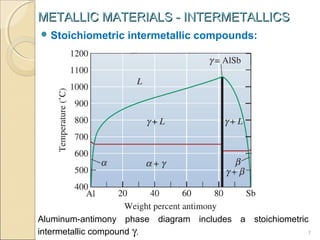
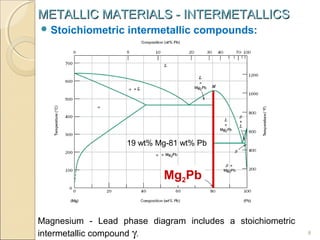
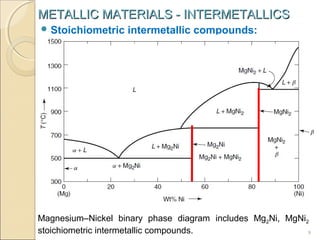
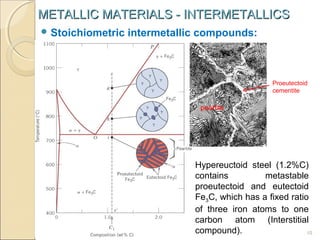
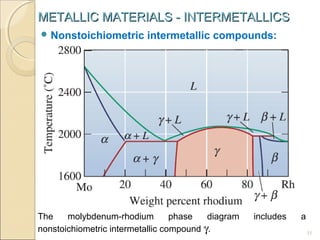
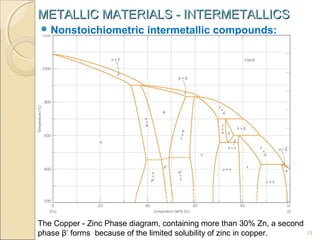
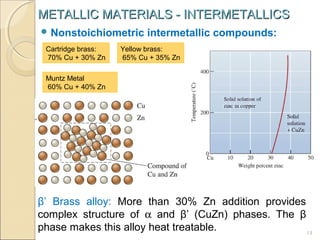
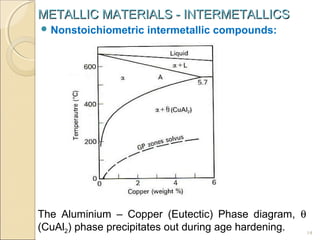
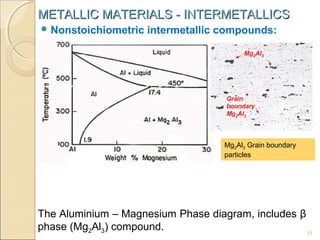
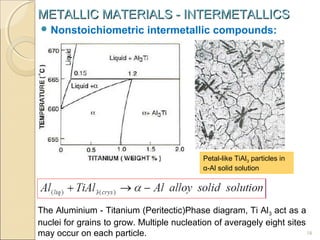
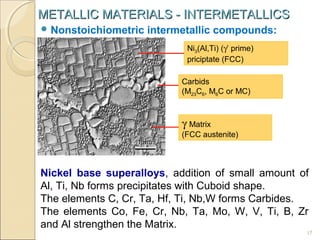
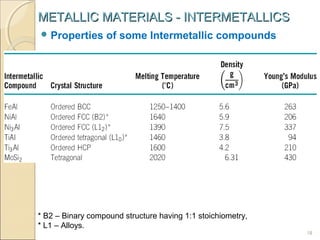
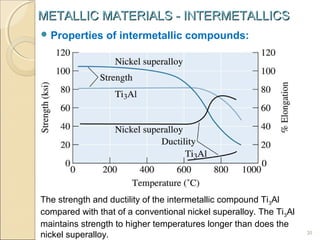
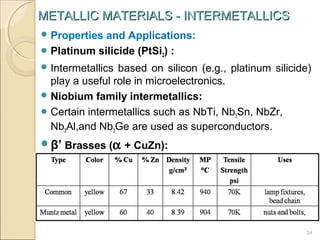
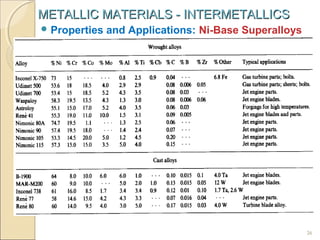
The document discusses intermetallic compounds, which are intermediate phases that form between two metals in an alloy system when the solute content exceeds the solid solubility limit. Intermetallics have a fixed stoichiometric composition and crystal structure different from the parent metals. They are very hard and brittle. Examples include Fe3C in steels and Mg2Ni in magnesium-nickel alloys. Intermetallics find use in applications requiring high strength and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, such as MoSi2 heating elements and TiAl turbine blades.