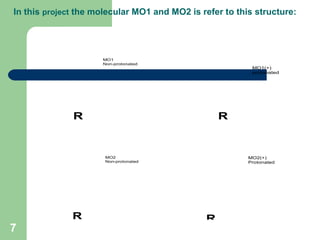
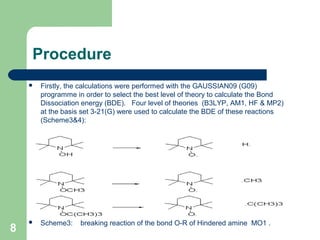
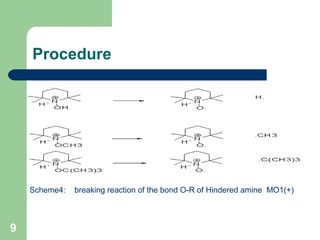
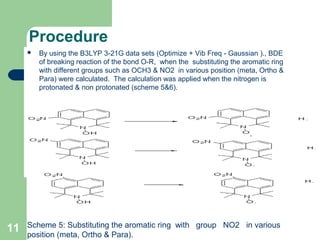
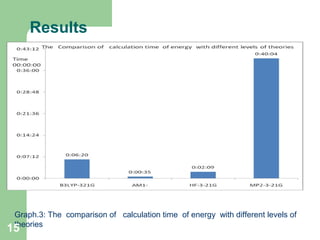
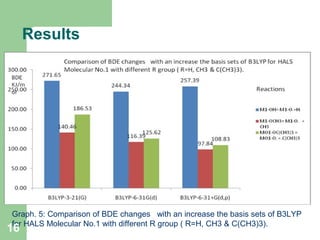
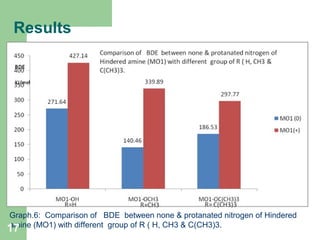
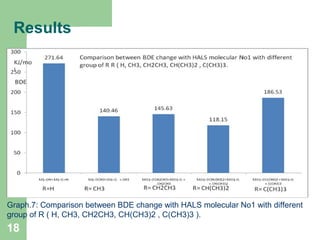
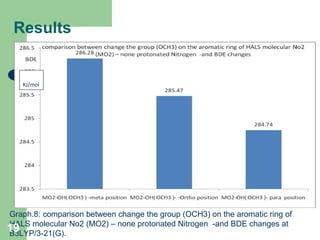
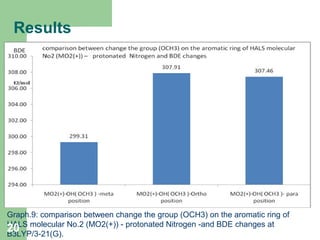
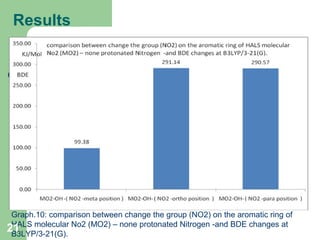
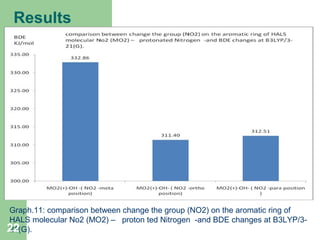
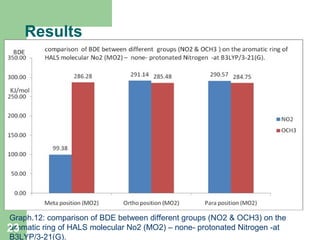
The document discusses computational studies of the bond dissociation energy (BDE) of hindered amine (HALS) stabilizers. Four theories (B3LYP, HF, AM1, MP2) were used to calculate the BDE of two HALS molecules with protonated and non-protonated nitrogen. The B3LYP theory provided results closest to experimental data. Substituting aromatic rings with OCH3 or NO2 groups did not significantly affect BDE. Protonated nitrogen forms had higher BDE, indicating greater stability, than non-protonated forms. Larger substituent groups on HALS molecules decreased BDE, with stability increasing from H to CH3 to C(CH







![Results:
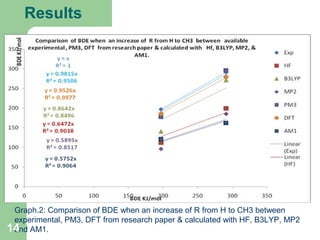
Table.1 Comparison between experimental and calculated BDE (O_R) for HALS Molecular 1 (MO1)
]kJmol_
1[ BDE 3LYP BDE AM1 BDE HF BDE MP2 BDE exp
)from research
BDEPM3
paper(
BDEDFT
M1-OH= M1-O.+H. 271.65 162.34 199.10 185.15 291 296 279
M1-OCH3= M1-O. + CH3 140.46 120.76 111.62 96.04 197 178 185
MO1-OC(CH3)3 = MO1-O.
+.C(CH3)3
186.53 172.98 100.71 74.72 n/a 94 n/a
Graph.1.: Comparison between experimental and calculated BDE (O-R) for HALS
Moleculer1.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hinderedaminestabilizes-141221094631-conversion-gate02/85/Hindered-amine-stabilizes-13-320.jpg)




![References:
1-Possi, Aventurini and A Zedda J. AM Chem .SCI (1999)121,,7914-7917
2-F,.Gugumus Polymer Degradation and Stability (1995) 50, 101-116
3- P.P. Klemchuk , M.E Gande Polymer Degradation and Stability (1988),22,241-274
4- T.A. Lowe, M.R.L Paine,D.L.Marshall.L.A.Hick,J.A.Boge,P.J.Barker , S.J.Blanksby J
Mass Spec (2010) 45(5) 486-496
5- G.Geuskens ,M.N.Kanda Polymer Degradation and Stability (1996),51, 227-232.
6- A Gaudel,S., D. Siri, P.Tordo ,ChemPhysChem,(2006),7,430-438
********************************
Paine, M. R. L., Barker, P. J. and Blanksby, S. J. "Desorption Electrospray Ionisation
Mass Spectrometry Reveals In Situ Modification of a Hindered Amine Light Stabiliser
Resulting From Direct N-OR bond cleavage" Analyst 2011, 136 (5), 904-912. [Cover
Article]
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hinderedaminestabilizes-141221094631-conversion-gate02/85/Hindered-amine-stabilizes-28-320.jpg)