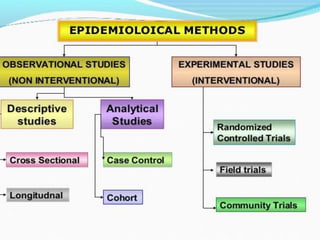
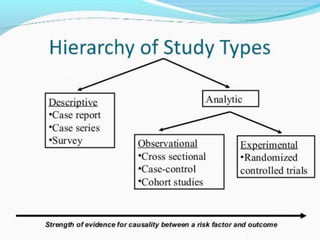
The document discusses different types of research methods including quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research. Quantitative research uses objective measurements and statistical analysis, while qualitative research explores underlying reasons and motivations through methods like interviews. Mixed methods research incorporates both quantitative and qualitative data collection. The document also describes observational studies like case studies and longitudinal studies, as well as experimental research methods like randomized controlled trials that manipulate variables and use control groups.