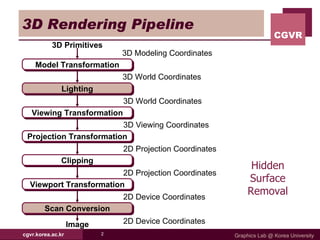
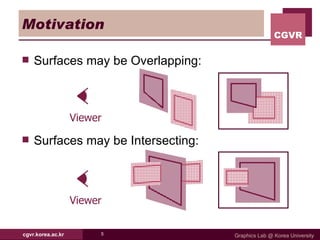
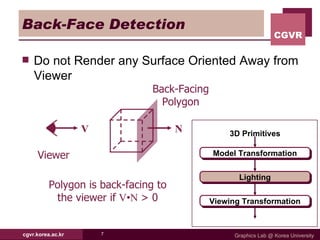
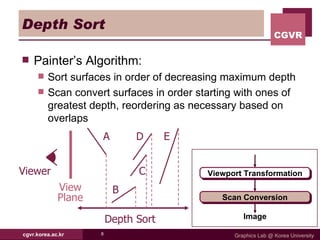
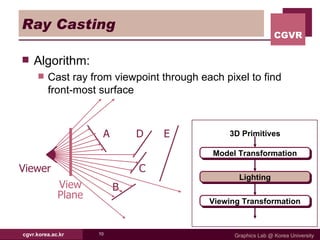
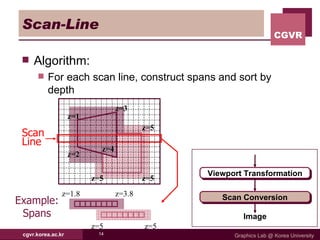
The document discusses algorithms for hidden surface removal in 3D graphics rendering. It describes several common algorithms including back-face detection, painter's algorithm, ray casting, z-buffer, and scan-line. The z-buffer algorithm stores the depth of closest surfaces for each pixel and is commonly implemented in graphics hardware. Scan-line algorithms process surfaces one scan line at a time for improved efficiency over fully computing every pixel. Area subdivision recursively subdivides regions where surfaces intersect.