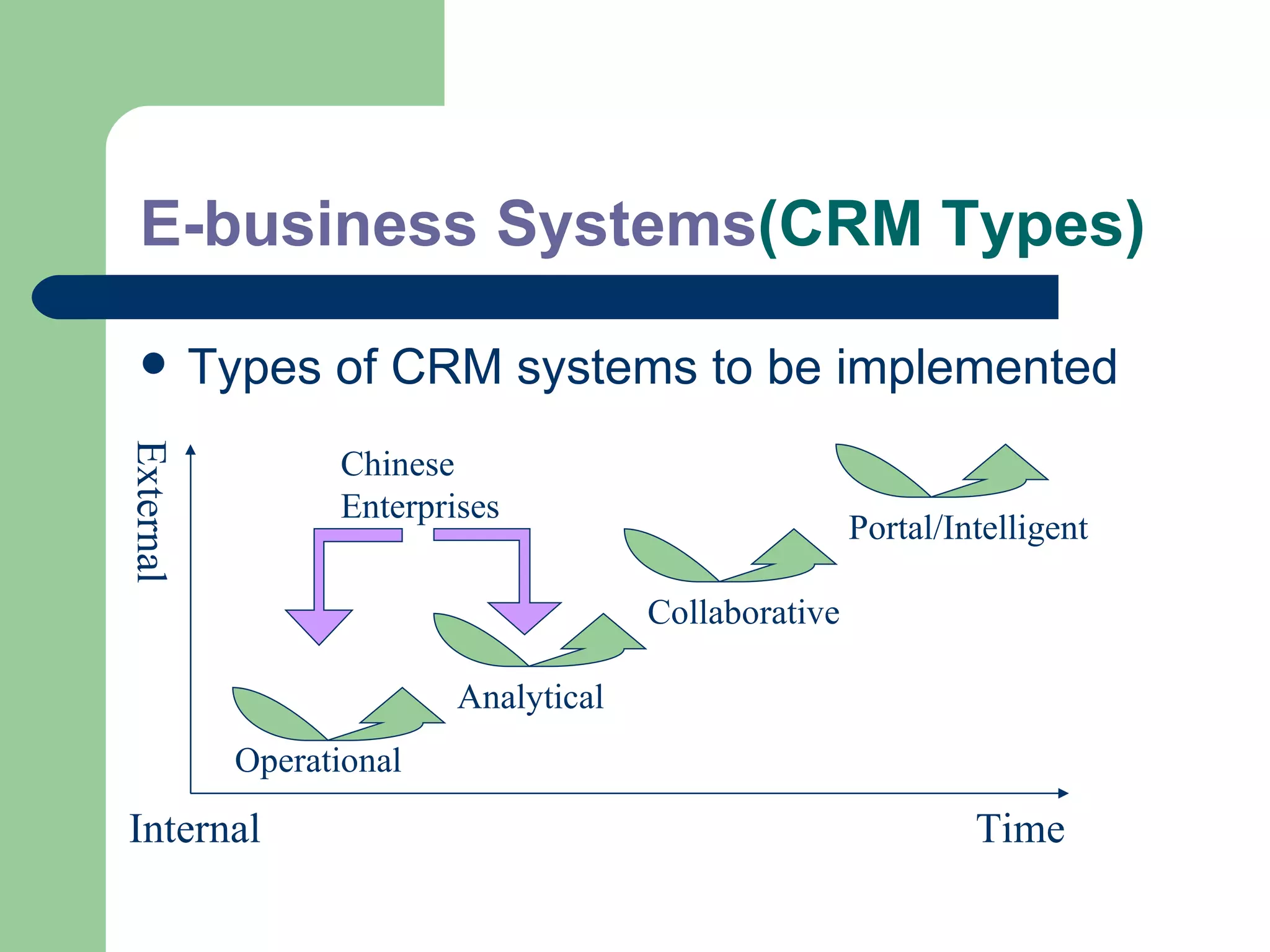
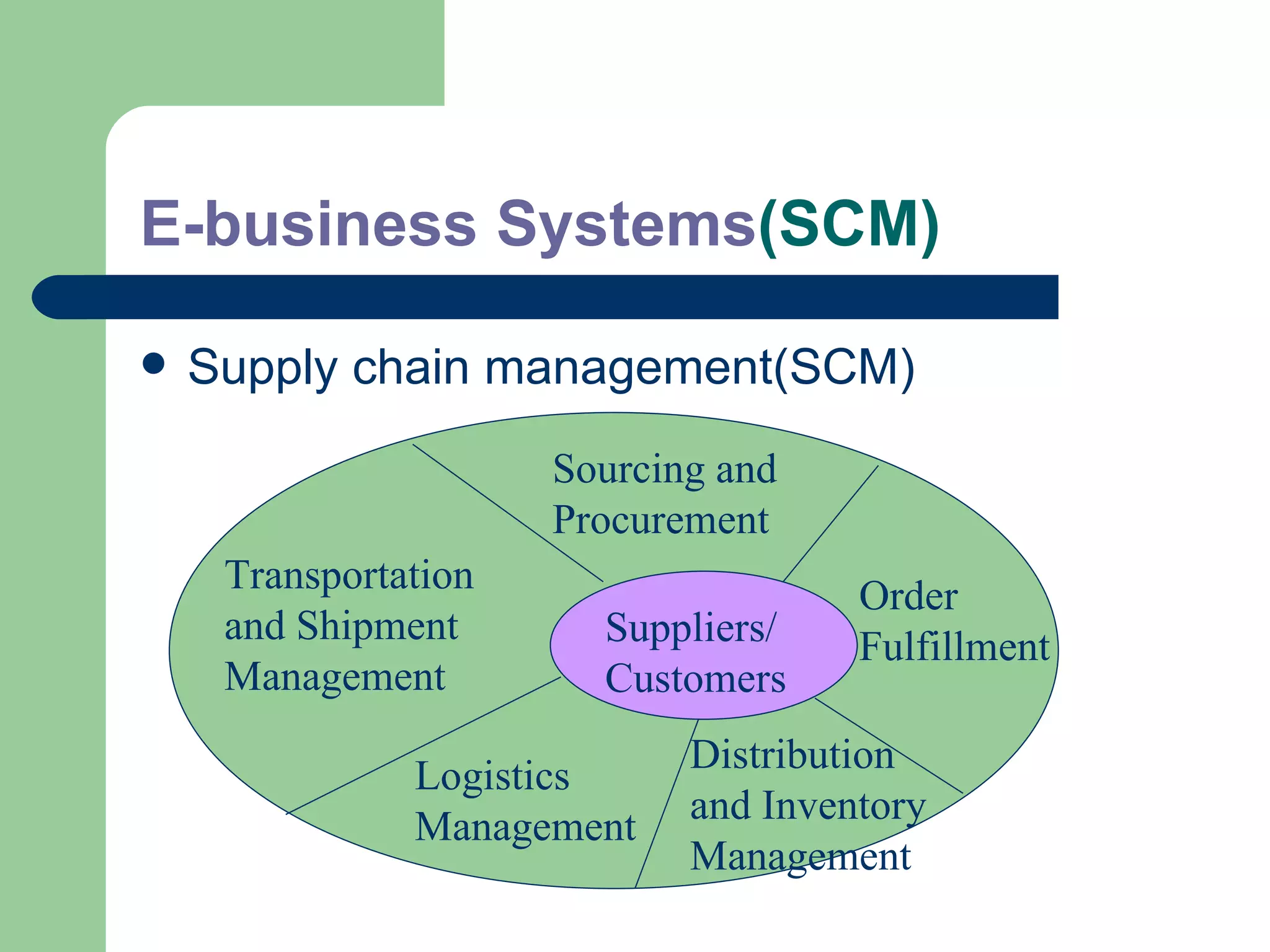
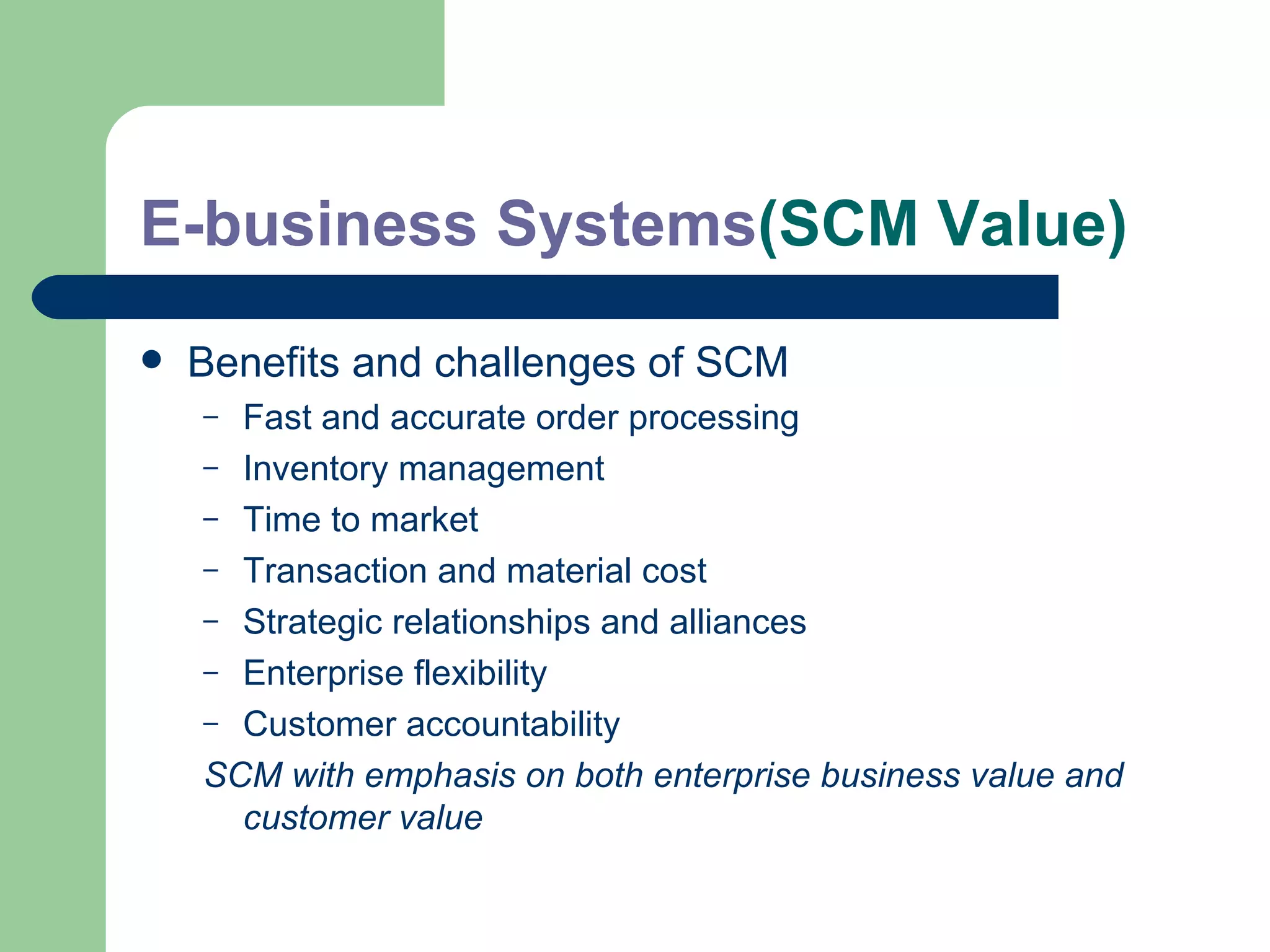
