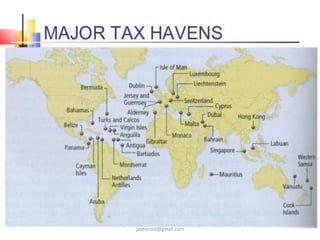
The document provides an overview of tax havens, outlining their definitions, characteristics, and uses, as well as detailing specific examples from around the world, such as the Cayman Islands. It discusses the implications of tax havens on the global economy, including both benefits and potential risks, such as money laundering and tax evasion. The document also addresses the responses of governments and the OECD towards enhancing transparency and cooperation in financial practices related to tax havens.