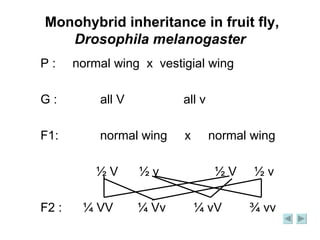
The document discusses Mendel's experiments on monohybrid crosses using pea plants. It explains that a monohybrid cross involves a single trait determined by one gene, such as tall vs dwarf plants. Mendel observed that the ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes in the F2 generation is 3:1, while the ratio of genotypes is 1:2:1. His experiments supported his laws of segregation and independent assortment.