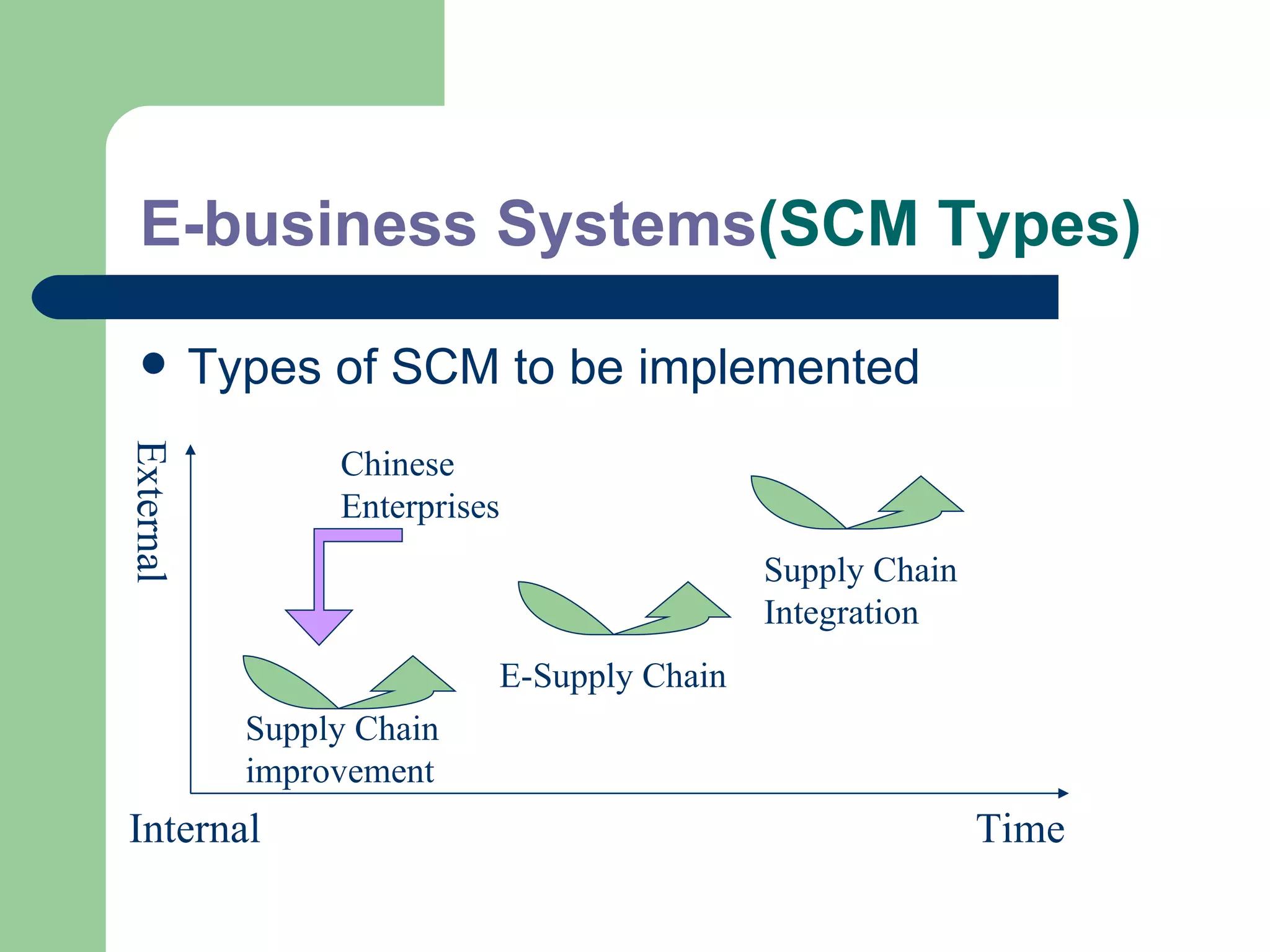
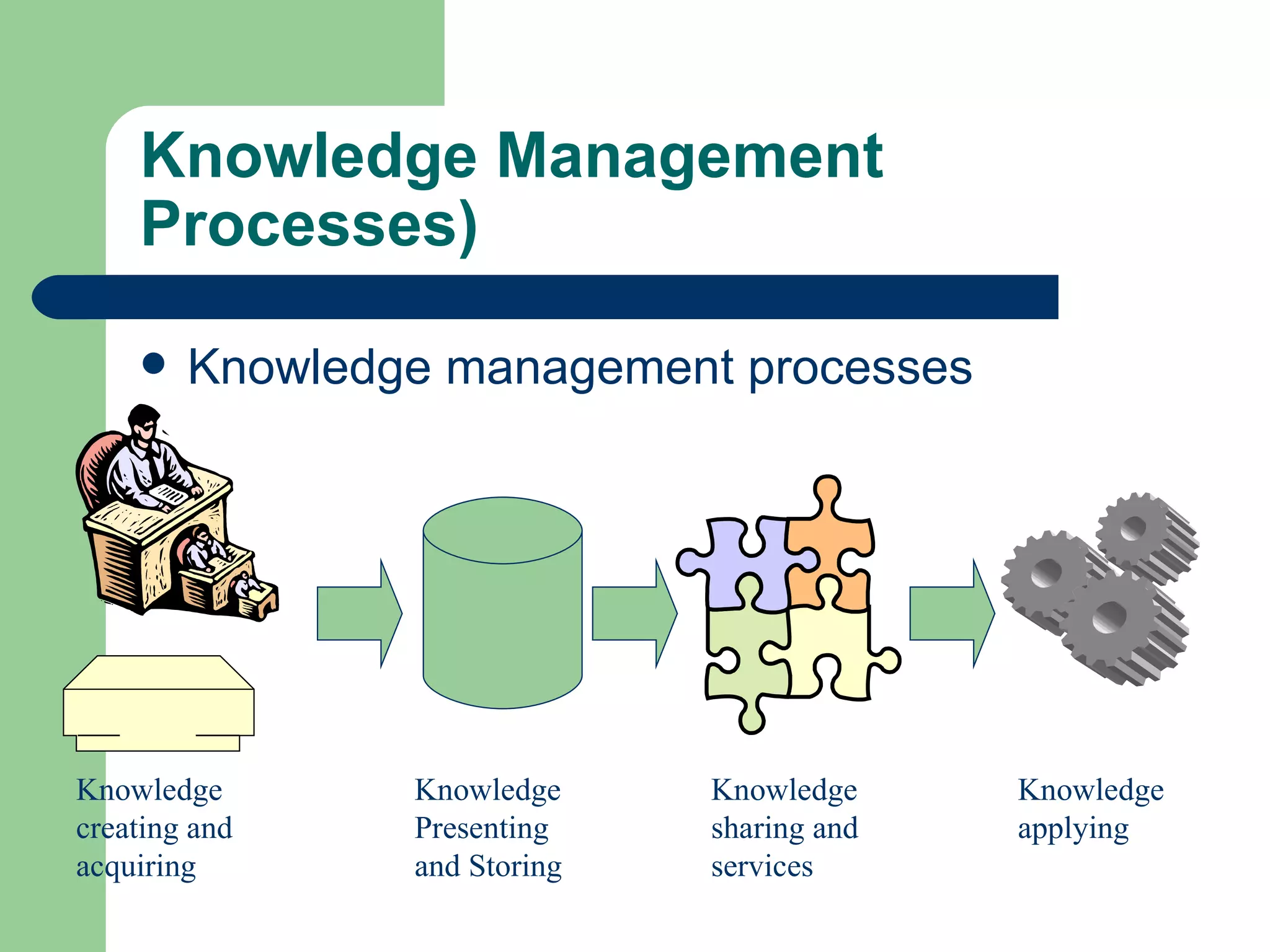
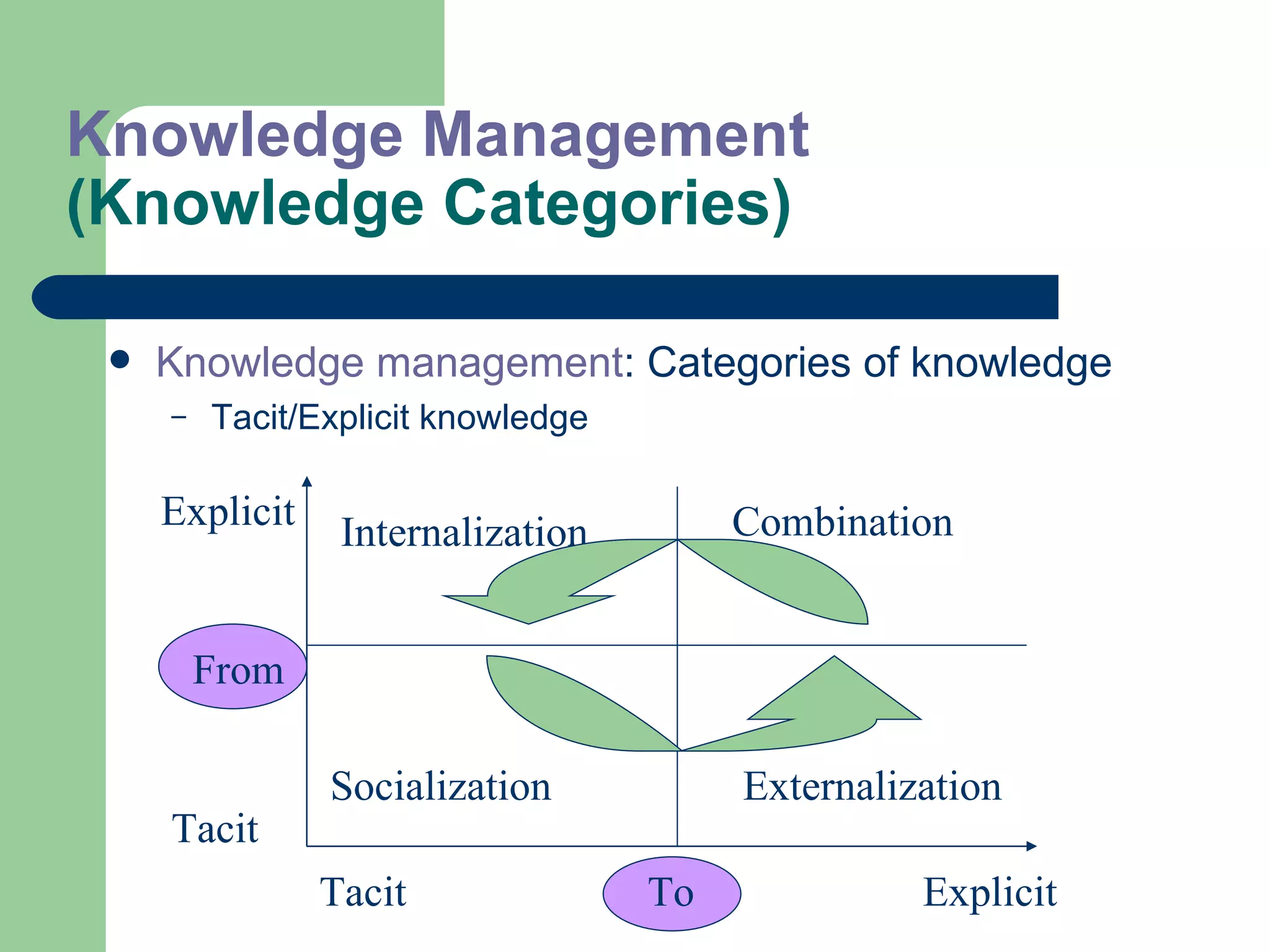
