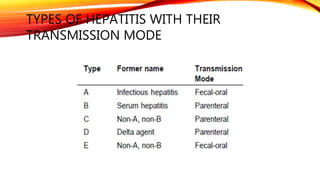
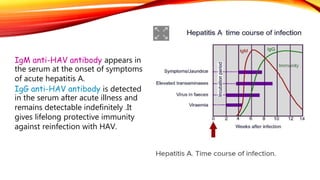
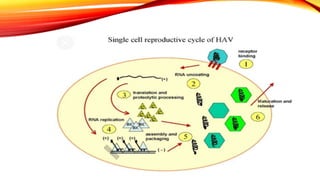
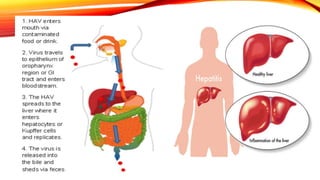
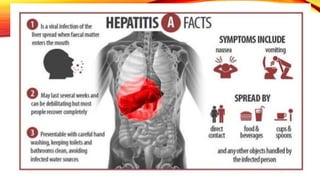
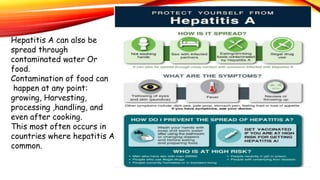
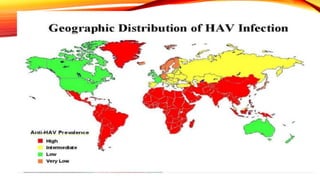
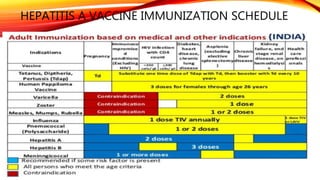
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the Hepatitis A virus. It is usually spread when a person ingests fecal matter from an infected person. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue and jaundice. There is no treatment for Hepatitis A other than supportive care. The best prevention is vaccination with an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine, which requires two doses.