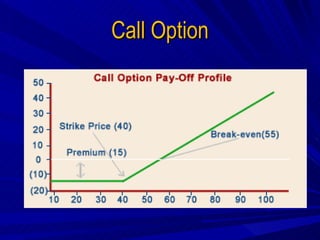
This document discusses hedging and hedge funds. It defines hedging as using tools like derivatives to reduce losses from negative events. It provides examples of common hedging instruments like forward contracts, futures contracts, and options. It then discusses the history of hedge funds, starting from Alfred Jones in the 1940s and important funds today like Goldman Sachs, Long Term Capital Management, Man Group, and Soros Fund Management. The document aims to explain hedging concepts and provide an overview of hedge funds.