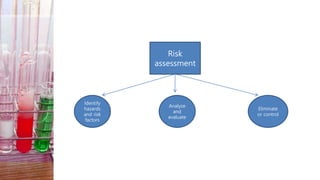
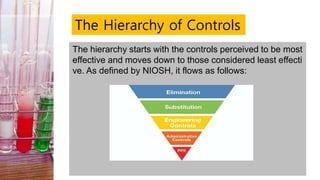
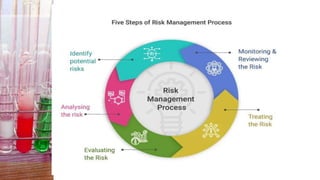
This document discusses hazard identification and management. It defines hazards, risks, and controls. It explains the types of hazards including biological, physical, ergonomic, chemical, and psychological hazards. It describes the process of hazard identification including speaking to employees, observing tasks, and reviewing accident records. It outlines the hierarchy of controls from elimination to personal protective equipment. Finally, it provides an assignment for students to identify hazards in different locations and recommend control measures using the hierarchy of controls.