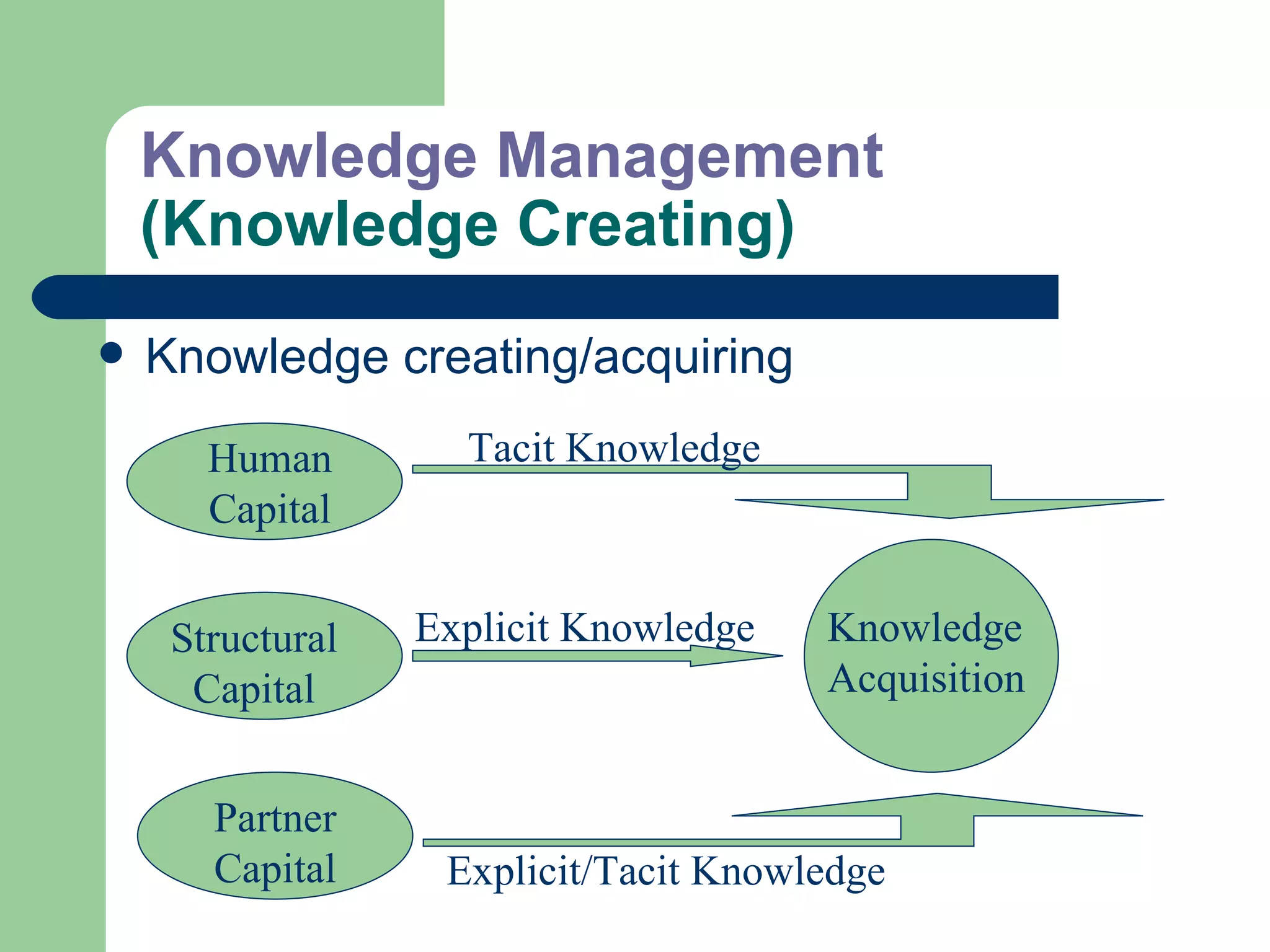
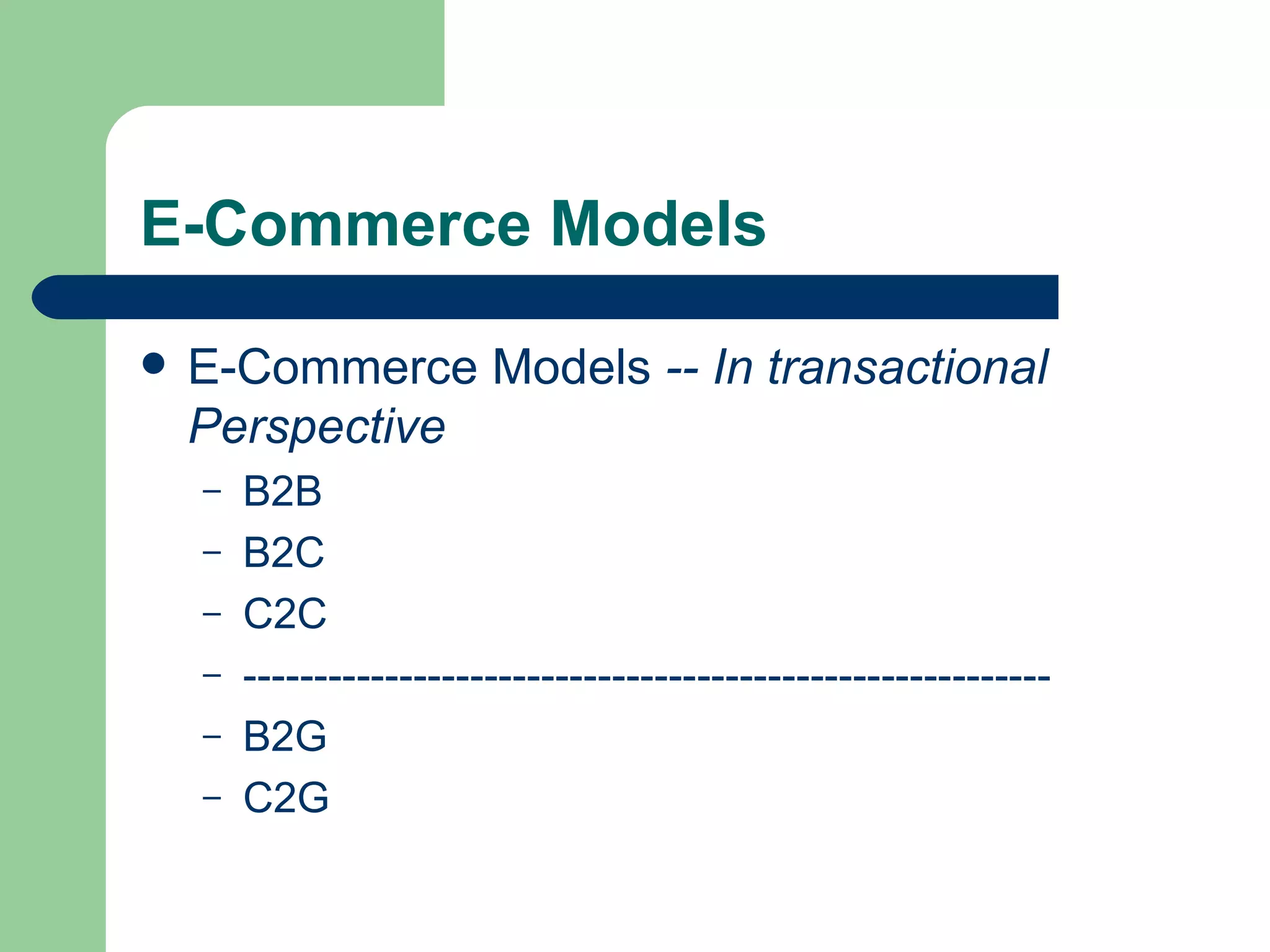
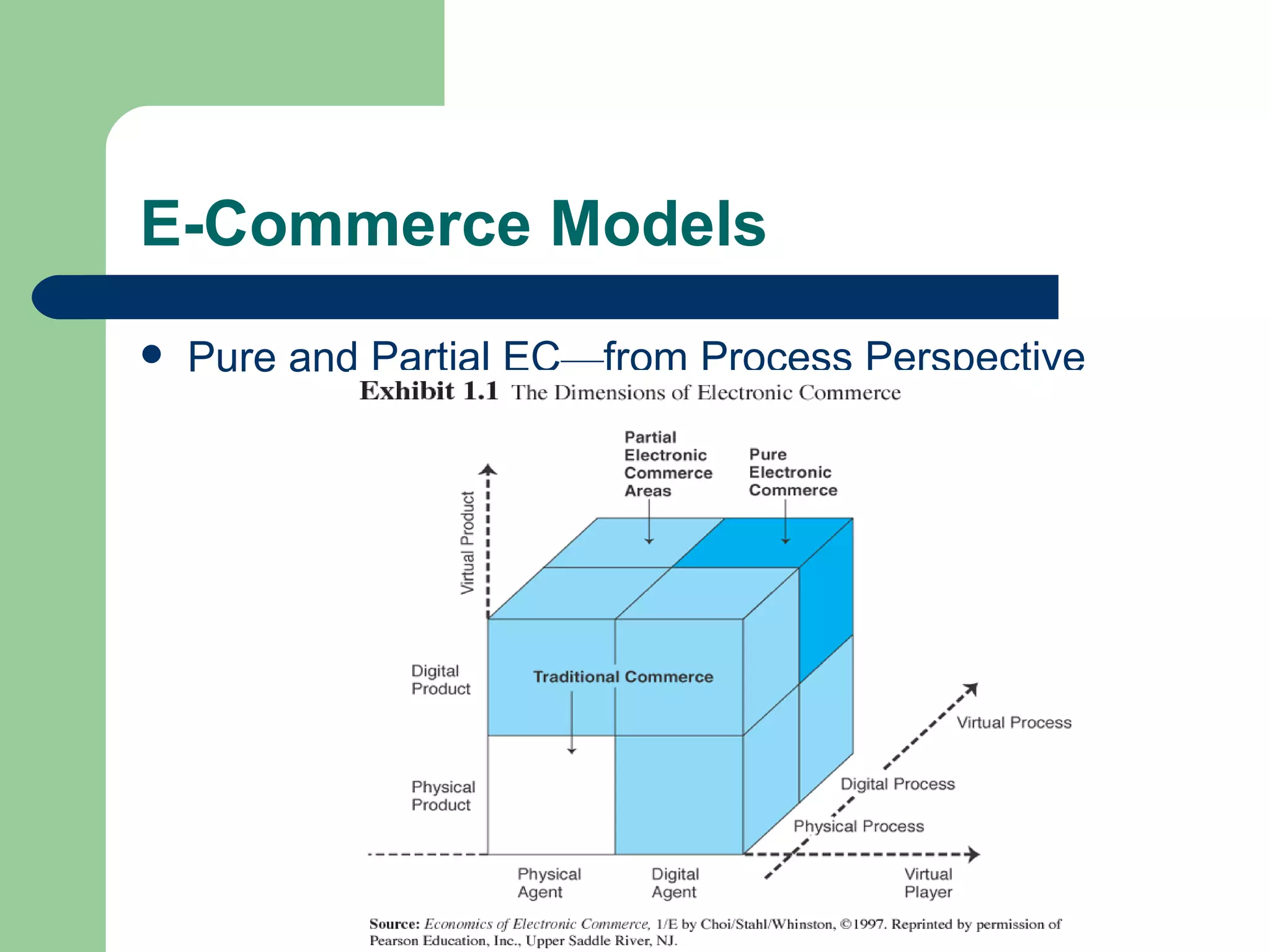
