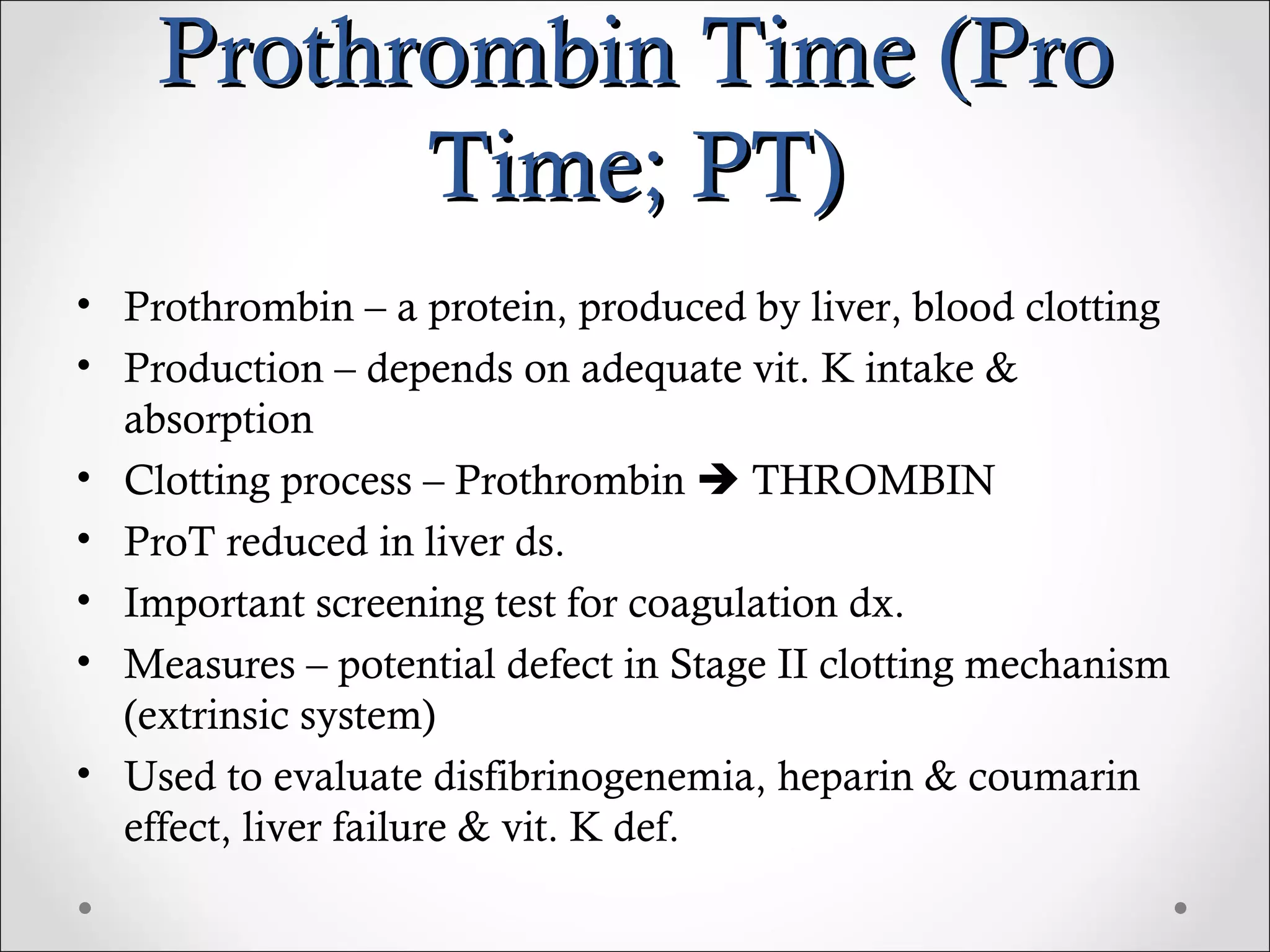
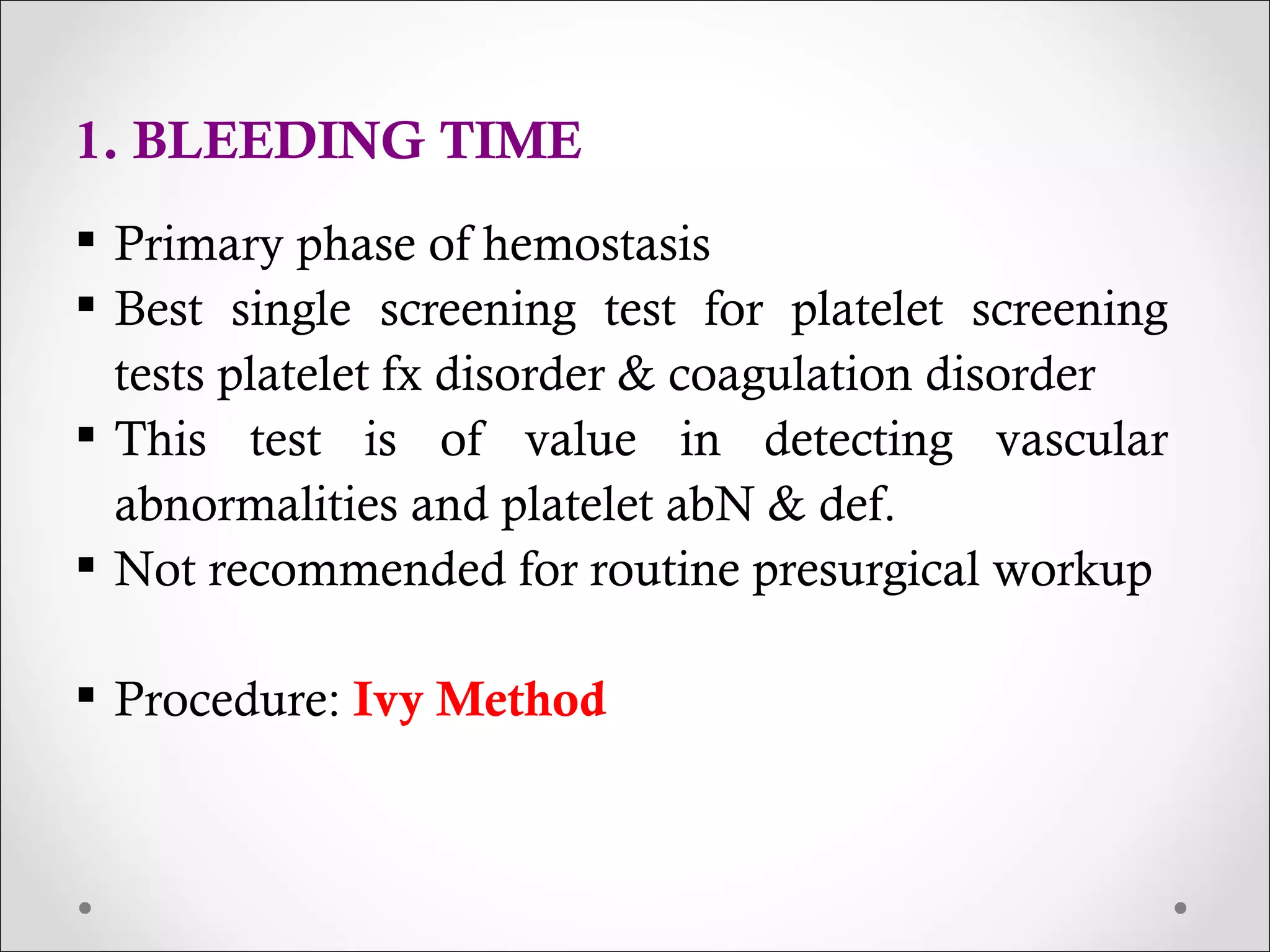
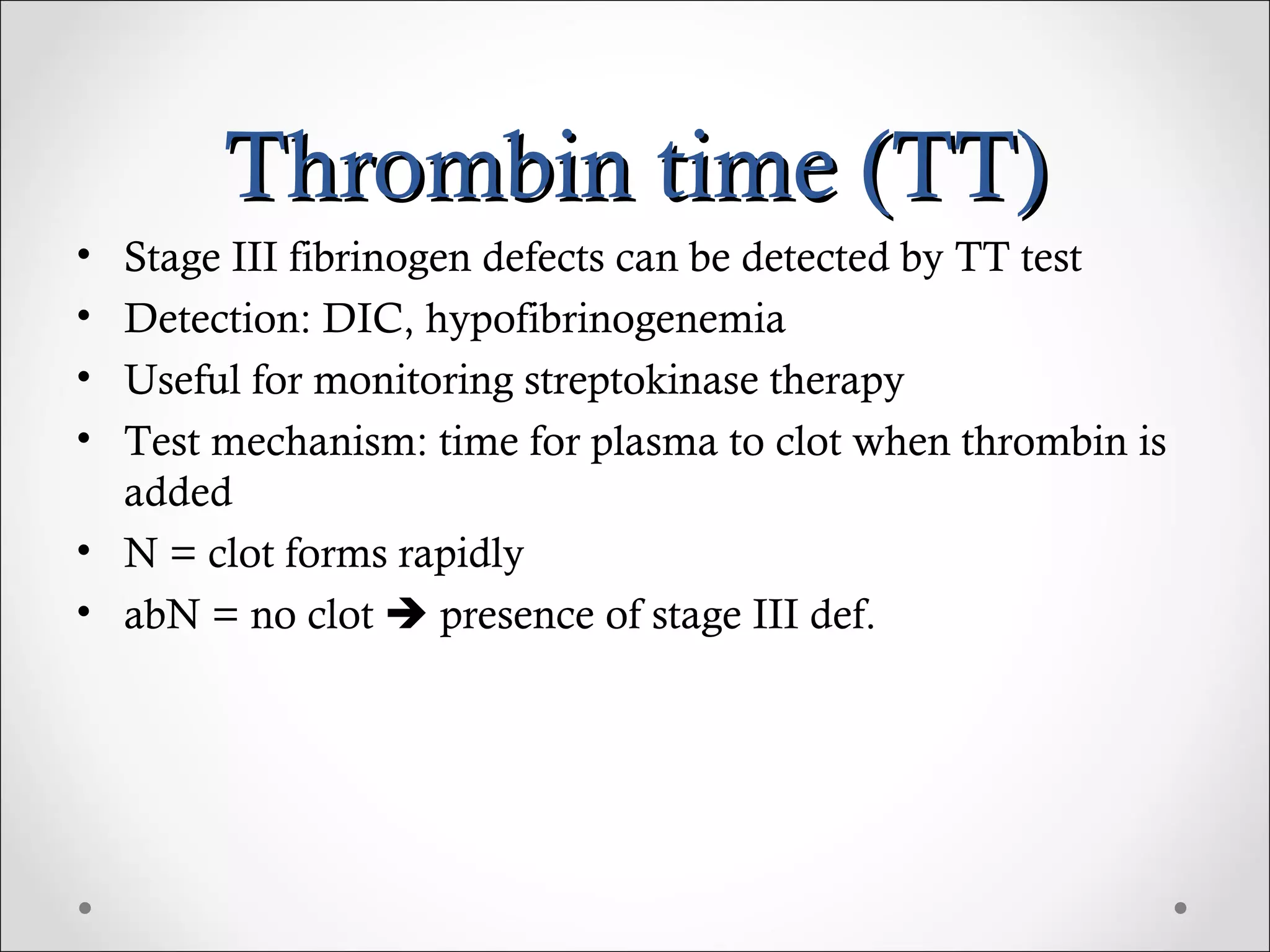
This document discusses various laboratory tests used to investigate hemostasis and coagulation disorders. It outlines five primary screening tests, including platelet count, bleeding time, prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and fibrinogen level. More specific coagulation factor assays and tests of fibrinolysis are also mentioned. Details are provided on procedures for common coagulation tests like PT, PTT, thrombin time (TT) and activated coagulation time (ACT). The document discusses the clinical implications of abnormal results and potential interfering factors for interpretation.




![Activated Coagulation Time (ACT) To evaluate coagulation status ACT responds linearly to heparin level changes Responds to wider range of [heparin] than does the APTT Bedside procedure – requires only 0.4mL of blood Routinely use during dialysis, coronary artery bypass procedures, arteriograms & percutaneous transluminal coronary arteriography HARD TO STANDARDIZE, NO CONTROLS AVAILABLE = results back-up with APTT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemapractical-03coagulation-110215082358-phpapp02/75/Hema-practical-03-coagulation-8-2048.jpg)