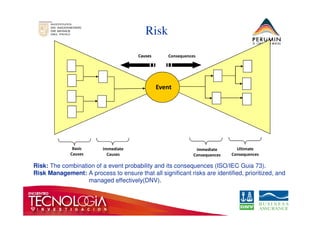
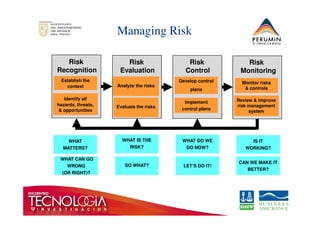
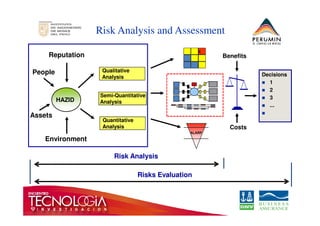
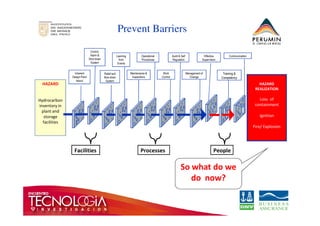
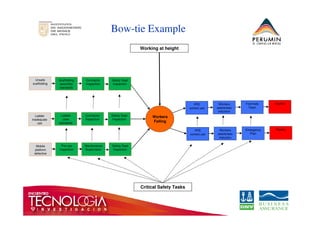
This document introduces the bow-tie risk analysis methodology. It describes how a bow-tie diagram visually maps the relationship between an undesirable event, its potential causes, consequences, and the barriers that prevent or mitigate these. The document provides examples of how to construct a bow-tie diagram by defining the hazard, threats, barriers, escalation factors, recovery measures, and critical safety tasks. It emphasizes that bow-tie analysis can help demonstrate control effectiveness and is a versatile structured approach to risk analysis.