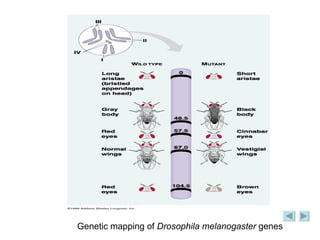
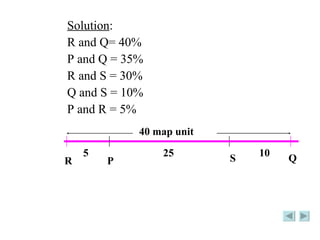
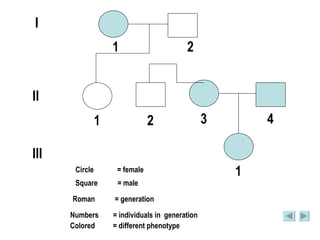
The document discusses genetic mapping and pedigree analysis. It defines genetic mapping as using recombination frequency data to determine the relative positions of genes on chromosomes. It provides an example of calculating recombination frequency and mapping genes in Drosophila. Pedigree analysis is defined as using standardized symbols in family trees to show genetic relationships and inheritance patterns across generations, like for inherited diseases.