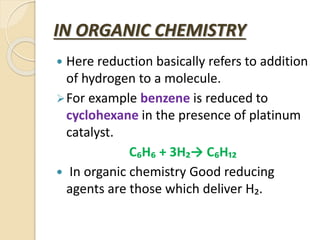
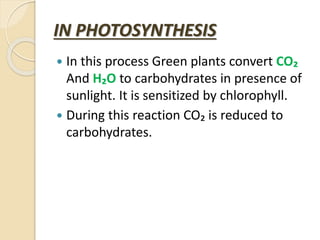
The document provides an overview of reduction and reducing agents in chemistry, defining reduction as the gain of electrons and describing reducing agents as substances that can donate electrons. It highlights the identification of reducing agents through oxidation states, lists common reducing reagents, and discusses their applications in various industries, organic chemistry, and analytical chemistry. Additionally, it explains the role of reducing agents in processes like photosynthesis and metal extraction.











![ELECTRON DONORS
Electron donors participate in electron
transfer reactions. So in this sense
reducing reagents are also known as
electron donors.
A well known reducing agent is
ferrocyanide [Fe(CN)₆]⁴⁻. It oxidizes or
donates an electron to form
ferricyanide[Fe(CN)₆]ᶟ⁻.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doc-20180925-wa0005-180925185545/85/REDUCTION-AND-REDUCING-AGENTS-12-320.jpg)