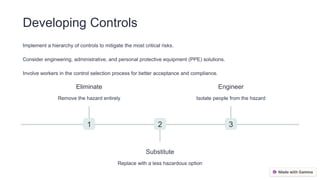
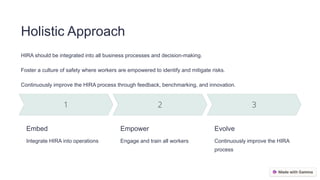
This training module outlines essential steps in hazard identification and risk assessment for workplace safety, emphasizing the significance of recognizing, evaluating, and mitigating risks. It details practices for identifying hazards, assessing risks through risk matrices, and implementing a hierarchy of controls involving worker engagement. Continuous monitoring and review, coupled with a systematic approach, are crucial for improving safety processes and fostering a culture of safety.