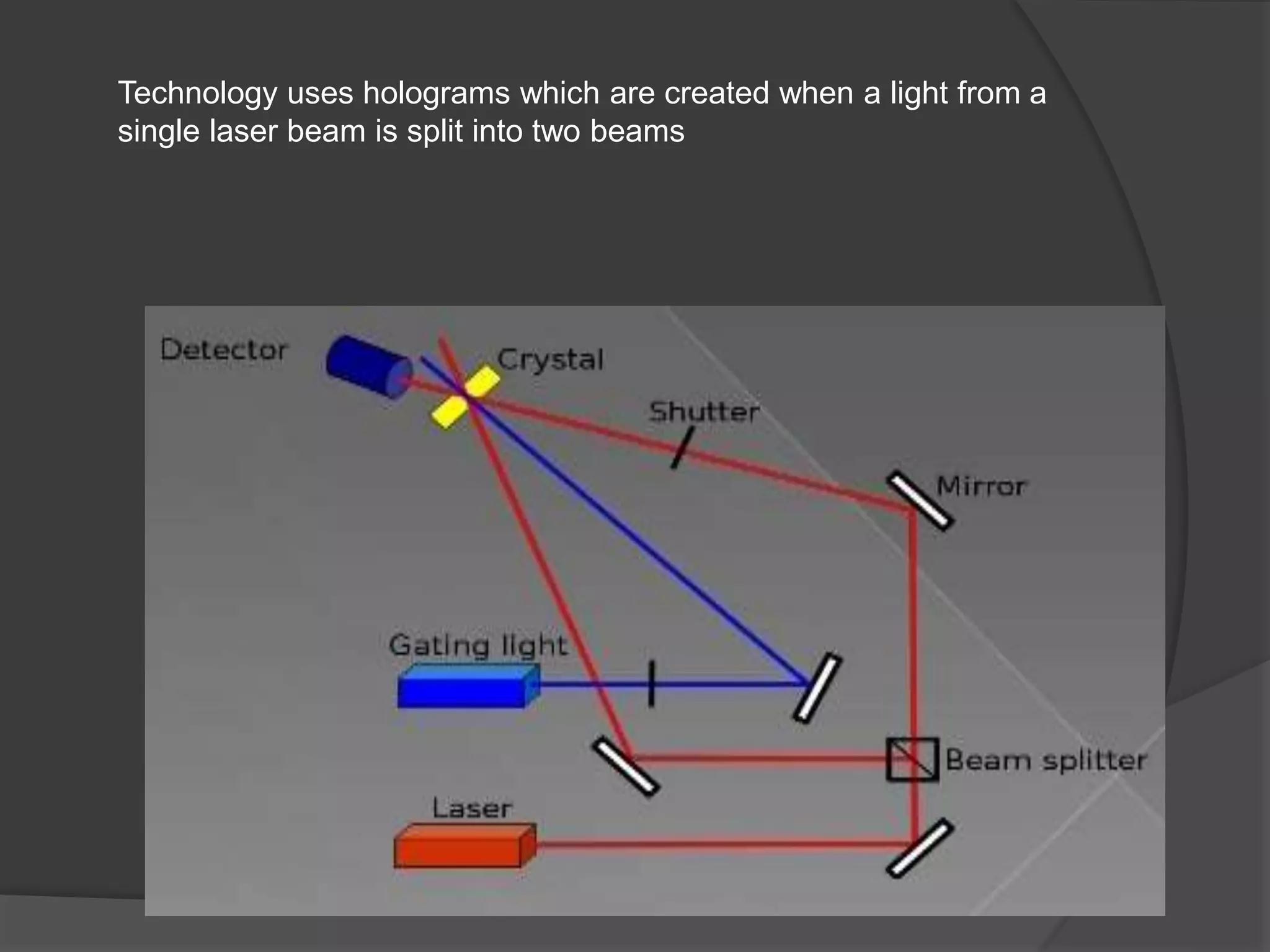
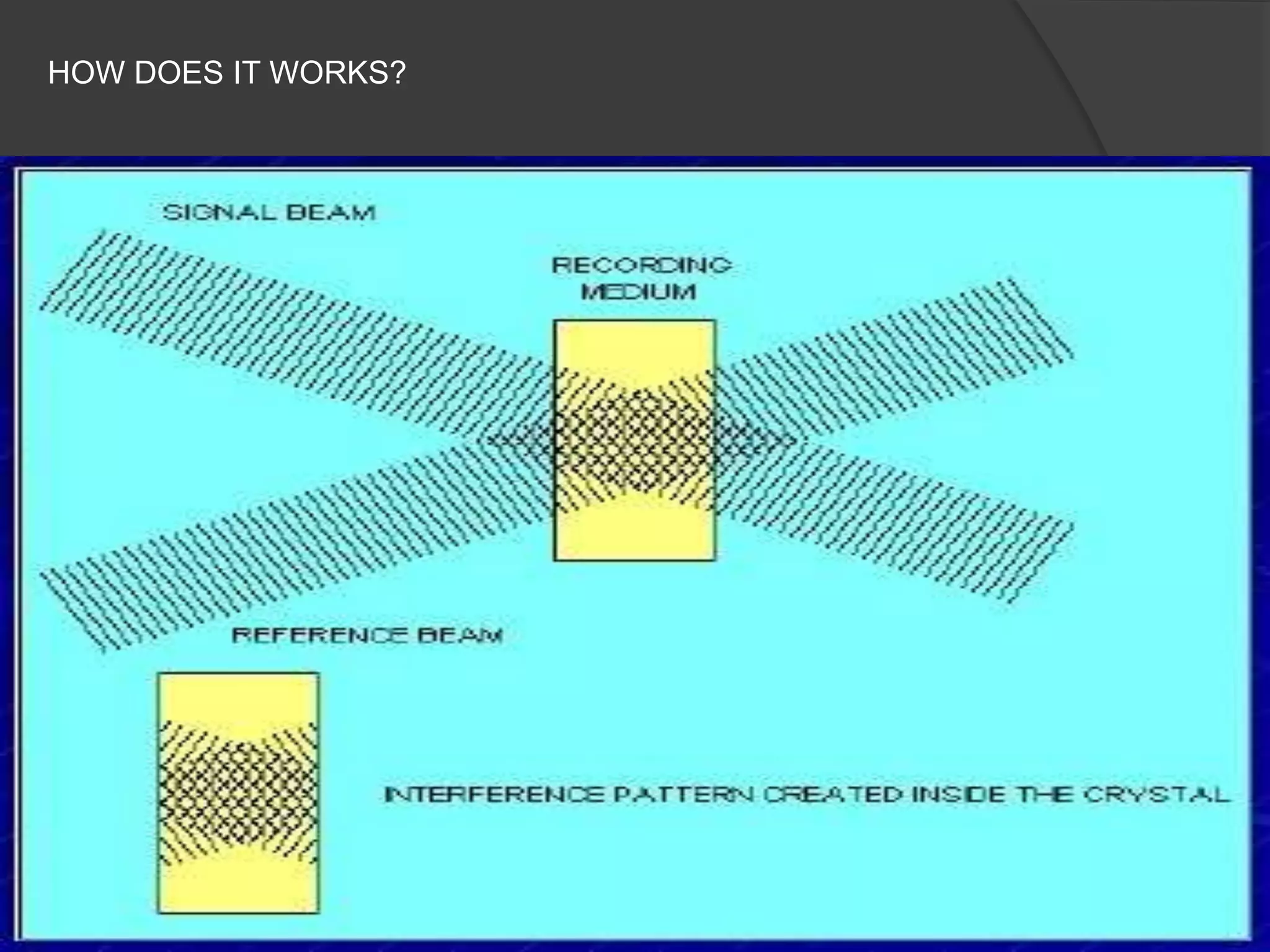
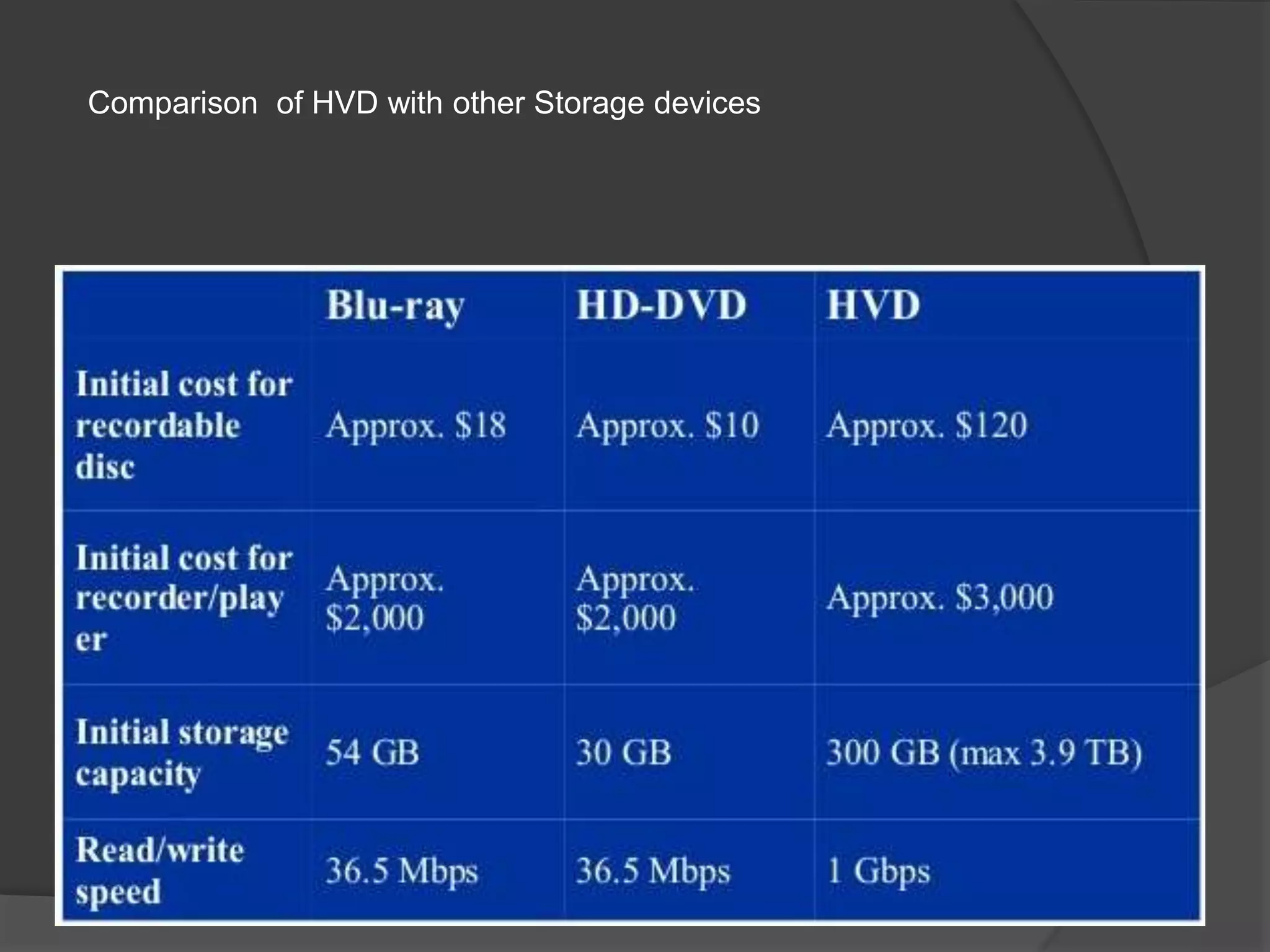
Holographic data storage uses interference patterns of laser light to store massive amounts of data in small volumes. It works by splitting a laser beam into a reference beam and data beam, and their interference patterns are recorded on a photosensitive storage medium. To read the data, the reference beam illuminates the interference pattern, projecting the data beam which is detected by a sensor. Key benefits are high storage capacity of terabytes in small spaces, rapid data retrieval, and increased security. Challenges include sensitivity of the storage medium and cost compared to existing technologies.