Embed presentation
Downloaded 67 times






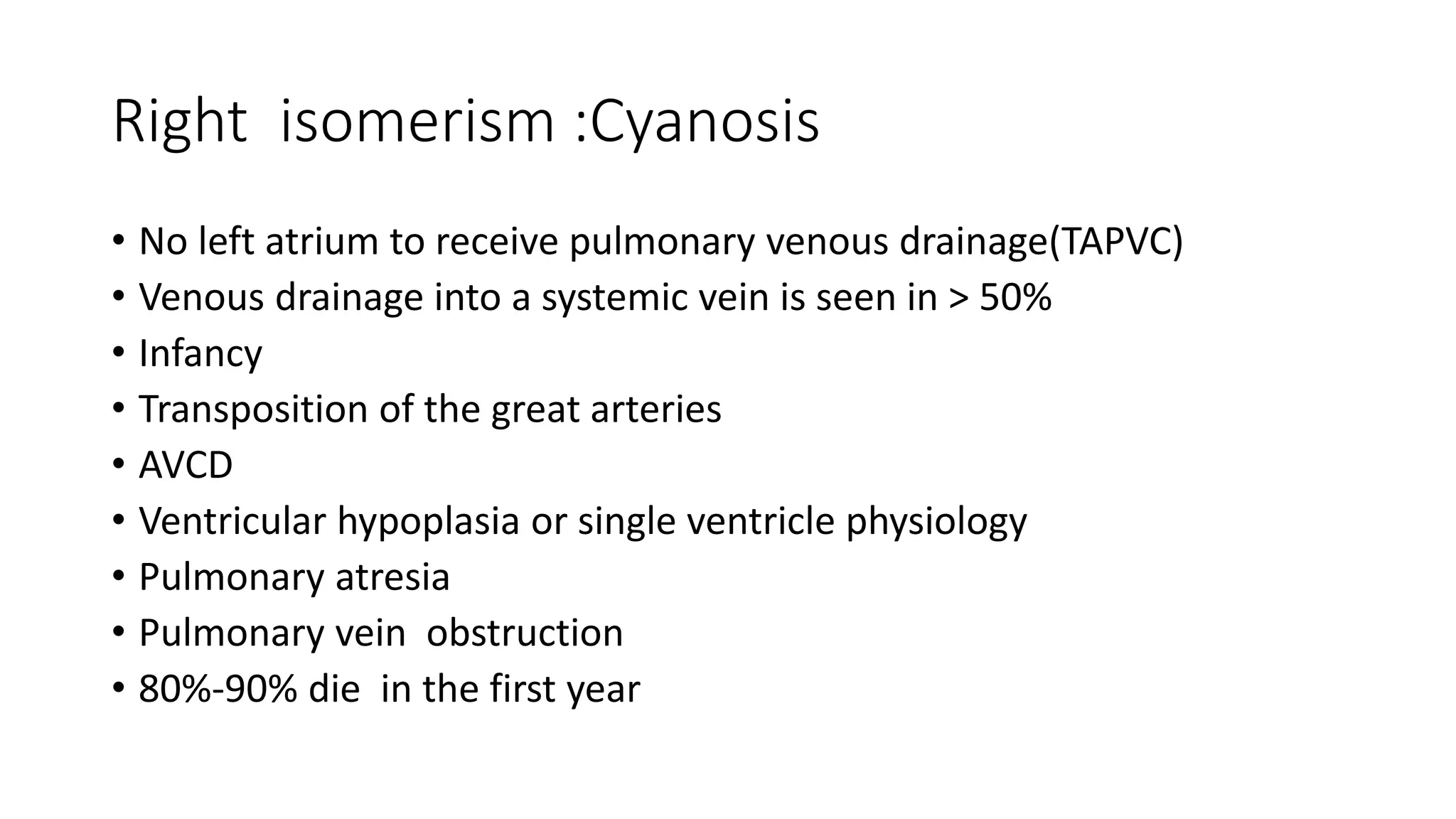


Heterotaxy is an abnormal and disorganized arrangement of organs within the abdominal cavity, in contrast to the normal orderly arrangement seen in situs inversus or situs solitus. There are two main categories of heterotaxy: situs ambiguous with polysplenia or left isomerism, and situs ambiguous with asplenia or right isomerism. Situs ambiguous with left isomerism involves bilateral symmetry of organs and a lower prevalence of congenital heart disease, while situs ambiguous with right isomerism involves more complex congenital heart defects and cyanosis.







