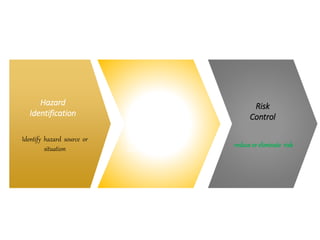
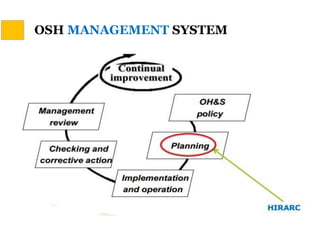
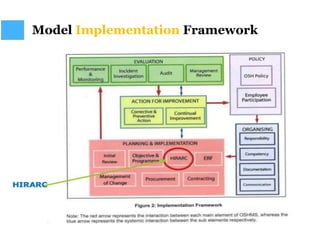
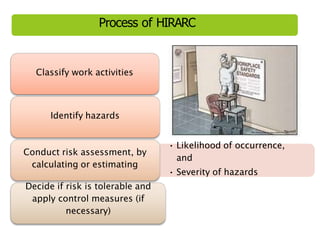
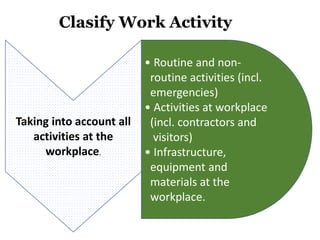
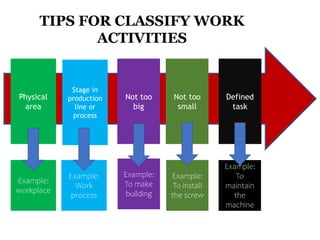
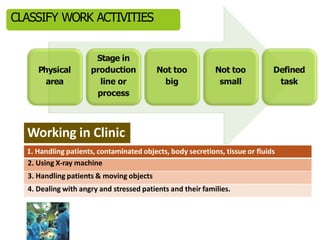
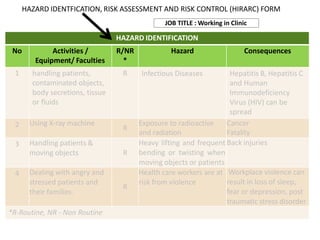
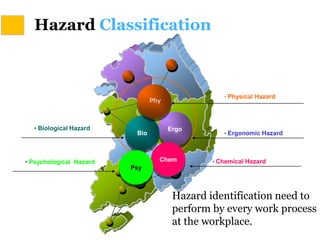
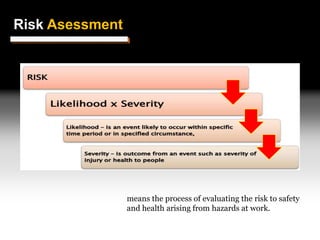
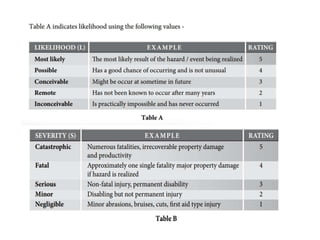
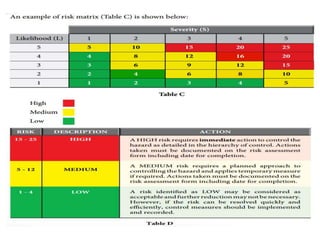
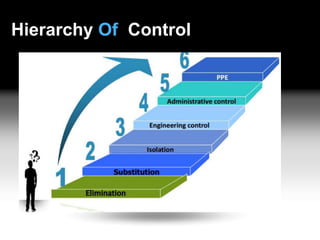
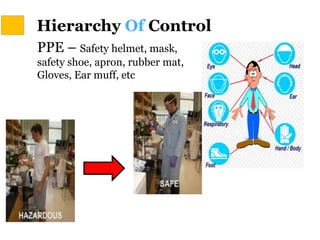
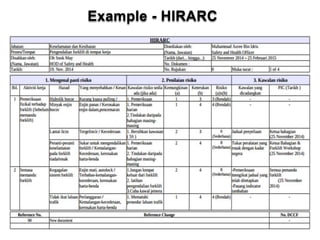
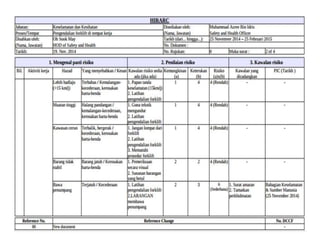
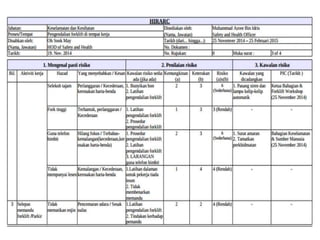
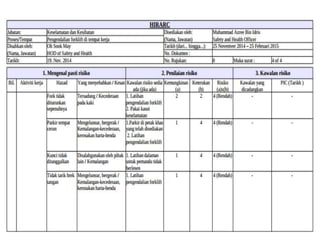
This document discusses Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment, and Risk Control (HIRARC), which is a process for identifying workplace hazards, assessing risks, and implementing risk controls. It defines key terms like hazard and risk. The purpose of HIRARC is to identify hazards, assess risks, and control risks to ensure workplace safety. It outlines the HIRARC process, which involves classifying work activities, identifying hazards, assessing risks, and controlling risks. Methods for hazard identification and risk assessment are also described. The hierarchy of controls from most to least effective are also provided.