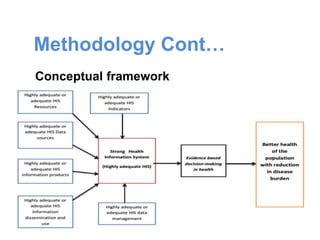
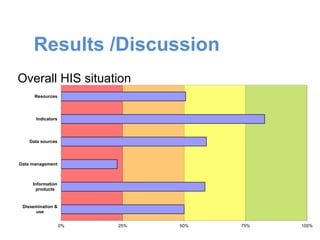
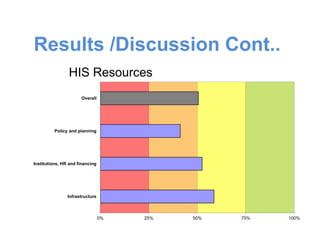
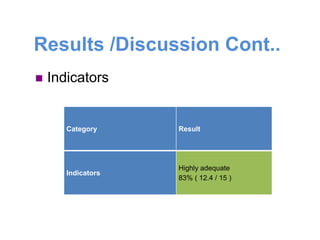
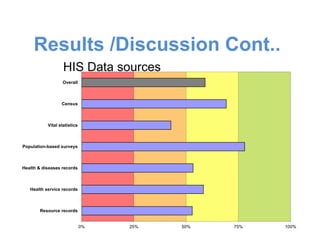
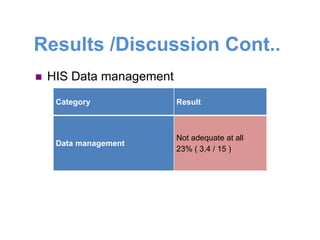
This document is the thesis submitted by Akumengwa Neba N to the Department of Public Health and Hygiene at the University of Buea in November 2014. The thesis assesses the health information system in Buea Health District. It includes background on health information systems and their components. The study aims to evaluate the adequacy of the health information system and identify priority areas for improvement. The methodology describes a cross-sectional study using interviews and assessment tools. The results found that data management was inadequate while other components were adequate or highly adequate. Key weaknesses identified were in data management, resources, and dissemination/use. Priority areas for improvement included strengthening data management, resources, vital statistics collection, and information analysis and