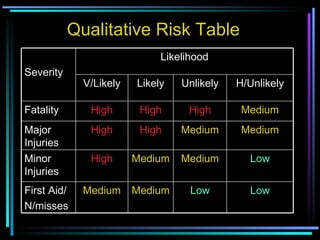
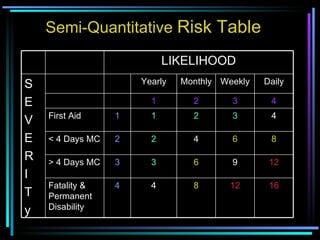
This document discusses hazard identification, risk assessment, and risk control. It defines key terms like hazard, danger, and risk. It outlines the risk management process of classifying activities, identifying hazards, assessing risks, implementing risk controls, and reviewing controls. Different types of risks are described like mechanical, electrical, chemical, and ergonomic risks. Methods of risk assessment include qualitative, semi-quantitative, and quantitative assessments using risk matrices to evaluate likelihood and severity of risks. Risk control actions are recommended to eliminate, substitute, isolate, use engineering or administrative controls, or personal protective equipment.