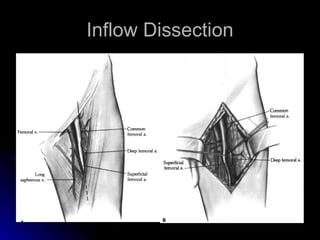
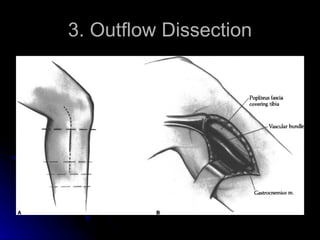
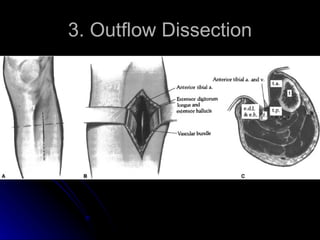
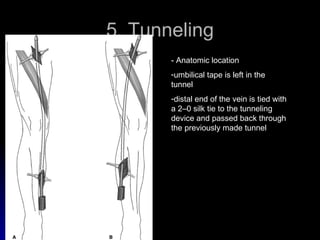
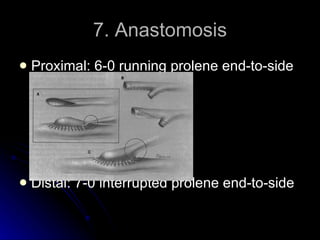
This document summarizes the key steps for a fem-distal bypass procedure, including: 1) preoperative arteriogram and vein mapping, 2) dissection of the femoral artery and preparation of the vein graft, 3) tunneling of the graft through the leg, 4) anastomosis of the graft to the femoral artery proximally and distal artery, and 5) post-operative care including staple removal and follow-up arterial exams.