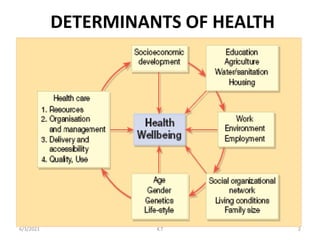
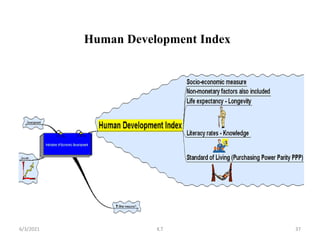
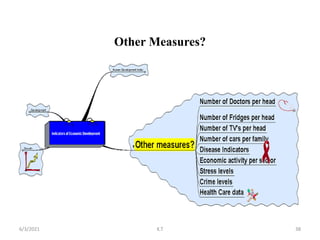
Wider determinants of health include community empowerment and anti-poverty measures. There are different perspectives on health: as a right, consumption good, or investment. Health as a right involves government responsibility to ensure access and equity. As a consumption good, health is a personal objective not requiring special government responsibilities. As an investment, health affects workforce productivity. Development encompasses improving standards of living and expanding economic and social opportunities. It differs from economic growth, which is a quantitative increase, by transforming society for better well-being. Health plays a key role in development by increasing productivity.