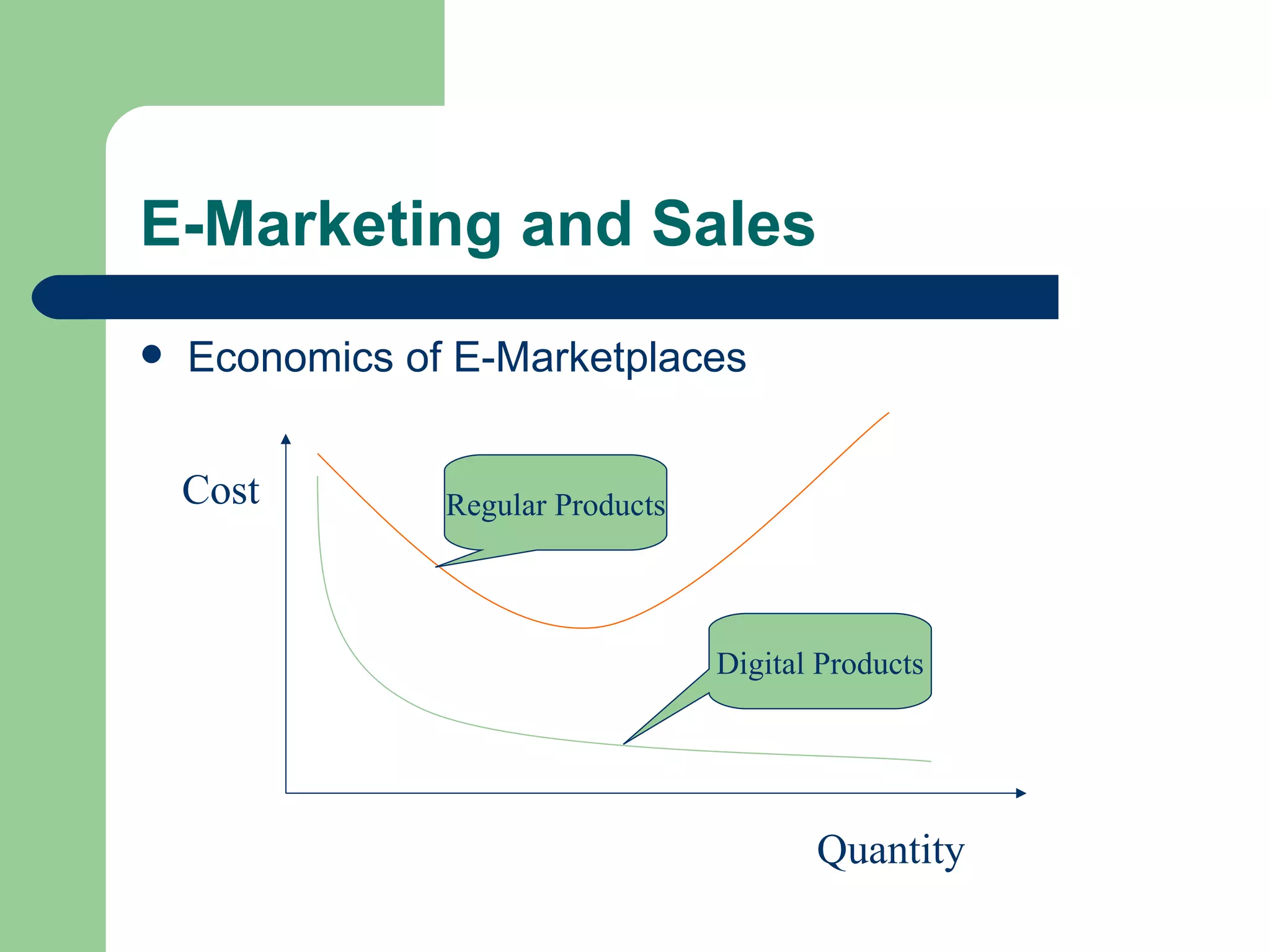
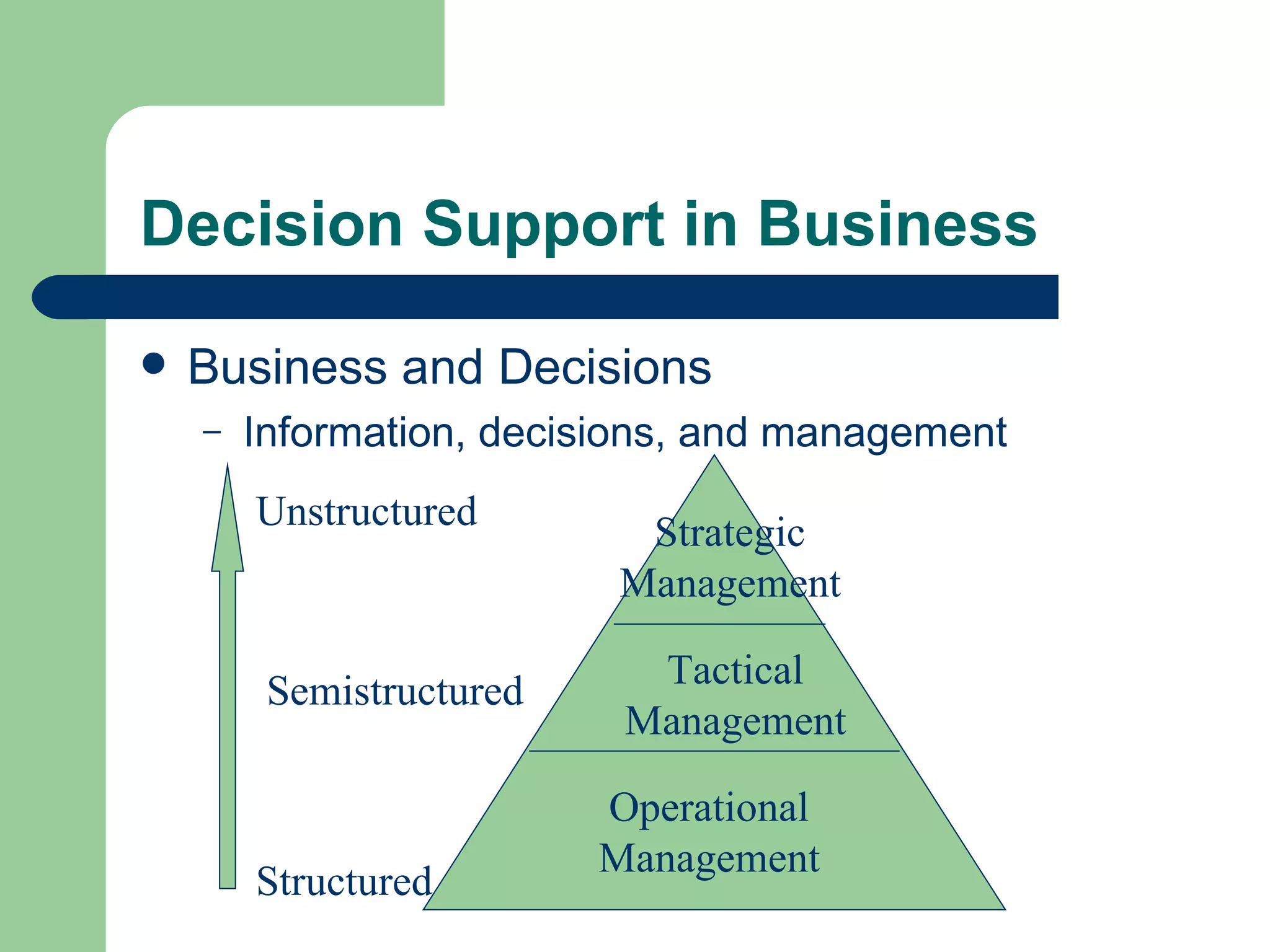
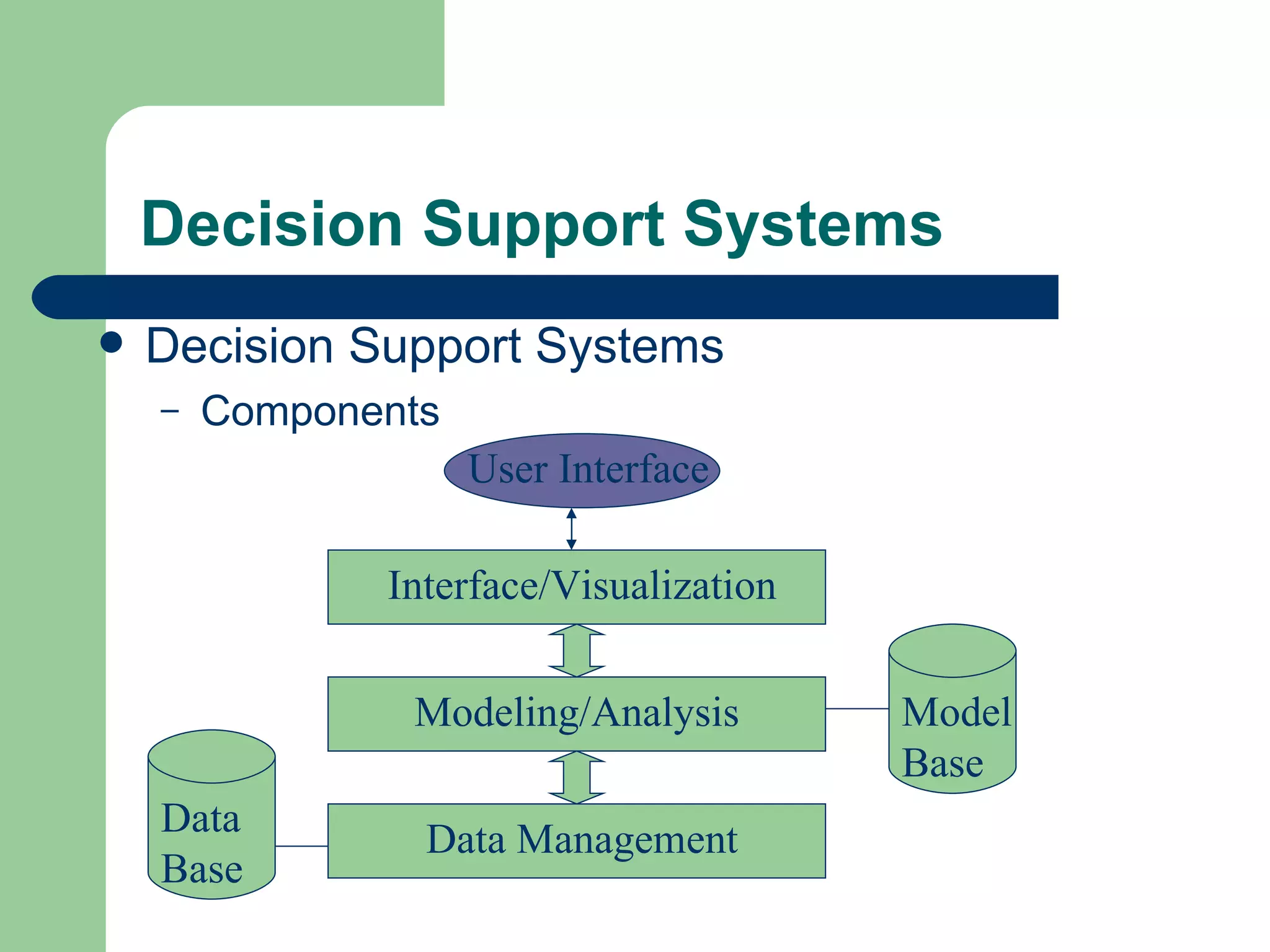
