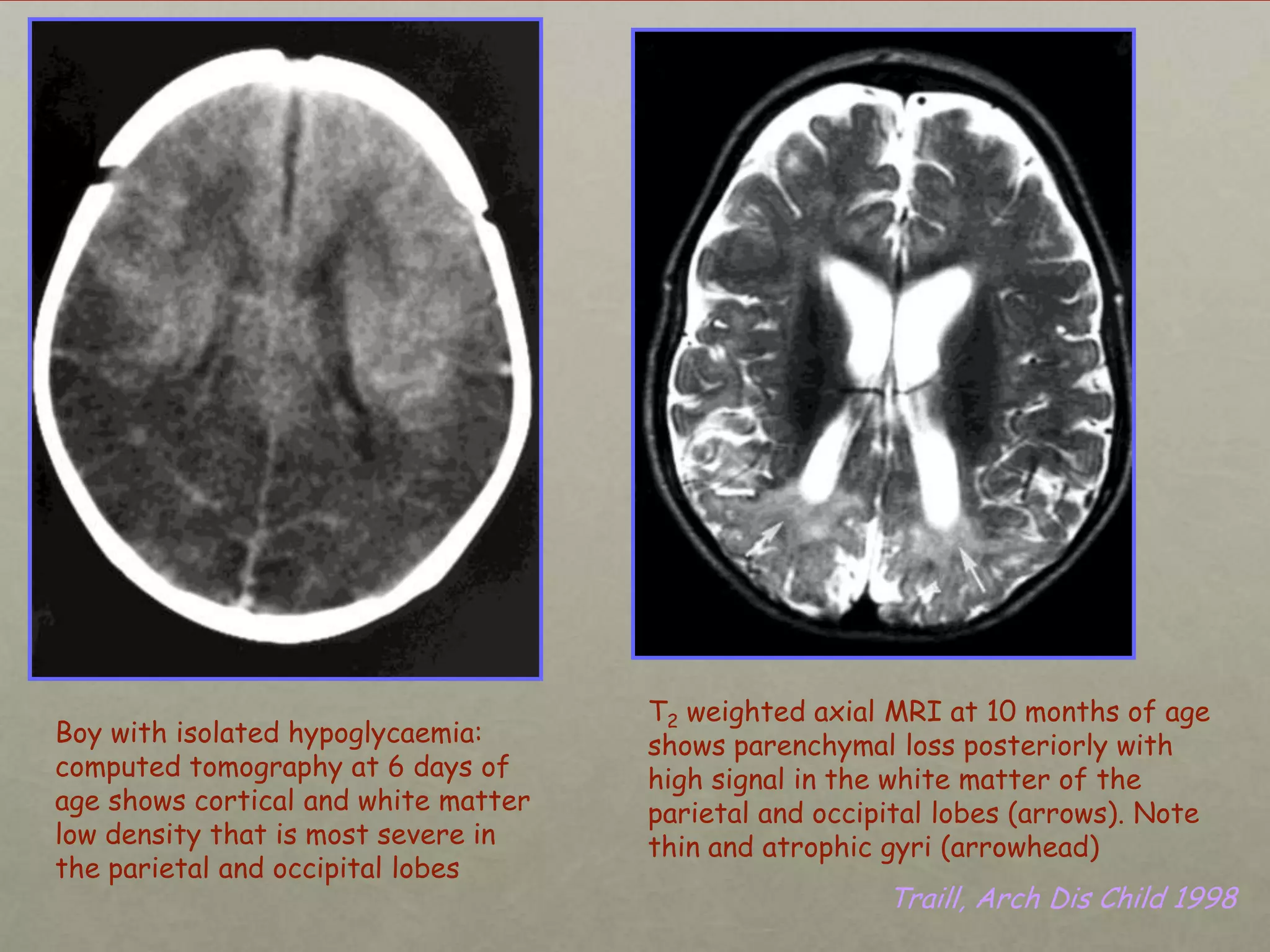
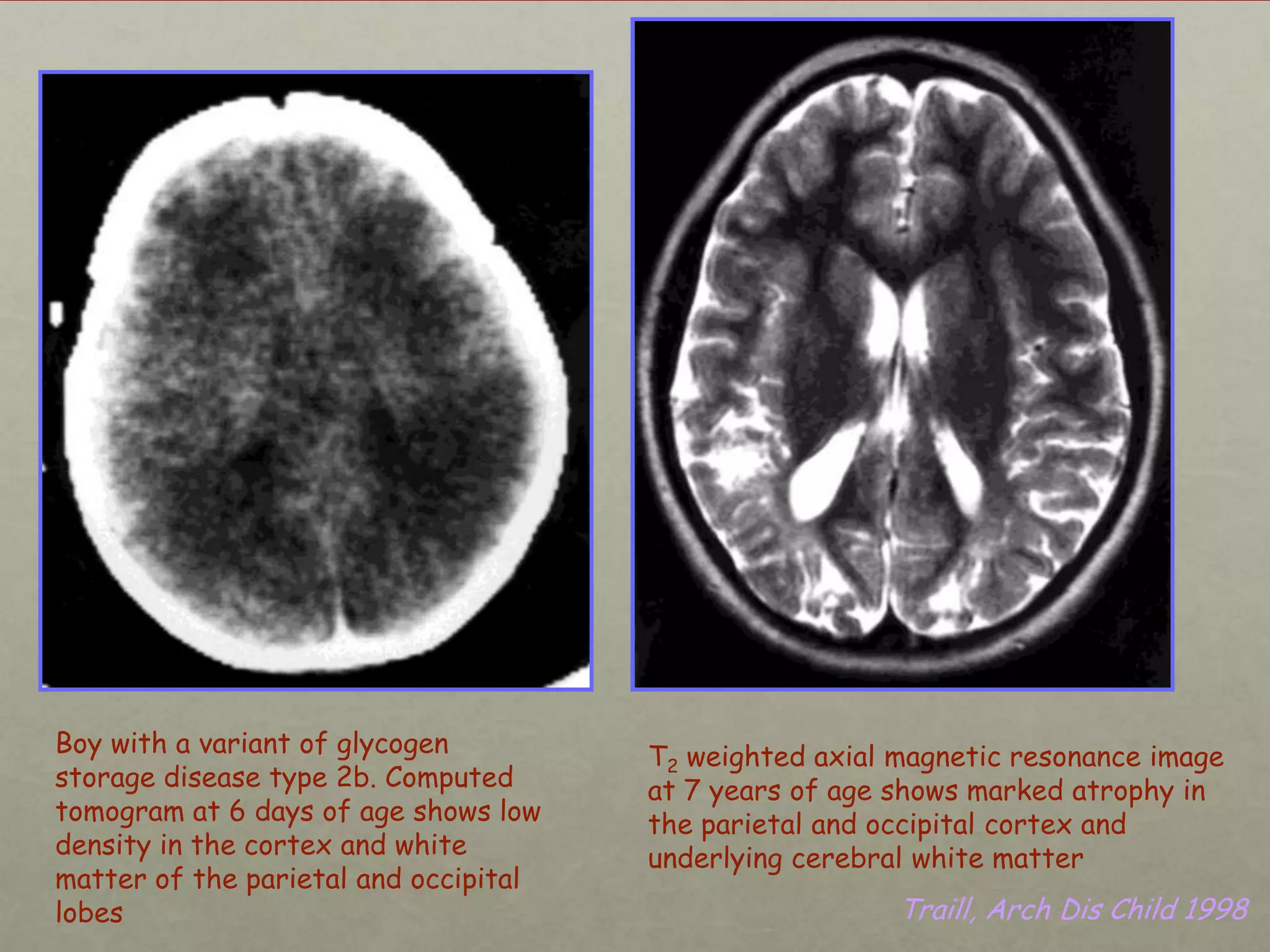
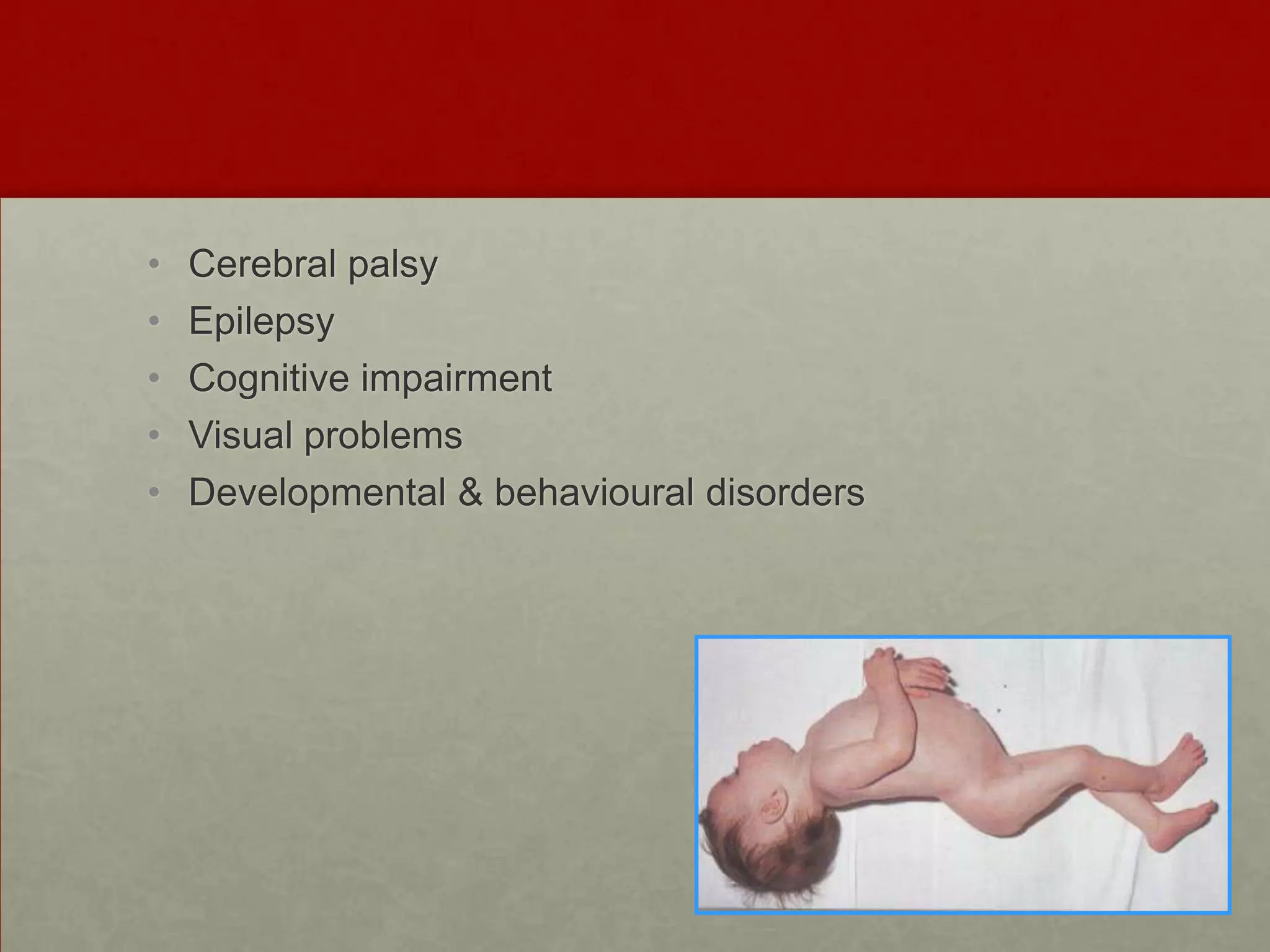
This document discusses neonatal hypoglycemia. It begins by defining hypoglycemia in newborns as a blood glucose level below 40 mg/dL, regardless of symptoms. The main causes of neonatal hypoglycemia include increased glucose utilization due to conditions like hyperinsulinism in infants of diabetic mothers, decreased glucose production due to prematurity or IUGR, or increased utilization combined with decreased production due to perinatal stress. Symptoms of hypoglycemia are non-specific. Management involves prevention by screening at-risk babies, treatment with IV dextrose or adjunctive therapies like glucagon or hydrocortisone if needed, and evaluating for underlying causes if hypoglycemia is persistent or recurrent. Prolong

















![Continuing therapy – based on Glucose Infusion Rate
GIR(mg/kg/min) = % dextrose x ml/kg/day
144
For eg.86 ml/kg/day of 10% D--GIR 6-8
[GIR of 8.33 = 80ml/kg/day of 15%D]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glucosetalk-140107134609-phpapp01/75/Neonatal-Hypoglycemia-18-2048.jpg)