Embed presentation
Download to read offline












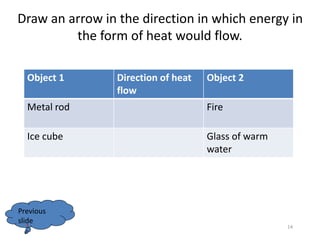
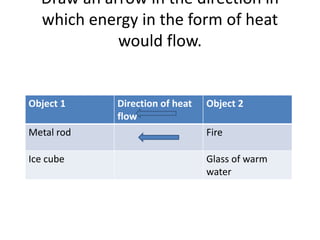
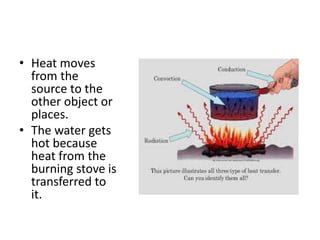





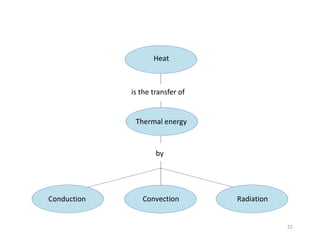
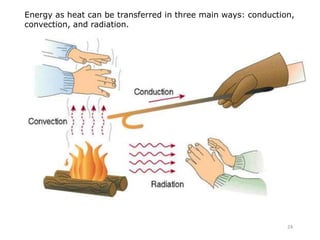



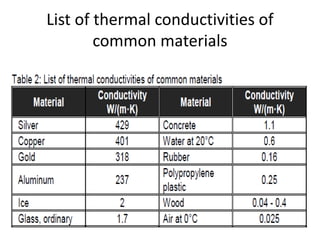

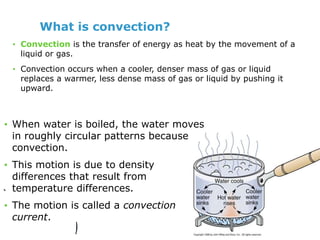

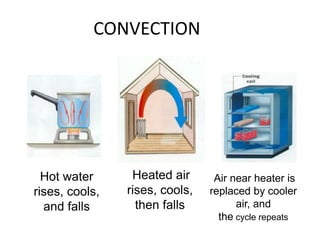
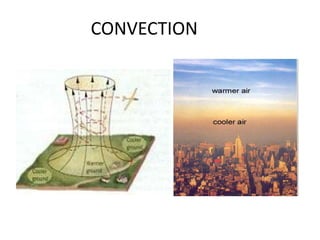
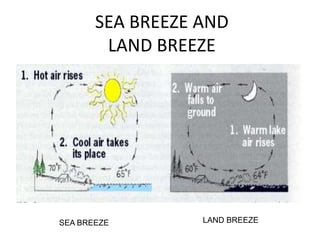





This document discusses heat transfer and the different methods by which heat is transferred. It defines heat as energy transferred between objects of different temperature, and explains that heat always flows from warmer to cooler objects. The three main methods of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves direct contact between objects, convection occurs through fluid movement, and radiation uses electromagnetic waves to transfer heat across empty space.






