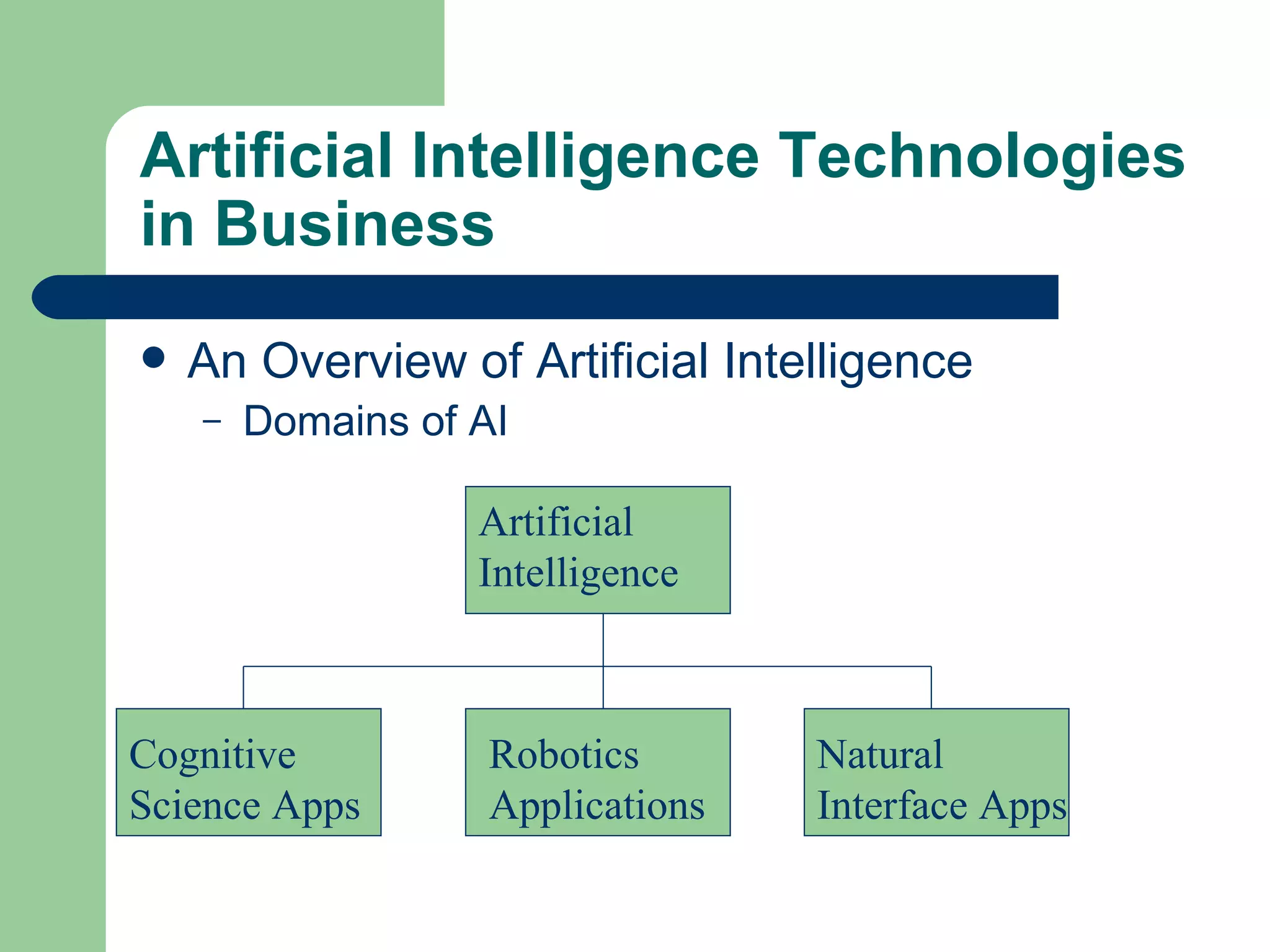
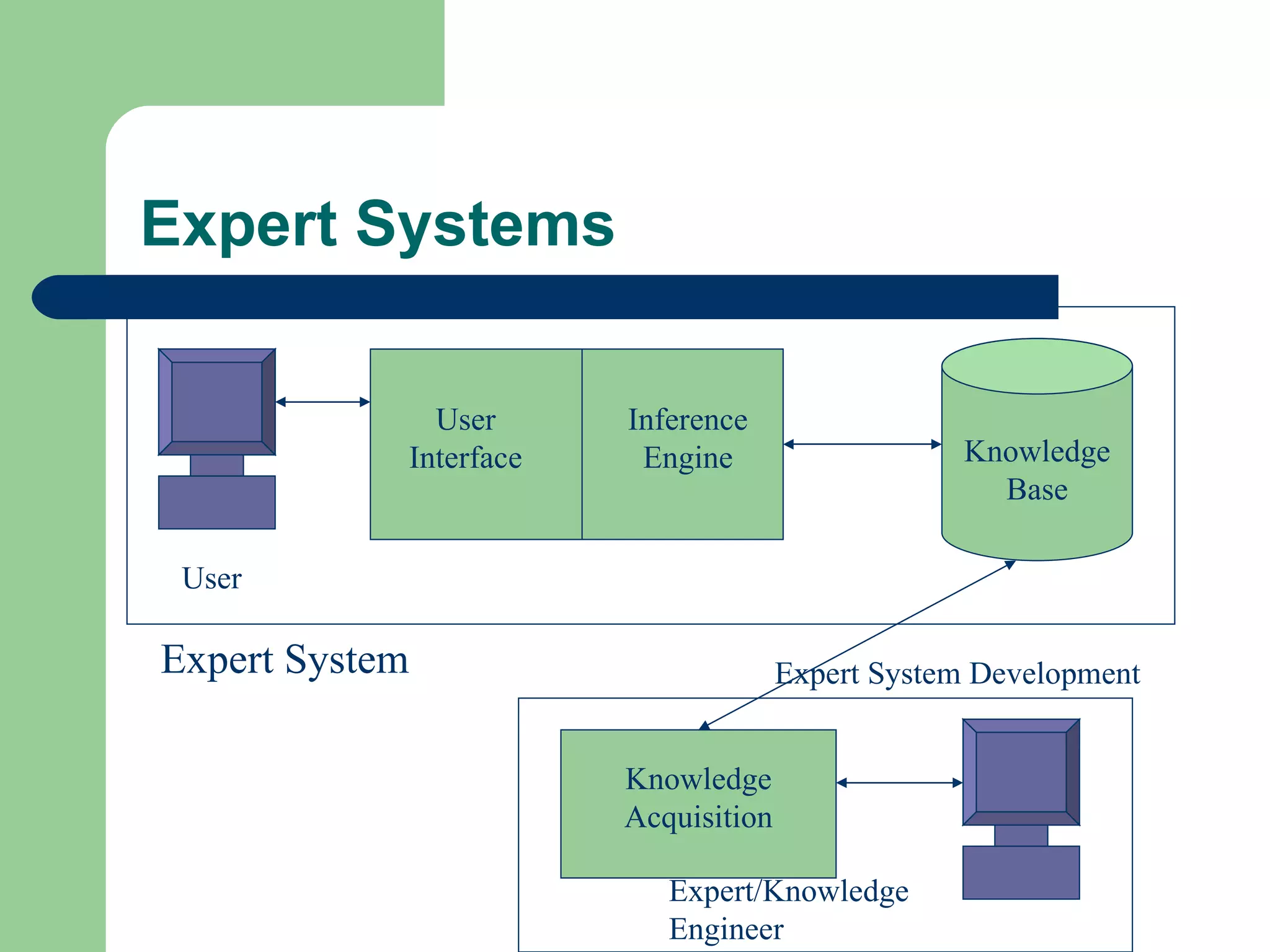
The document discusses various enterprise functional systems and e-business systems. It outlines systems for marketing, production/operations, accounting, finance, and human resource management. It also discusses e-business systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and knowledge management systems, describing their components, value, types, and issues.