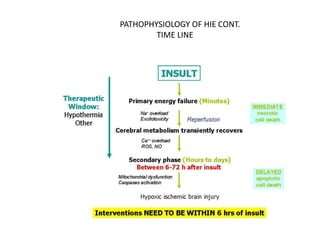
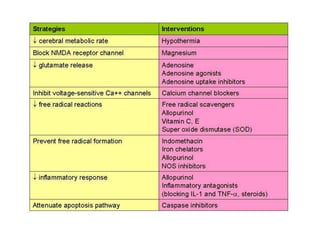
1) Hypothermia therapy involves cooling infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy to 33-35°C for 72 hours and is the standard treatment. It decreases cerebral metabolic rate and excitotoxic neurotransmitter release, reducing apoptosis, edema, and injury.
2) Other promising neuroprotective strategies include oxygen free radical inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, erythropoietin, excitatory amino acid antagonists like magnesium, preventing excess nitric oxide formation, attenuating apoptosis, and stem cell transplantation.
3) While hypothermia therapy reduces mortality and disability, ongoing research aims to develop more effective combination therapies targeting multiple injury mechanisms.