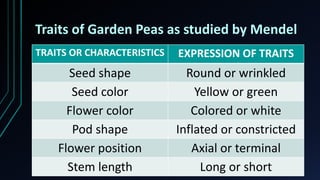
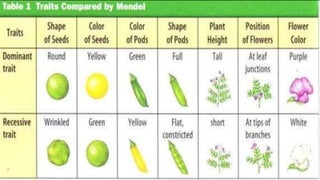
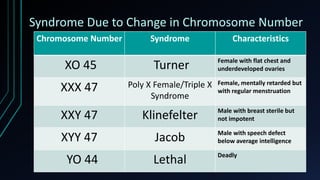
Gregor Mendel studied traits in garden peas and established the principles of heredity through quantitative experiments. He found that traits like seed shape, color, and flower position were inherited based on dominant and recessive alleles. Mendel's work laid the foundation for genetics and showed that heritable traits are passed from parents to offspring via discrete units now known as genes. Genetics further studies how heredity works, including patterns of inheritance, mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and genetic testing techniques like amniocentesis.