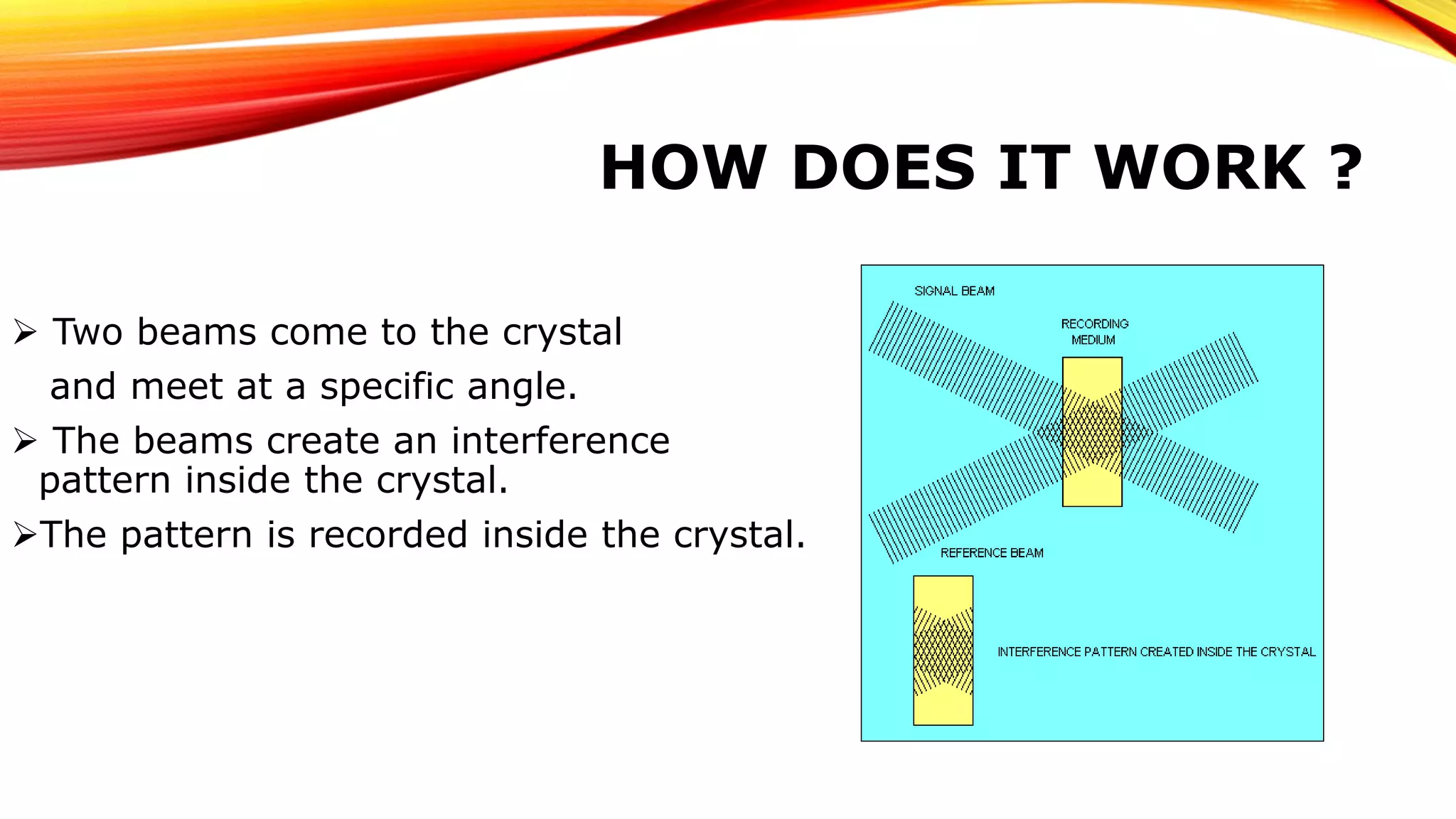
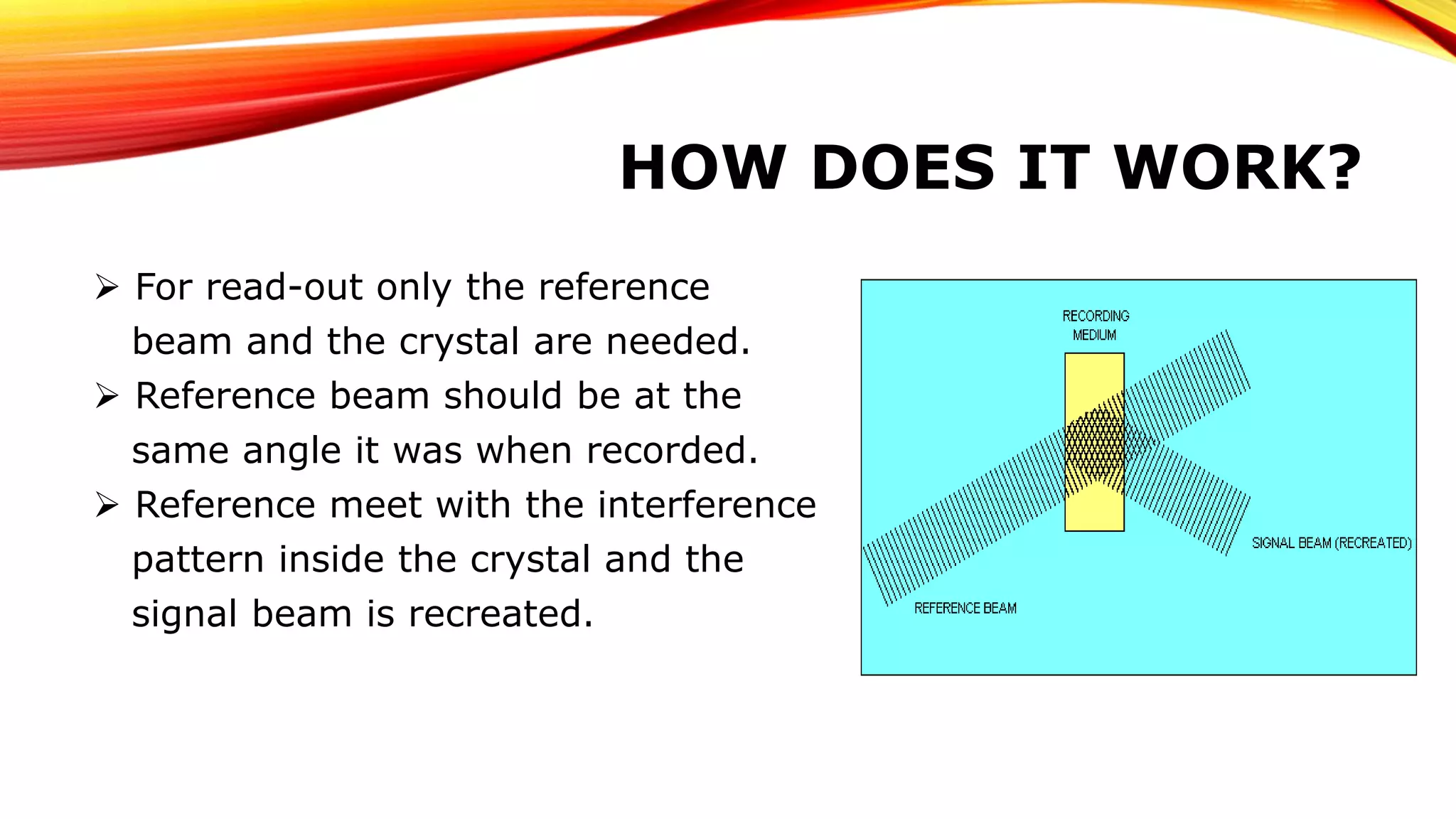
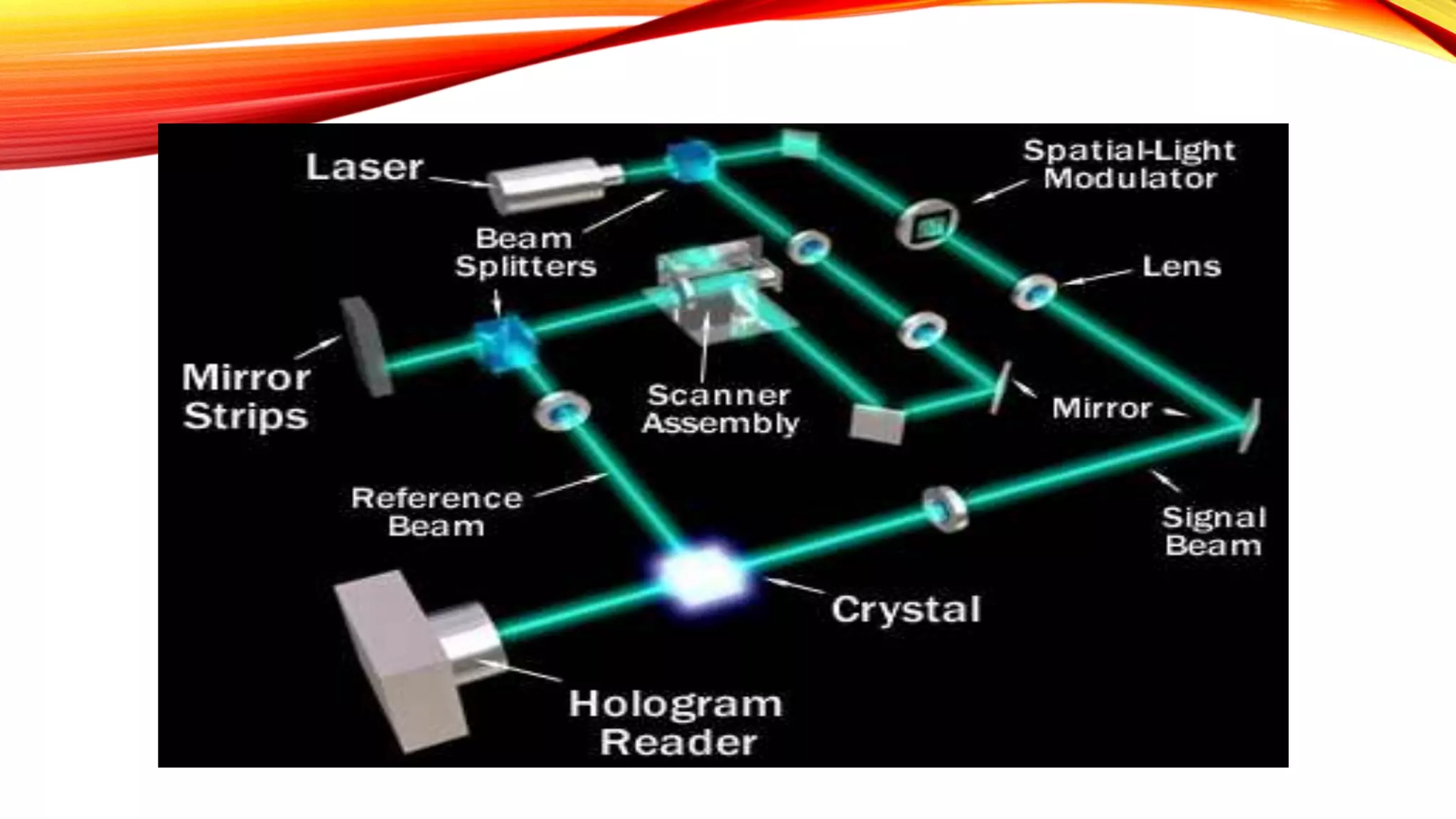
Holographic data storage was invented in 1948 and promises to be the data storage system of the future. It can store up to 1000 GB of data in a 1 cm3 recording medium by recording information throughout the volume using light at different angles. During recording, two laser beams intersect inside a crystal to create an interference pattern. During readout, only a reference beam is needed, which interacts with the interference pattern to recreate the data. Holographic storage allows for faster read/write speeds and longer archival life compared to existing technologies, but challenges remain in developing inexpensive recording materials and parallel recording methods.